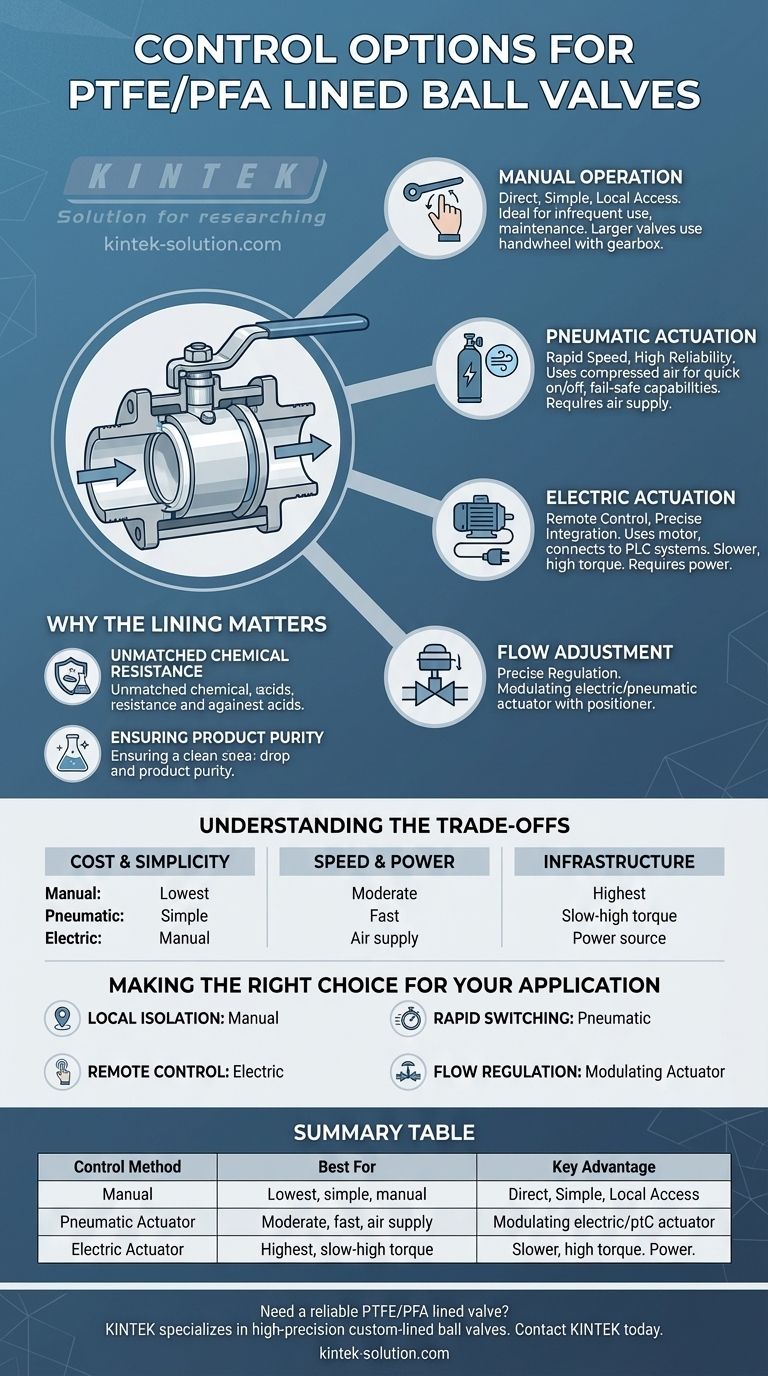
At its core, a PTFE/PFA lined ball valve can be controlled through four primary methods. These include simple manual operation with a lever, handwheel-driven gear operation for larger valves, and automated control via electric or pneumatic (gas source) actuators. The choice depends entirely on whether you need simple on/off functionality or more complex flow adjustment.
The control mechanism for a PTFE/PFA lined valve is not dictated by its corrosion-resistant lining, but by the operational requirements of your system. The fundamental choice is between direct manual control for local access and automated actuation for remote, frequent, or integrated process control.

Why the Lining Matters
Before selecting a control option, it's crucial to understand why you are using a PTFE/PFA lined valve in the first place. This context informs the entire decision.
### Unmatched Chemical Resistance
The primary function of the PTFE/PFA lining is to create an inert barrier between the process fluid and the metal body of the valve.
This makes the valve exceptionally resistant to corrosion from aggressive media like strong acids, alkalis, salts, and various organic solvents.
### Ensuring Product Purity
These valves are essential in industries like pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, and chemical processing where preventing contamination is critical.
The non-reactive lining ensures that the fluid remains pure and that the valve itself is not degraded by the process media.
A Breakdown of Control Options
With the valve's purpose established, you can evaluate the control methods based on your system's needs for access, speed, and automation.
### Manual Operation
This is the most direct and simple method of control, typically used for straightforward on/off applications.
It is ideal for valves that are easily accessible and do not need to be operated frequently, such as for system maintenance or manual process changeovers. For larger valves requiring more force, a handwheel with a gearbox is used instead of a simple lever.
### Pneumatic Actuation (Gas Source)
Pneumatic actuators use compressed air to open and close the valve rapidly. This is a common choice in industrial plants where a compressed air supply is readily available.
They are known for their reliability, high cycle speed, and fail-safe capabilities (e.g., automatically closing upon loss of air pressure).
### Electric Actuation
Electric actuators use a motor to operate the valve, making them perfect for remote control and integration with centralized process control systems like a PLC.
While typically slower than pneumatic actuators, they offer precise control and do not require a separate compressed air infrastructure, only an electrical power source.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Each control method comes with distinct advantages and disadvantages related to cost, complexity, and performance.
### Cost and Simplicity
Manual valves are the least expensive and simplest to install and maintain.
Automated options (pneumatic and electric) have a higher upfront cost and require more complex installation, including air lines or electrical wiring and control signals.
### Speed and Power
Pneumatic actuators offer the fastest actuation speed, making them ideal for emergency shutdown (ESD) systems or quick process diversions.
Electric actuators are slower but can be specified to deliver very high torque, which is beneficial for operating large or high-pressure valves.
### Infrastructure and Environment
The choice between pneumatic and electric often depends on existing plant infrastructure. If compressed air is widely available, pneumatic is a natural fit.
For remote locations without an air supply, electric actuation is the more practical solution. Both types have options available for hazardous or explosive environments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be based on the specific operational goal within your corrosive media pipeline.
- If your primary focus is simple, local isolation: A manual lever or handwheel-operated valve is the most reliable and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is rapid, automated on/off switching: A pneumatically actuated valve provides the speed and reliability you need, assuming an air supply is present.
- If your primary focus is remote or integrated system control: An electric actuator offers the best compatibility with modern process automation and control systems.
- If your primary focus is regulating or adjusting flow: Select a modulating electric or pneumatic actuator equipped with a positioner for precise control.
Ultimately, aligning the control method with your operational strategy ensures both safety and efficiency in your process.
Summary Table:
| Control Method | Best For | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Manual (Lever/Handwheel) | Simple on/off, local access, low cost | Direct, reliable operation |
| Pneumatic Actuator | Rapid on/off, automated systems, safety shutdowns | High speed and reliability |
| Electric Actuator | Remote control, process integration, precise flow adjustment | Seamless integration with PLCs and control systems |
Need a reliable PTFE/PFA lined valve for your aggressive media?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE and PFA components, including custom-lined ball valves for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you need a simple manual valve or a fully automated solution, our team can provide the right configuration—from prototypes to high-volume production.
Let us help you ensure process purity and reliability. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific application requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the disadvantages of PTFE Lined Globe Valves? Key Limitations to Consider
- What are the applications of barium sulphate fillers in PTFE? Enhance Chemical Purity & Dimensional Stability
- What is the importance of torque checks in PTFE butterfly valves? Prevent Leaks & Extend Valve Life
- Can PTFE machined parts be customized according to specific requirements? Achieve Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the mechanical properties of PTFE O-rings? A Guide to Low Friction, Chemical Resistance, and Trade-offs
- How is PTFE used in the pharmaceutical industry? Ensuring Product Purity and Safety
- How can sticking or hard operation of a PTFE butterfly valve be resolved? A 3-Step Guide to Restore Smooth Performance
- What are the different operation mechanisms for PTFE butterfly valves? Choose the Right Operator for Your System



















