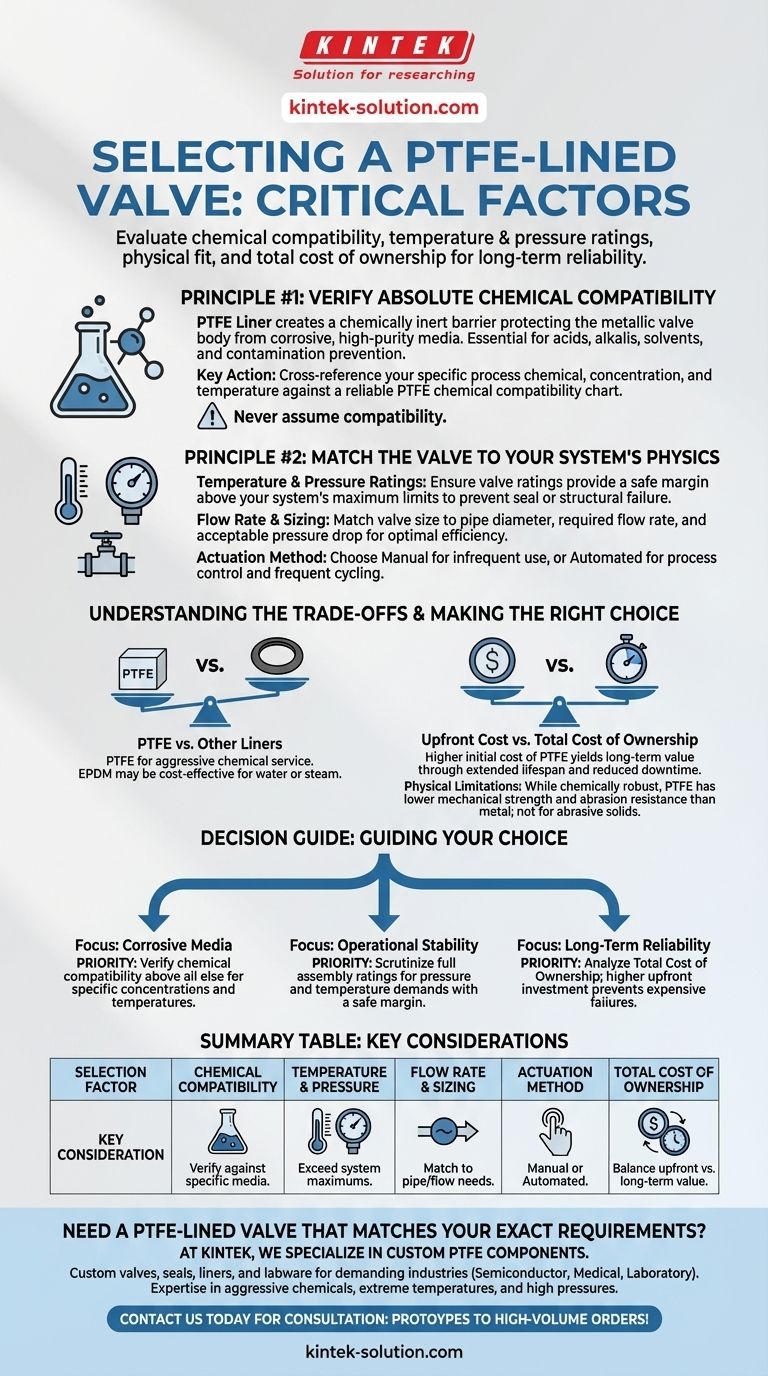
When selecting a PTFE-lined valve, the critical factors you must evaluate are its chemical compatibility with your process media, the valve's ability to withstand your system's specific operating temperature and pressure, its physical fit within your installation, and its total cost of ownership. These elements work together to ensure the valve not only functions correctly but also provides long-term reliability and safety.
A successful selection process moves beyond simply choosing a valve with a PTFE liner. It involves a holistic assessment of the entire valve assembly against the precise chemical, thermal, and mechanical stresses of your specific application to prevent premature failure and costly downtime.

Principle #1: Verify Absolute Chemical Compatibility
The primary reason to specify a PTFE-lined valve is for its exceptional resistance to corrosion and chemical attack. This must be your first and most critical checkpoint.
The Purpose of the PTFE Liner
A PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) lining creates a chemically inert barrier. This barrier protects the valve's metallic body (typically iron or steel) from direct contact with corrosive or high-purity media.
Beyond Common Corrosives
While excellent for aggressive substances like acids and alkalis, PTFE's compatibility extends to a vast range of solvents, bases, and other chemicals. It also prevents contamination, which is critical in industries like pharmaceuticals and food processing.
Always Confirm Your Media
Never assume compatibility. Always cross-reference your specific process chemical, including its concentration and potential impurities, against a reliable PTFE chemical compatibility chart.
Principle #2: Match the Valve to Your System's Physics
A valve is a mechanical device that must operate reliably under physical stress. The PTFE liner is only one component of a larger system that must meet your operational demands.
Temperature and Pressure Ratings
Every valve has defined temperature and pressure limits. Exceeding these can lead to seal failure, leakage, or catastrophic structural failure. Ensure the valve's ratings provide a safe margin above your system's maximum operating conditions.
Flow Rate and Valve Sizing
Proper sizing is crucial for performance. The valve's size must be matched to the pipe diameter, required flow rate, and acceptable pressure drop. An improperly sized valve can create unwanted turbulence, reduce efficiency, or fail to provide adequate control.
Actuation Method
Consider how the valve will be operated. Manual operation is suitable for infrequent adjustments, while automated or actuated valves are necessary for process control systems, remote operation, or frequent cycling.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a PTFE-lined valve involves weighing its distinct advantages against its limitations and cost. Objectivity here is key to making a sound engineering decision.
PTFE vs. Other Liners
PTFE is the premier choice for aggressive chemical service. However, for less demanding applications like water or steam, an EPDM seat or liner may be a more cost-effective solution. The key is to match the material to the media.
Upfront Cost vs. Total Cost of Ownership
PTFE-lined valves typically have a higher initial purchase price than standard valves. However, their value lies in their extended lifespan and the prevention of failure in corrosive environments. The total cost of ownership—factoring in reduced maintenance and averted downtime—is often much lower.
Physical Limitations
While chemically robust, PTFE has a lower mechanical strength and abrasion resistance compared to metal. It is not ideal for services with significant abrasive solids or slurries unless the valve is specifically designed for such duty.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by the single most critical priority for your system's integrity and performance.
- If your primary focus is handling highly corrosive media: Prioritize the verification of chemical compatibility above all other factors, ensuring the PTFE liner is suitable for your specific chemical concentrations and temperatures.
- If your primary focus is operational stability under stress: Scrutinize the valve's full assembly ratings for pressure and temperature, ensuring they exceed your system's maximum demands with a safe margin.
- If your primary focus is long-term reliability and cost-effectiveness: Analyze the total cost of ownership, recognizing that a higher upfront investment can prevent far more expensive failures and process interruptions down the line.
Selecting the right valve is an investment in the safety, efficiency, and longevity of your entire process.
Summary Table:
| Selection Factor | Key Consideration |
|---|---|
| Chemical Compatibility | Verify against specific process media using a PTFE compatibility chart. |
| Temperature & Pressure | Ensure valve ratings exceed your system's maximum operating conditions. |
| Flow Rate & Sizing | Match valve size to pipe diameter and required flow to avoid turbulence. |
| Actuation Method | Choose manual for infrequent use or automated for process control. |
| Total Cost of Ownership | Balance upfront cost with long-term reliability and downtime prevention. |
Need a PTFE-lined valve that matches your exact requirements? At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components—including custom valves, seals, liners, and labware—for demanding industries like semiconductor, medical, and laboratory. Our expertise ensures your valve will handle aggressive chemicals, extreme temperatures, and high pressures with reliability. Contact us today for a consultation on custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the main applications of PTFE type Teflon? Unlock Its Versatility for Your Industry
- What factors should be considered when choosing between Nylon and PTFE? Select the Right Material for Your Application
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What fabrication services are available for PTFE? Shearing, Stamping, Laser Cutting, Molding & Machining
- What design considerations are important for custom PTFE parts? Design for Performance & Reliability



















