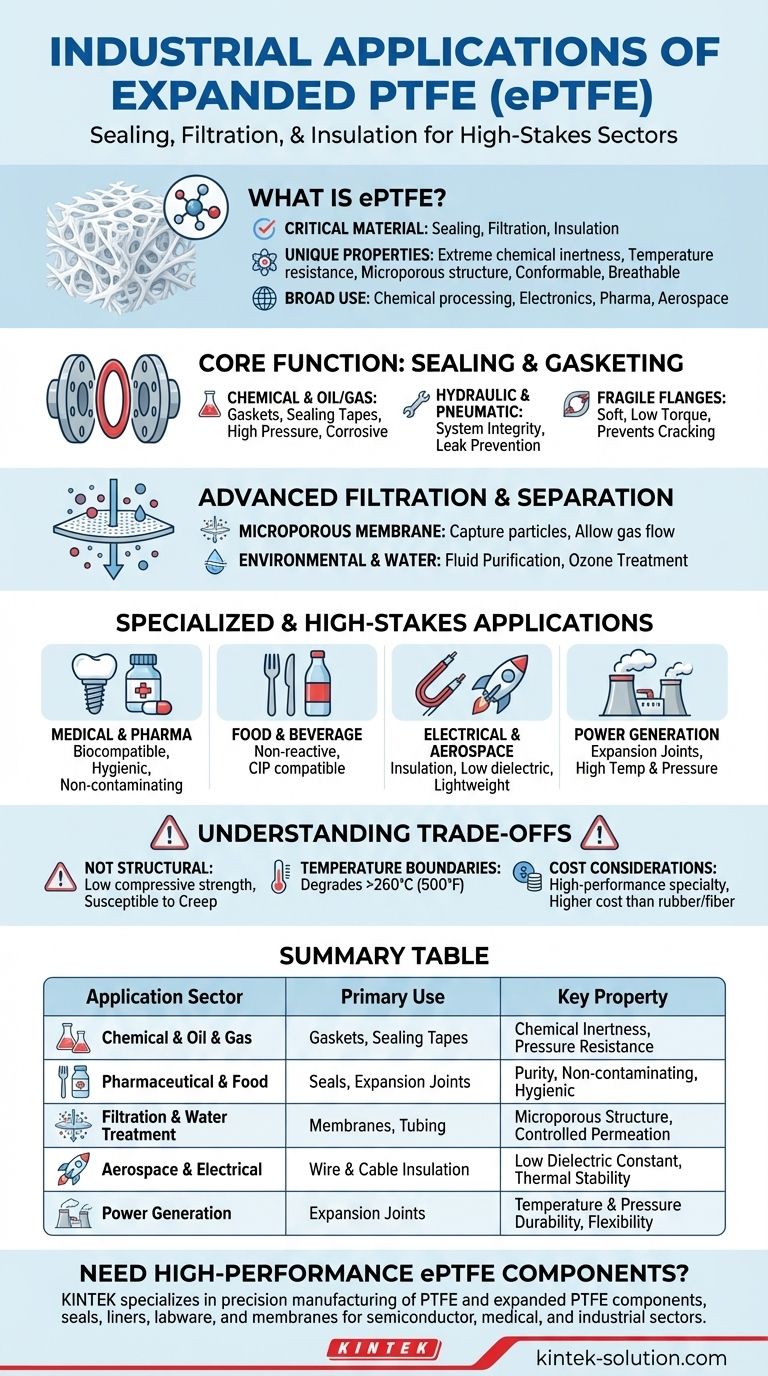
In short, expanded PTFE (ePTFE) is a critical material used for sealing, filtration, and insulation across a wide range of high-stakes industrial sectors. You will find it in chemical processing plants, advanced electronic components, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and aerospace applications where performance under extreme conditions is non-negotiable.
The core reason for ePTFE's broad industrial use is its unique combination of properties: the extreme chemical inertness and temperature resistance of standard PTFE, enhanced with a microporous structure that makes it highly conformable, breathable, and an exceptional filter medium.

The Core Function: Sealing and Gasketing
One of the most common applications for ePTFE is creating a perfect seal in demanding environments. Its softness and malleability allow it to fill imperfections in flange surfaces, ensuring a leak-proof connection.
In Chemical and Oil & Gas Industries
ePTFE is the material of choice for gaskets and sealing tapes on chemical pipe flanges. It can withstand highly corrosive chemicals and the extreme pressures found in oil and gas pipelines.
It is often supplied as a cord or tape, allowing for the creation of custom-fit gaskets on-site, which is invaluable for large or non-standard flanges.
In Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems
You will find ePTFE sealing flange joints in critical infrastructure like fire hydrants, municipal pipelines, and high-pressure hydraulic systems. Its reliability prevents leaks and ensures system integrity over long periods.
For Fragile or Irregular Flanges
Because ePTFE is soft and requires low bolt torque to create a seal, it is ideal for fragile materials. It is commonly used to seal plastic or glass flanges and pressure vessels where excessive force would cause cracking.
Advanced Filtration and Separation
The "expansion" process creates a complex network of pores and nodes within the PTFE, turning it into a high-performance membrane.
The Microporous Advantage
This structure makes ePTFE an exceptional filter. It can be engineered to have specific pore sizes, allowing it to capture microscopic particles while allowing air or other gases to pass through freely.
Environmental and Water Treatment
ePTFE's porous nature is leveraged in fluid purification. For example, ePTFE tubing can be submerged in iron-rich water while ozone gas is passed through it; the gas permeates the tube wall to treat the water without the need for direct injection.
Specialized and High-Stakes Applications
Beyond sealing and filtering, ePTFE's inherent properties make it indispensable in industries where purity, safety, and performance are paramount.
Medical and Pharmaceutical
ePTFE is biocompatible and chemically inert, making it suitable for medical devices and implants. In pharmaceutical manufacturing, it's used in expansion joints and seals to meet strict hygiene and safety standards without contaminating the product.
Food and Beverage Processing
Similar to pharmaceuticals, the food and beverage industry relies on ePTFE for seals and expansion bellows. Its non-reactive surface maintains product purity and can withstand aggressive clean-in-place (CIP) chemicals and high temperatures.
Electrical and Aerospace Insulation
PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator with a very low dielectric constant. In its expanded form, it is used as a high-performance insulator for wires and cables, especially in aerospace applications where weight, temperature resistance, and signal integrity are critical.
Power Generation
Power plants utilize ePTFE expansion joints in piping systems. These components must withstand the high-pressure steam and fluctuating temperatures common in power generation, and ePTFE provides the necessary durability and flexibility.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly versatile, ePTFE is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Not a Structural Material
ePTFE is a soft, conformable material designed for sealing and filtration. It has low compressive strength and is susceptible to creep (slow deformation under constant stress), meaning it should not be used for load-bearing structural components.
Temperature Boundaries
While its temperature range is impressive, it is not infinite. At extremely high temperatures (typically above 260°C or 500°F), PTFE will begin to degrade. It is crucial to operate within its specified service temperature limits.
Cost Considerations
As a high-performance specialty polymer, ePTFE is more expensive than conventional gasketing or filtration materials like rubber or fiber. Its use is justified in applications where failure is not an option and its unique properties are required.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right material depends entirely on the primary challenge you need to solve.
- If your primary focus is sealing aggressive chemicals or preventing leaks in critical pipelines: ePTFE gaskets and tapes provide unmatched chemical resistance and conformability for a reliable seal.
- If your primary focus is advanced filtration or controlled gas transfer: The unique microporous structure of ePTFE membranes allows for precise separation and diffusion in demanding environments.
- If your primary focus is ensuring purity in food or pharmaceutical processing: ePTFE's inertness and compliance with hygiene standards make it the ideal choice for non-contaminating seals and components.
- If your primary focus is high-performance insulation for electronics or aerospace: The low dielectric constant and thermal stability of ePTFE are essential for maintaining signal integrity and reliability.
Ultimately, choosing ePTFE is a strategic decision for applications where superior performance and long-term reliability cannot be compromised.
Summary Table:
| Application Sector | Primary Use of ePTFE | Key Property Leveraged |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical & Oil & Gas | Gaskets, Sealing Tapes | Chemical Inertness, Pressure Resistance |
| Pharmaceutical & Food | Seals, Expansion Joints | Purity, Non-contaminating, Hygienic |
| Filtration & Water Treatment | Membranes, Tubing | Microporous Structure, Controlled Permeation |
| Aerospace & Electrical | Wire & Cable Insulation | Low Dielectric Constant, Thermal Stability |
| Power Generation | Expansion Joints | Temperature & Pressure Durability, Flexibility |
Need high-performance ePTFE components for your critical application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in the precision manufacturing of PTFE and expanded PTFE components—including custom seals, liners, labware, and membranes. Whether you require prototypes or high-volume production for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sectors, we deliver solutions that meet the highest standards of reliability and performance.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our custom ePTFE fabrication can solve your most demanding sealing, filtration, or insulation challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the main drawbacks of PEEK? Key Limitations for High-Performance Applications
- How does the low friction property of PTFE benefit industrial applications? Boost Efficiency & Durability
- Why is PTFE highly resistant to chemicals? Unmatched Inertness for Demanding Applications
- What substances can affect the carbon-fluorine bonds in PTFE? Uncover the Limits of its Chemical Inertness
- What are some alternatives to PTFE and how do they compare? A Guide to Fluoropolymer Selection
- Why is PTFE valuable in automotive and aerospace industries? The Ultimate Material for Extreme Environments
- Can PTFE be modified with additives? Enhance Performance for Demanding Applications
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments



















