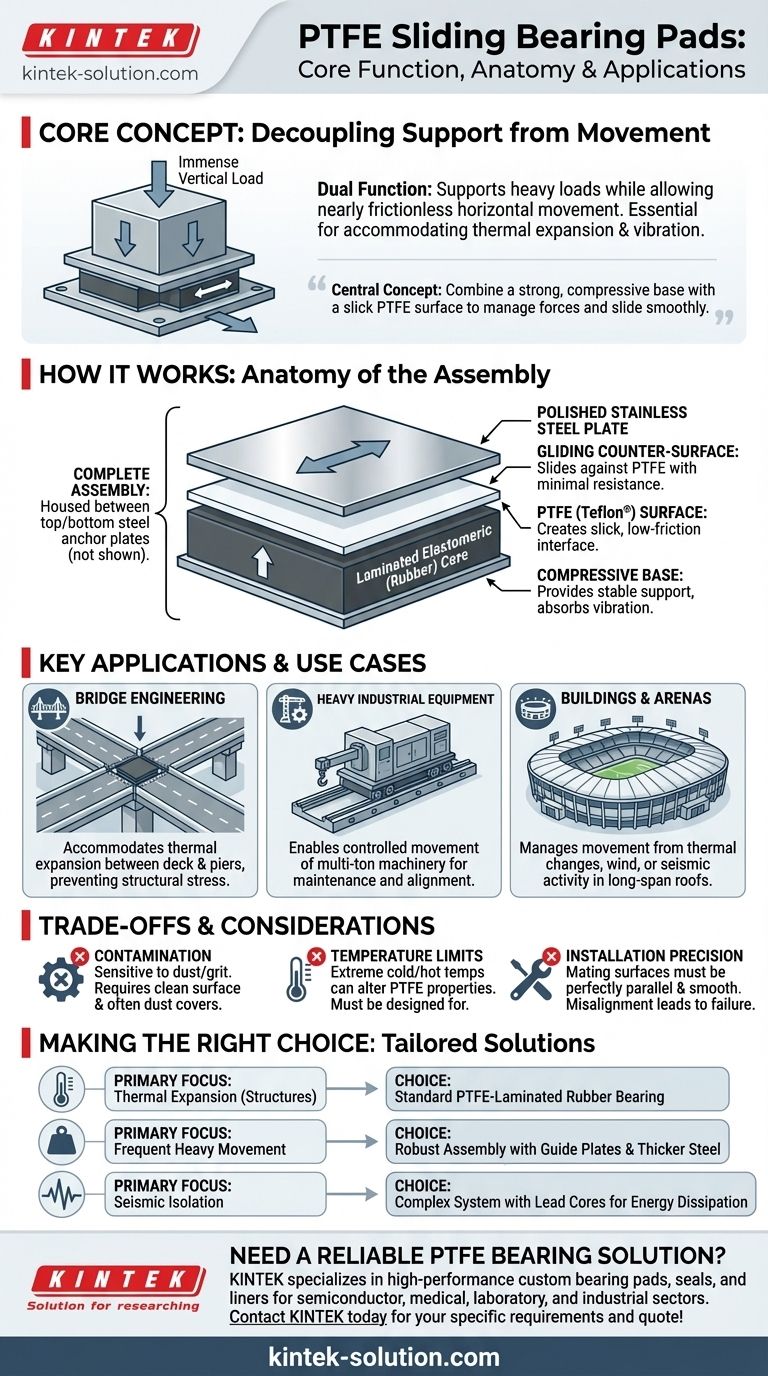
At its core, a PTFE sliding bearing pad is a composite component designed to perform two critical functions simultaneously: support immense vertical loads and allow for nearly frictionless horizontal movement. It accomplishes this by bonding a low-friction Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) layer to a load-bearing element, typically a laminated rubber pad. This design is essential for structures and equipment that must accommodate movement caused by thermal expansion, vibration, or other dynamic forces.
The central concept is decoupling vertical support from horizontal movement. By combining a strong, compressive base with a slick PTFE surface, engineers can safely manage the immense forces of a structure while allowing it to slide smoothly and predictably.
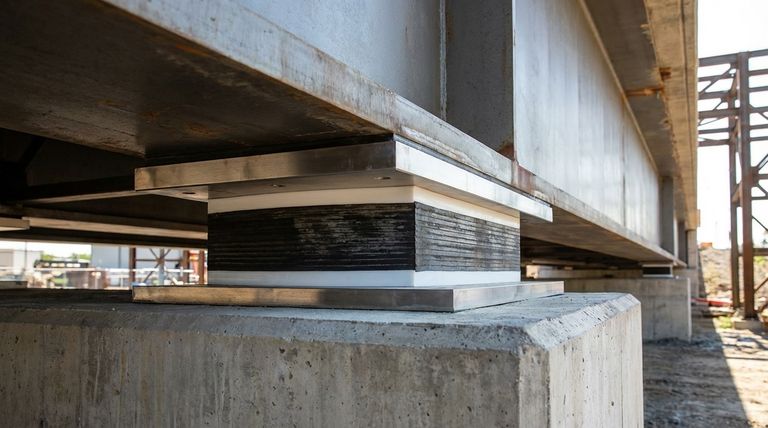

How a PTFE Sliding Bearing Works
A PTFE sliding bearing isn't just a single pad; it's a system where each component has a specific job. Understanding these parts reveals how it effectively manages both load and movement.
The Load-Bearing Core
The foundation of the bearing is typically a laminated elastomeric (rubber) pad. This core is designed to compress under heavy vertical loads, providing stable support. It can also absorb vibrations and accommodate slight rotational movements, making it a versatile base.
The Low-Friction Surface
Bonded to the top of the rubber pad is the key component: a sheet of PTFE. This material, widely known by the brand name Teflon, has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid. Its purpose is solely to create a slick surface that allows another plate to glide over it with minimal resistance.
The Complete Assembly
In a typical installation, the PTFE pad is part of a larger assembly. This often includes a polished stainless steel plate that is fixed to the upper structure. The PTFE surface slides against this smooth steel plate, ensuring a consistently low-friction interface. The entire system is often housed between top and bottom steel plates that anchor the bearing to the structure's foundation and the beam or equipment it supports.
Key Applications and Use Cases
The unique ability to handle both heavy loads and sliding makes these bearings indispensable in several fields. They are not just for bridges but for any application where controlled movement under load is a design requirement.
Bridge and Structural Engineering
This is the most common application. Bridges expand and contract with temperature changes. PTFE bearings are placed between the bridge deck and the support piers to allow for this thermal movement without transferring destructive stress to the support structure.
Heavy Industrial Equipment
Large industrial machinery or vessels often need to be moved for maintenance or adjusted for alignment. PTFE slide bearings provide a way to move these multi-ton objects with controlled force, preventing damage to the equipment or its foundation.
Buildings and Arenas
In large-scale construction, particularly for structures with long roof spans like stadiums or convention centers, PTFE bearings accommodate movement from thermal changes, wind loads, or seismic activity. This prevents the buildup of stress in the primary structural frame.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, PTFE sliding bearings are not without limitations. Their performance is contingent on proper design and installation.
Sensitivity to Contamination
The effectiveness of the low-friction surface depends on it being clean and smooth. Dust, debris, or grit between the PTFE and the stainless steel plate can score the surfaces, increasing friction and compromising the bearing's function. This is why assemblies often include dust covers.
Temperature Limitations
While PTFE has a wide operating temperature range, its properties can change at extreme cold or hot temperatures. This must be accounted for in the design phase, especially for applications in harsh climates.
Installation Precision
Proper performance requires that the mating surfaces be perfectly parallel and smooth. Any misalignment can cause uneven loading and wear, which can lead to premature failure of the bearing system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct bearing configuration depends entirely on the specific forces and movements you need to manage.
- If your primary focus is thermal expansion in structures: Your main concern is accommodating slow, predictable horizontal movement, making a standard PTFE-laminated rubber bearing an ideal choice.
- If your primary focus is frequent movement of heavy equipment: You may need a more robust assembly with guide plates to control the direction of sliding and thicker steel components to handle dynamic loads.
- If your primary focus is seismic isolation: You will need a more complex bearing system, often incorporating additional elements like lead cores, designed specifically to dissipate energy and allow for large, multi-directional movements.
Ultimately, a PTFE sliding bearing is a sophisticated engineering solution that solves the fundamental problem of allowing massive structures to move safely.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Load-Bearing Core | Compresses under vertical loads; absorbs vibrations. |
| PTFE Surface | Provides a low-friction interface for horizontal sliding. |
| Stainless Steel Plate | Acts as a smooth, durable counter-surface for the PTFE. |
| Key Applications | Bridge expansion joints, heavy equipment movement, seismic isolation in buildings. |
Need a Reliable PTFE Bearing Solution?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including custom bearing pads, seals, and liners. Our precision production ensures your structures and equipment can handle immense loads and critical movements safely and efficiently.
Whether you're in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sector, we provide custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific requirements and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What is fluid compatibility in ball valve seats? Ensure Reliable Sealing and Prevent Failure
- How is PTFE processed into usable shapes? From Powder to Precision Parts
- What types of movements can PTFE slide bearings accommodate? Handling Thermal, Seismic, and Structural Shifts
- What does the leakage rate indicate about PTFE gaskets? Understanding the Sealing Performance Trade-off
- How should the right PTFE washer thickness be selected? Balance Sealing, Creep, and Pressure
- Where are PTFE valve seat rings commonly used? Ensuring Purity and Reliability in Critical Processes
- Why is the non-reactivity of PTFE fasteners important in medical devices? Ensuring Patient Safety and Device Integrity
- What are the best applications for standard PTFE gaskets? Ideal for Chemical & High-Temp Sealing



















