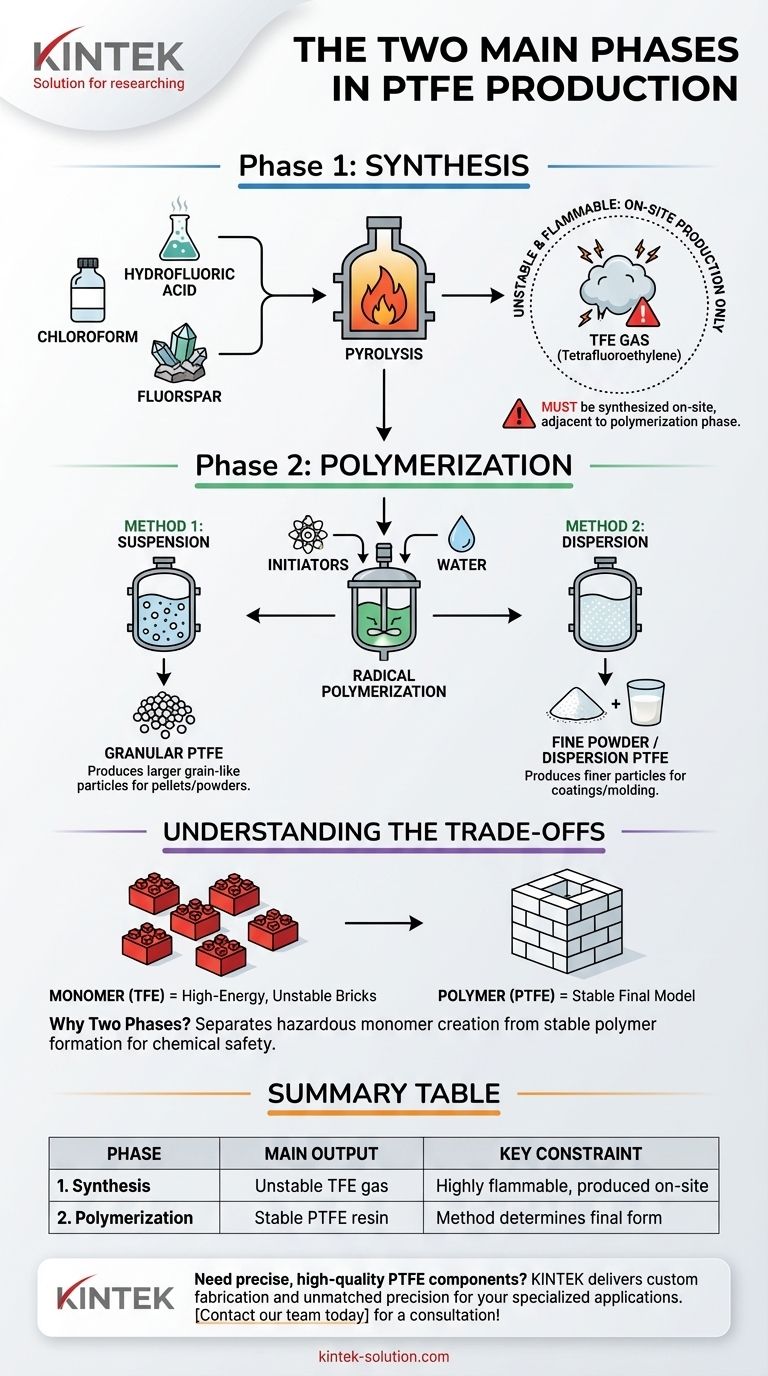
In short, the two main phases of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) production are synthesis and polymerization. First, the chemical building block, a gas called Tetrafluoroethylene (TFE), is created from raw materials. Second, this unstable gas is immediately converted into the stable, solid PTFE polymer through a process called radical polymerization.
The entire manufacturing process is a carefully controlled, two-act sequence. It begins by creating a highly reactive and flammable monomer (TFE) on-site, which is then immediately transformed into the famously inert and stable final polymer (PTFE).

Phase 1: Synthesizing the Monomer (TFE)
This initial phase is about creating the fundamental building block of PTFE. It involves a multi-step chemical synthesis that starts with common industrial chemicals.
The Raw Materials
The process begins with chloroform, hydrofluoric acid, and fluorspar. These materials are reacted to produce intermediate compounds.
The Chemical Transformation
Through a high-temperature process known as pyrolysis, these precursors are first converted into chlorodifluoromethane. This intermediate is then heated further to create the final monomer: Tetrafluoroethylene (TFE).
A Critical Safety Constraint
TFE gas is extremely flammable and chemically unstable. Because of this high risk, it cannot be stored or transported. TFE must be synthesized on-site, immediately adjacent to the facility where the next phase will occur.
Phase 2: Polymerizing TFE into PTFE
With the TFE monomer created, the second phase focuses on linking these individual molecules together into the long, stable chains that constitute the PTFE polymer.
The Core Mechanism: Radical Polymerization
This process uses chemical initiators and water to trigger a chain reaction. The TFE molecules (monomers) rapidly link end-to-end, forming the long molecular chains of the PTFE polymer.
Method 1: Suspension Polymerization
In this method, the polymerization occurs with the TFE suspended in water. This process results in larger, grain-like particles of PTFE, often processed into pellets or granular powders.
Method 2: Dispersion Polymerization
Alternatively, dispersion polymerization produces much finer PTFE particles. This creates a milky, aqueous dispersion suitable for coatings or a fine powder used for specific molding applications. These two methods are alternative paths, not sequential steps.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The distinction between the two phases is fundamental and driven by chemical necessity. Understanding this separation is key to grasping the entire manufacturing logic.
Monomer vs. Polymer
Think of TFE as individual, high-energy LEGO bricks that are difficult to handle. PTFE is the final, stable model you build from those bricks. The process first makes the bricks, then immediately builds the model before the bricks can cause a problem.
Why a Two-Phase Process is Essential
The extreme reactivity of the TFE monomer dictates this structure. Separating its synthesis from its polymerization allows for control over a hazardous material. The first phase manages the creation of a dangerous gas, while the second safely and immediately converts it into one of the most stable plastics known.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The two phases directly influence the logistics and final properties of the material.
- If your primary focus is on chemical safety and logistics: The on-site synthesis of the volatile TFE monomer is the most critical constraint of the entire process.
- If your primary focus is on material properties: The choice between suspension or dispersion polymerization in the second phase is what determines the final physical form (e.g., granular powder vs. fine dispersion) of the PTFE.
This two-stage transformation is a masterclass in chemical engineering, turning common materials into a volatile gas and then locking it into a remarkably stable and useful final product.
Summary Table:
| Phase | Key Process | Main Output | Key Constraint |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Synthesis | Creating TFE monomer from raw materials (e.g., chloroform) | Unstable Tetrafluoroethylene (TFE) gas | TFE is highly flammable and must be produced on-site |
| 2. Polymerization | Converting TFE into PTFE polymer chains | Stable PTFE resin (granular or fine powder) | Choice of method (suspension/dispersion) determines final material form |
Need precise, high-quality PTFE components?
At KINTEK, we are experts in PTFE, leveraging our deep understanding of its manufacturing to deliver superior custom components. Whether you're in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sector, we provide:
- Custom Fabrication: From prototypes to high-volume orders.
- Unmatched Precision: Ensuring the inert and stable properties of PTFE meet your exact specifications for seals, liners, labware, and more.
Let us put our material expertise to work for your specialized application. Contact our team today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature rating for PTFE gaskets? Maximize Performance from -200°C to 260°C
- What benefits does the low friction coefficient of PTFE provide for fasteners? Enhance Assembly & Prevent Seizing
- What are PTFE compounds and how are they used? Enhance Performance for Demanding Applications
- Why is the quality of PTFE resin important for structured and expanded PTFE? Ensure Long-Term Sealing Integrity
- What are the key characteristics of PTFE gaskets? Achieve Superior Sealing in Harsh Environments
- What are the common plumbing applications of PTFE? Ensure Leak-Proof, Durable Seals
- What are some common alternatives to Teflon sheets for heat press applications? Find the Right Protective Sheet
- How does the corrosion resistance of PTFE fasteners benefit medical applications? Ensure Device Safety and Reliability



















