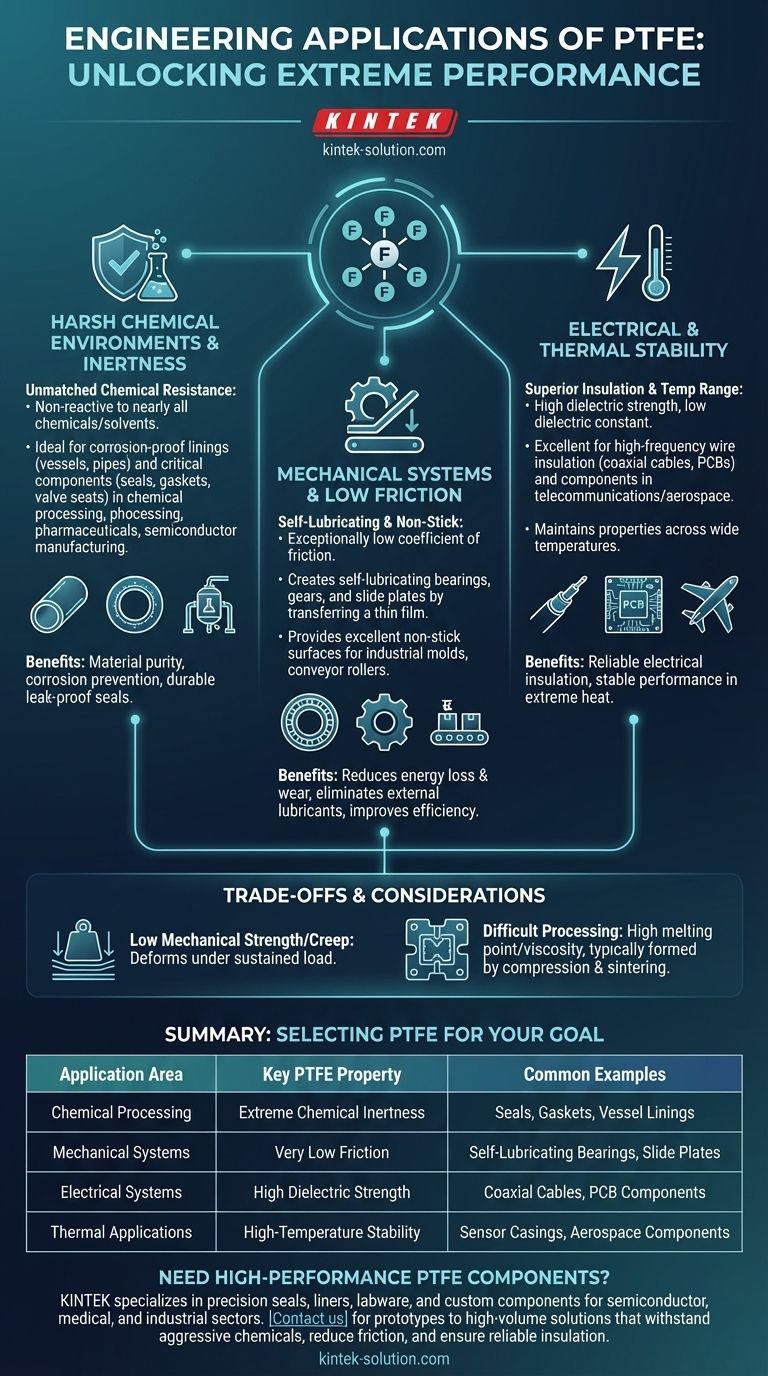
In engineering, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is primarily used for applications that demand extreme chemical resistance, very low friction, and high-performance electrical insulation. Its key applications include creating non-stick surfaces, self-lubricating bearings, corrosion-proof linings for pipes and vessels, high-frequency wire insulation, and critical seals or gaskets for aggressive chemical environments.
The true value of PTFE in engineering stems from its unique combination of three core properties: it is almost completely chemically inert, it possesses one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid, and it is an exceptional electrical insulator.

Why PTFE is a Go-To Material for Harsh Chemical Environments
The defining characteristic of PTFE is its extreme resistance to chemical attack. This property makes it an indispensable material for handling corrosive and reactive substances.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE’s molecular structure, consisting of a strong carbon-fluorine bond, makes it non-reactive to nearly all chemicals and solvents. This allows it to be used for containers, vessel linings, and pipework that transport highly aggressive materials without degrading.
This inertness is critical in industries like chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and semiconductor manufacturing, where material purity and corrosion prevention are paramount.
Application in Seals and Gaskets
Because it doesn't degrade when exposed to harsh chemicals, PTFE is an ideal material for seals, gaskets, and valve components like seats and plugs. It ensures a durable, leak-proof seal in systems handling everything from industrial acids to high-purity fluids.
The Role of Low Friction in Mechanical Systems
PTFE is famous for its exceptionally low coefficient of friction, often compared to wet ice on wet ice. Engineers leverage this property to reduce energy loss and wear in moving parts.
Creating Self-Lubricating Components
PTFE is used to make self-lubricating bearings, gears, and slide plates. As these components operate, they transfer a thin film of PTFE to the mating surface, drastically reducing friction and eliminating the need for external liquid lubricants.
This is especially valuable in applications where lubrication is difficult, such as in food processing equipment or in cleanroom environments.
Developing High-Performance Non-Stick Surfaces
The same low-friction property that makes PTFE "slippery" also gives it excellent non-stick capabilities. While known for cookware, this is vital in industrial settings like commercial bakeware, conveyor belt rollers, and molds where easy release of materials is essential for efficiency.
Leveraging Electrical and Thermal Properties
Beyond its mechanical and chemical performance, PTFE’s electrical and thermal stability opens up another range of high-stakes applications.
Superior Electrical Insulation
PTFE has a very high dielectric strength and low dielectric constant, making it an outstanding electrical insulator. It is frequently used for insulating high-frequency wiring and cables, such as coaxial cables, and in components for printed circuit boards (PCBs).
Its performance is stable across a wide range of frequencies, a critical factor in telecommunications and aerospace electronics.
Stability at Extreme Temperatures
This material maintains its properties across a wide temperature range. Its durability in harsh thermal environments makes it suitable for components on aircraft, temperature sensor casings, and equipment used in high-temperature industrial processes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly versatile, PTFE is not the solution for every engineering problem. Its limitations are as important to understand as its strengths.
Mechanical Strength and Creep
Compared to other engineering plastics, PTFE has relatively low mechanical strength and is susceptible to "creep" or cold flow. Under a sustained load, the material can slowly deform, which must be accounted for in structural designs like bearings or high-pressure seals.
Processing and Fabrication
PTFE has a very high melting point and viscosity, which makes it difficult to process using conventional techniques like injection molding. It is typically formed through compression and sintering, which can be more complex and costly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting PTFE should be a deliberate decision based on the primary challenge you need to solve.
- If your primary focus is handling corrosive materials: Use PTFE for linings, gaskets, and fluid handling components to ensure maximum chemical resistance and longevity.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction and wear: Specify PTFE for bearings, slide plates, or non-stick coatings where self-lubrication is a key requirement.
- If your primary focus is high-performance electrical insulation: Choose PTFE for wiring, cables, and circuit board substrates in applications demanding low signal loss, especially at high frequencies.
Ultimately, PTFE's power lies in its ability to perform reliably in environments where most other materials would quickly fail.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key PTFE Properties Utilized | Common Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Processing | Extreme Chemical Inertness | Seals, Gaskets, Vessel Linings |
| Mechanical Systems | Very Low Friction | Self-Lubricating Bearings, Slide Plates |
| Electrical Systems | High Dielectric Strength | Coaxial Cables, PCB Components |
| Thermal Applications | High-Temperature Stability | Sensor Casings, Aerospace Components |
Need high-performance PTFE components for your critical application? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom components for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We combine material expertise with custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—to deliver solutions that withstand aggressive chemicals, reduce friction, and ensure reliable insulation. Contact us today to discuss your project requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What factors should be considered when choosing between Nylon and PTFE? Select the Right Material for Your Application
- What industrial benefits do PTFE-machined parts offer? Achieve Peak Performance in Demanding Applications
- What challenges arise when machining PTFE (Teflon)? Overcome Softness, Heat, and Instability
- What are the main applications of PTFE type Teflon? Unlock Its Versatility for Your Industry
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications



















