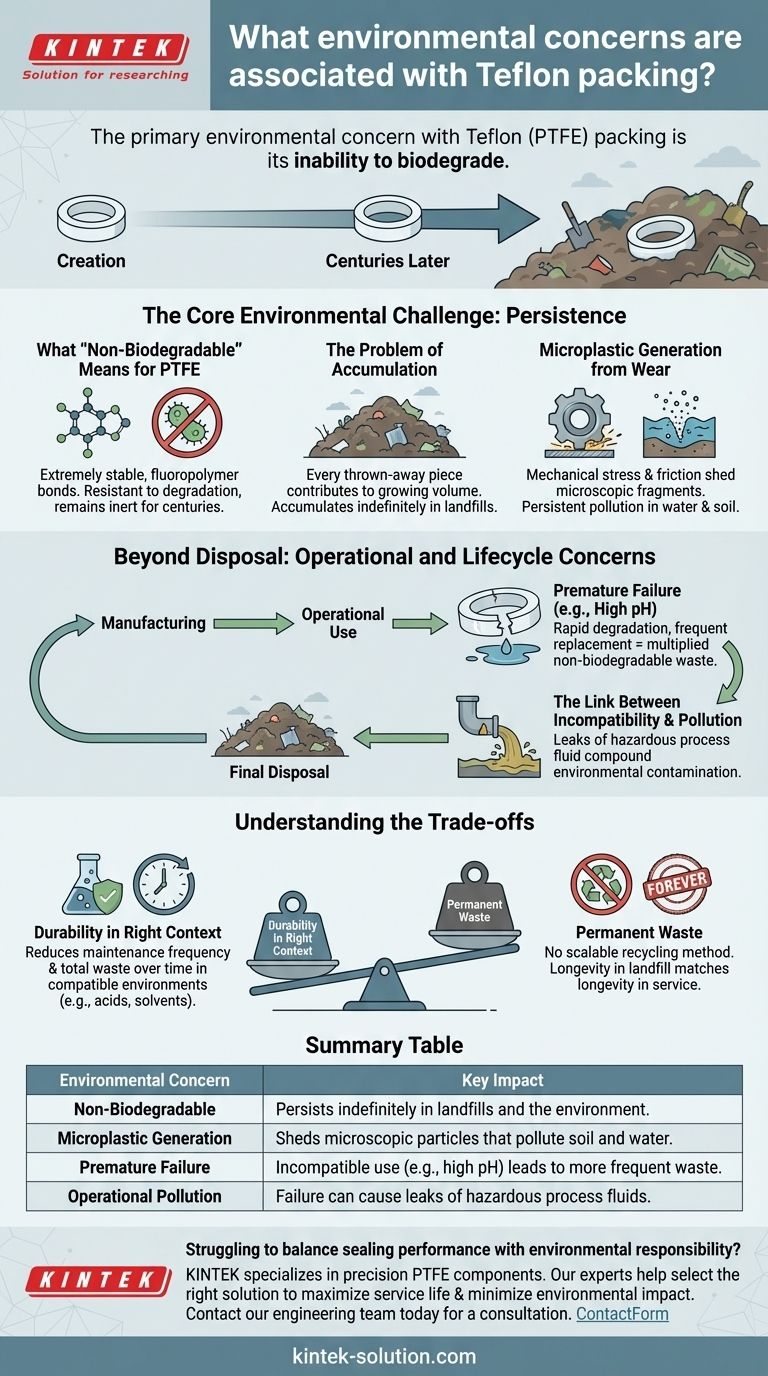
The primary environmental concern with Teflon (PTFE) packing is its inability to biodegrade. Because it is an extremely stable and inert synthetic polymer, it does not break down naturally. This means that once discarded, it persists indefinitely in landfills or as pollution in the environment.
While its non-biodegradable nature is the headline issue, the true environmental impact of Teflon packing is tied to its entire lifecycle, from manufacturing and operational wear to its final disposal as persistent waste.
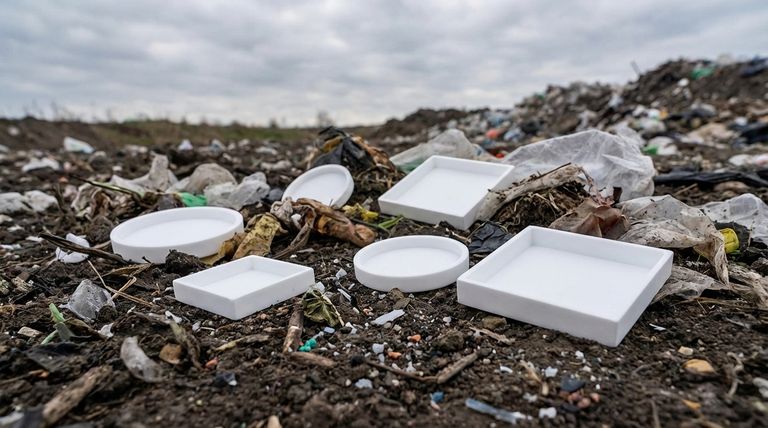

The Core Environmental Challenge: Persistence
The same chemical stability that makes Teflon packing a durable sealing solution also makes it an environmental liability at the end of its life.
What "Non-Biodegradable" Means for PTFE
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), the chemical compound known as Teflon, is a fluoropolymer. Its molecular bonds are exceptionally strong, making it resistant to chemical attack, thermal degradation, and microbial action.
Unlike organic materials, it will not decompose into simpler, harmless substances. It simply remains in its original form for centuries.
The Problem of Accumulation
Every piece of used Teflon packing that is thrown away contributes to a growing volume of permanent waste. Over time, this material accumulates in landfills, taking up space without breaking down.
Microplastic Generation from Wear
The reference to packing "peeling" over time points to a more subtle but significant issue. During operation, mechanical stress and friction can cause the packing to shed microscopic particles.
These tiny fragments of PTFE can enter process fluids or be released into the environment during maintenance. As a form of microplastic, they contribute to the persistent pollution of water and soil ecosystems.
Beyond Disposal: Operational and Lifecycle Concerns
A full assessment of Teflon packing's environmental footprint requires looking beyond just the end-of-life disposal problem.
How Premature Failure Increases Waste
Teflon packing is not universally effective. As noted, it performs poorly in highly alkaline conditions.
Using it in an incompatible application leads to rapid degradation, leaks, and premature failure. This requires more frequent replacement, which multiplies the amount of non-biodegradable waste generated over the equipment's lifespan.
The Link Between Incompatibility and Pollution
When packing fails, it can lead to leaks of the process fluid. If the substance being sealed is hazardous, this failure results in direct environmental contamination, compounding the waste issue of the packing material itself.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a packing material always involves balancing competing priorities. Teflon's environmental drawbacks must be weighed against its unique performance benefits.
The Benefit: Durability in the Right Context
In chemically compatible environments (e.g., strong acids, solvents), Teflon's inertness provides an exceptionally long service life.
This durability can reduce the frequency of maintenance and replacement compared to less-resistant materials. In these specific cases, using Teflon can actually minimize the total volume of waste generated over time.
The Drawback: Permanent Waste
The fundamental trade-off is that this durability becomes a permanent liability. There is currently no common or scalable method to recycle or safely break down used PTFE packing. Its longevity in service is matched by its longevity in the landfill.
The Application is Key
The environmental cost of Teflon packing is lowest when it is used correctly—in applications where its long service life is fully realized. Misapplication not only causes operational problems but significantly worsens its environmental impact by creating waste more quickly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the appropriate packing requires a clear understanding of your operational needs and environmental priorities.
- If your primary focus is maximizing reliability in corrosive environments (excluding high pH): Teflon packing's chemical resistance can be an asset, reducing waste by extending the time between replacements.
- If your primary focus is minimizing long-term environmental persistence: Explore alternatives made from graphite or natural fibers (like flax or ramie), which are either more inert or biodegradable.
- If your primary focus is sealing highly alkaline products: Avoid Teflon packing to prevent premature failure, equipment damage, and the creation of unnecessary waste.
Ultimately, a responsible choice is an informed one that considers the material's performance within your specific system and its impact from creation to disposal.
Summary Table:
| Environmental Concern | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| Non-Biodegradable | Persists indefinitely in landfills and the environment. |
| Microplastic Generation | Sheds microscopic particles that pollute soil and water. |
| Premature Failure | Incompatible use (e.g., high pH) leads to more frequent waste. |
| Operational Pollution | Failure can cause leaks of hazardous process fluids. |
Struggling to balance sealing performance with environmental responsibility? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including seals and packing. We understand the critical trade-offs. Our experts can help you select or custom-fabricate the right sealing solution for your specific application—whether in semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial settings—to maximize service life and minimize environmental impact. Let's find a durable, responsible solution together.
Contact our engineering team today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are some important physical property values for PTFE? Master Its Extreme Performance for Demanding Applications
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What is the temperature range that PTFE can withstand? From -200°C to +260°C for Demanding Applications
- What are some applications of CNC machined PTFE parts? Critical Components for Medical, Electrical & Food Industries
- Why is PTFE considered a significant discovery? A Material That Revolutionized Industry



















