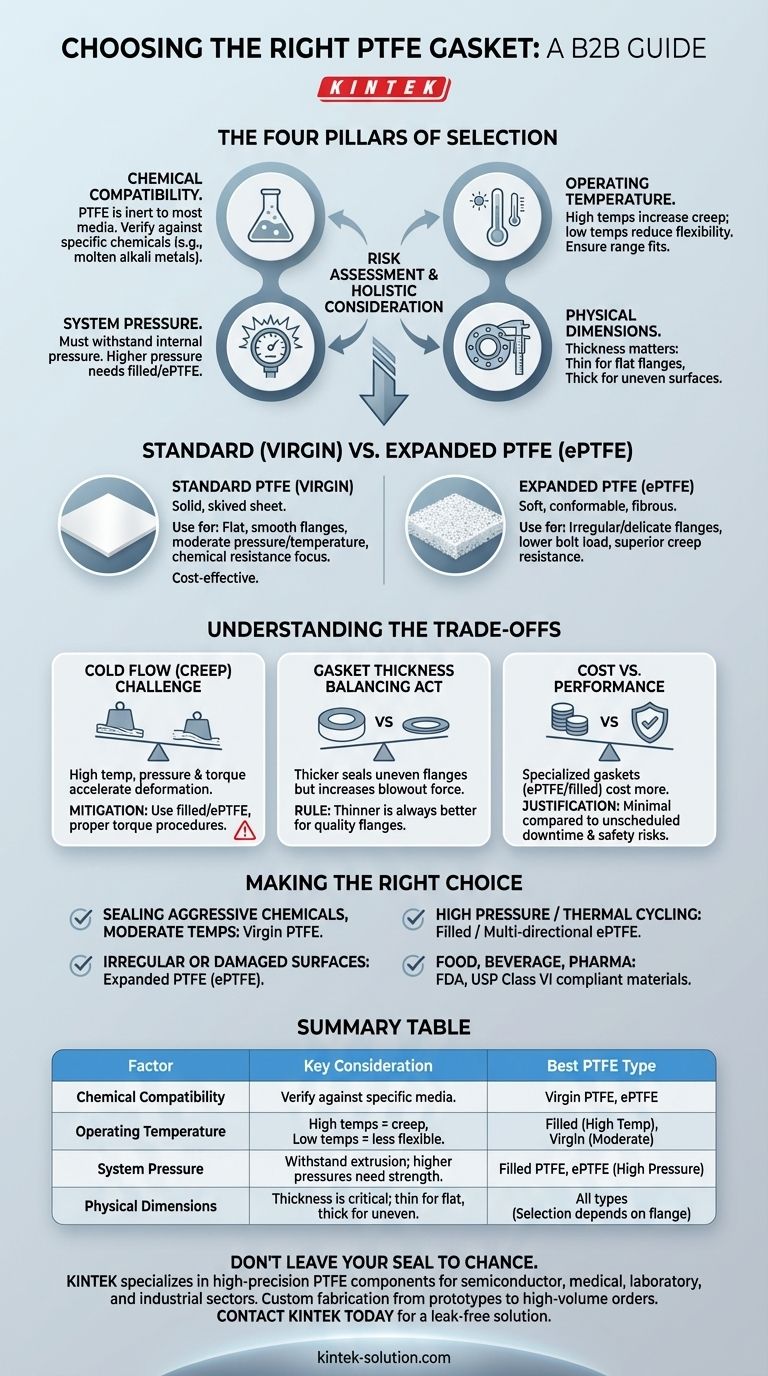
To select the right PTFE gasket, you must evaluate four primary factors against your specific application: chemical compatibility, operating temperature, system pressure, and the physical dimensions of the flange. These criteria work together to ensure a reliable, long-lasting seal, preventing leaks and costly system downtime.
Choosing a PTFE gasket is not about finding a single "best" material, but about conducting a risk assessment. You are matching the specific properties of a PTFE variant to the unique operational stresses of your system to guarantee its integrity.
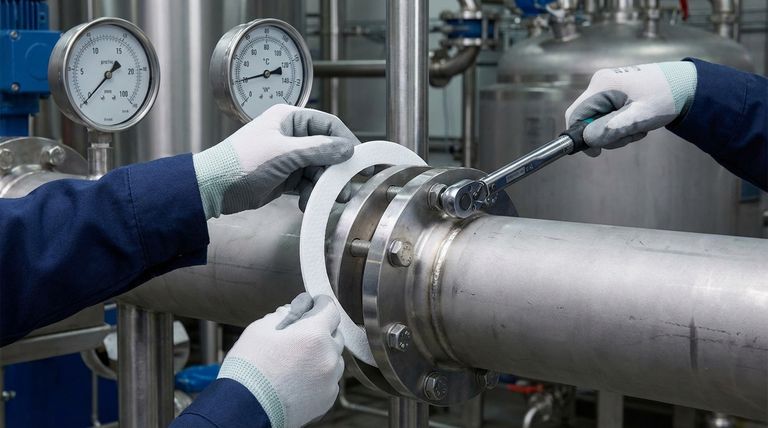

The Four Pillars of Gasket Selection
A failure in any one of these core areas can lead to a complete failure of the seal. They must be considered holistically.
Evaluating Chemical Compatibility
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is renowned for being chemically inert to most substances. This is often its primary selection advantage.
However, you must still verify its compatibility with your specific media. In rare cases, materials like molten alkali metals or certain fluorine compounds can attack PTFE. Always cross-reference your process chemicals against a reliable compatibility chart.
Assessing Temperature Limits
PTFE has a wide operating temperature range, but its mechanical properties change significantly at its extremes.
As temperatures rise, PTFE becomes softer and more susceptible to creep, or "cold flow," where the material slowly deforms under pressure. Conversely, at cryogenic temperatures, it can become less flexible. You must ensure your minimum and maximum operating temperatures fall comfortably within the gasket material's specified range.
Understanding Pressure Containment
The gasket must withstand the maximum internal pressure of your system without being extruded or blown out.
For standard pressures, virgin PTFE is often sufficient. For higher pressure applications, a filled PTFE (mixed with glass or carbon) or expanded PTFE (ePTFE) is necessary. These materials offer enhanced strength and resistance to deformation under load.
Ensuring Correct Physical Dimensions
A gasket can only work if it fits correctly. This goes beyond simple inner and outer diameters.
The gasket thickness is a critical choice. A thinner gasket provides a stronger, more stable seal on smooth, flat flanges. A thicker gasket can better conform to and seal uneven or damaged flange surfaces, but it is also more prone to extrusion.
Beyond the Basics: Standard vs. Expanded PTFE
Not all PTFE is the same. The manufacturing process creates two distinct types with different strengths.
When to Use Standard (Virgin) PTFE
Standard, or virgin, PTFE is a solid, skived sheet material. It is an excellent general-purpose choice for many applications.
Choose standard PTFE for flat, smooth flange surfaces in moderate pressure and temperature applications where chemical resistance is the primary driver. It is typically the most cost-effective option.
When to Choose Expanded PTFE (ePTFE)
Expanded PTFE is a soft, highly conformable material created by expanding virgin PTFE, resulting in a fibrous structure.
Choose ePTFE when dealing with irregular, warped, or delicate flanges (like glass-lined steel). Its softness allows it to create a tight seal with much lower bolt torque, reducing the risk of flange damage and providing superior resistance to creep.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right gasket involves balancing competing factors. Being aware of the inherent limitations of PTFE is crucial for making a reliable decision.
The Challenge of Cold Flow (Creep)
Creep is the primary failure mode for PTFE gaskets. It is the tendency of the material to slowly deform and flow away from the applied pressure of the bolts, leading to a loss of sealing stress and an eventual leak.
High temperatures, high pressures, and excessive bolt torque all accelerate creep. Using filled PTFE or ePTFE and following proper bolt torque procedures are the most effective ways to mitigate this risk.
Gasket Thickness: A Balancing Act
While a thick gasket can save a leaking seal on a poor flange, it is not a universal solution.
The thicker the material, the more surface area is exposed to internal pressure, increasing the force trying to push it out. For high-pressure systems with quality flanges, thinner is always better.
Cost vs. Performance
Specialized gaskets like filled PTFE or ePTFE are more expensive than virgin PTFE.
However, the cost of a gasket is minimal compared to the cost of an unscheduled shutdown, product loss, or a safety incident. Justifying a higher-performance gasket is easy in critical applications where seal reliability is paramount.
Making the Right Choice for Your System
Your final selection should be a deliberate choice based on the complete operational context of the flange joint.
- If your primary focus is sealing aggressive chemicals at moderate temperatures: A standard virgin PTFE gasket is often the most cost-effective starting point.
- If you are dealing with irregular or damaged flange surfaces: Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) will provide superior conformability and a more reliable seal at lower bolt loads.
- If your application involves high pressure or significant thermal cycling: A filled PTFE or multi-directionally expanded PTFE is necessary to mitigate the risk of creep and seal failure.
- If you operate in a food, beverage, or pharmaceutical environment: You must select a gasket material that explicitly meets FDA, USP Class VI, or other relevant regulatory standards.
By systematically matching the gasket's properties to your system's demands, you transform the selection process from a guess into an engineering decision.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Key Consideration | Best PTFE Type for the Job |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Compatibility | Verify against specific media; PTFE is inert to most chemicals. | Virgin PTFE, ePTFE |
| Operating Temperature | High temps cause creep (cold flow); low temps reduce flexibility. | Filled PTFE (high temp), Virgin PTFE (moderate) |
| System Pressure | Must withstand pressure without extrusion; higher pressures need stronger materials. | Filled PTFE, ePTFE (high pressure) |
| Physical Dimensions | Thickness is critical: thin for flat flanges, thick for uneven surfaces. | All types; selection depends on flange condition |
Don't Leave Your Seal to Chance
Selecting the right PTFE gasket is critical for the safety and efficiency of your operations in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including seals, liners, and labware. We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring your gasket is perfectly matched to your application's chemical, temperature, and pressure demands.
Let our expertise guide you to a leak-free solution. Contact KINTEB today for a consultation and get a quote for your specific needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What design considerations are important for custom PTFE parts? Design for Performance & Reliability
- What challenges arise when machining PTFE (Teflon)? Overcome Softness, Heat, and Instability
- What finishing techniques are effective for machined Teflon parts? Achieve Functional Performance and Dimensional Stability
- What industrial benefits do PTFE-machined parts offer? Achieve Peak Performance in Demanding Applications
- What fabrication services are available for PTFE? Shearing, Stamping, Laser Cutting, Molding & Machining



















