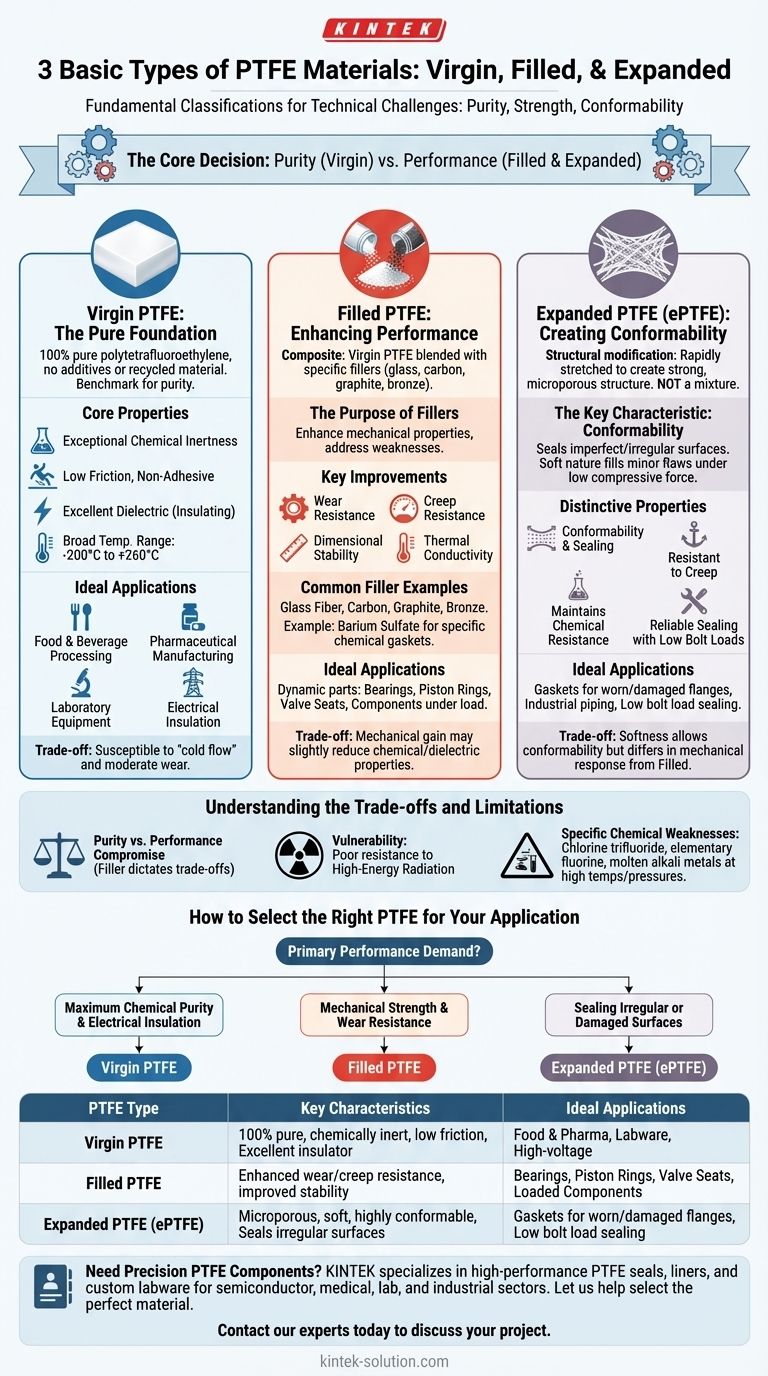
The three fundamental types of PTFE material are Virgin, Filled, and Expanded. These classifications are not arbitrary; they define how the base polytetrafluoroethylene polymer is processed and whether it has been enhanced with additives. Understanding these distinctions is crucial because each type is engineered to solve a different set of technical challenges, from chemical purity to mechanical strength.
The core decision is a trade-off between the absolute purity of Virgin PTFE and the targeted performance enhancements offered by Filled and Expanded variants. Your specific application—whether it demands extreme chemical inertness, high wear resistance, or superior sealing—will dictate the correct choice.

Understanding Virgin PTFE: The Pure Foundation
What is Virgin PTFE?
Virgin PTFE is 100% pure, unadulterated polytetrafluoroethylene. It contains no recycled material or additional filler compounds.
This purity makes it the benchmark material against which all other PTFE types are measured.
Core Properties
The defining characteristics of Virgin PTFE are its exceptional chemical inertness and a very low coefficient of friction, giving it a non-adhesive surface.
It also boasts excellent dielectric (electrical insulating) properties and operates across a vast temperature range, typically from –200°C to +260°C.
Ideal Applications
Virgin PTFE is the standard for applications where purity is paramount. This includes food and beverage processing, pharmaceutical manufacturing, laboratory equipment, and high-voltage electrical insulation.
Enhancing Performance with Filled PTFE
What is Filled PTFE?
Filled PTFE is a composite material created by blending Virgin PTFE resin with specific additives or fillers before it is molded.
These fillers are integrated to enhance the mechanical properties that are relative weaknesses in the pure material.
The Purpose of Fillers
While Virgin PTFE is chemically robust, it can be susceptible to "cold flow" (creep under pressure) and has moderate wear resistance.
Fillers are added to significantly improve properties like wear resistance, creep resistance, dimensional stability, and thermal conductivity.
Common Filler Examples
Common additives include glass fiber, carbon, graphite, and bronze. As an example, a barium sulfate-filled variant is often used to create gaskets for highly specific chemical environments, such as those involving hydrofluoric acid.
Creating Conformability with Expanded PTFE (ePTFE)
What is Expanded PTFE?
Expanded PTFE, or ePTFE, is not a mixture but a structural modification of Virgin PTFE. It is produced by rapidly stretching the material, which creates a strong, microporous structure.
This process results in a material that is simultaneously strong and remarkably soft and flexible.
The Key Characteristic: Conformability
The defining feature of ePTFE is its ability to conform to and seal imperfect or irregular surfaces. Its soft nature allows it to fill in minor scratches and flaws under low compressive force.
This is why biaxially expanded PTFE is a premier material for gaskets used on worn or damaged equipment flanges.
Distinctive Properties
Beyond conformability, ePTFE is highly resistant to creep and cold flow, maintains the excellent chemical resistance of Virgin PTFE, and provides reliable sealing with low bolt loads.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
The Purity vs. Performance Compromise
Adding fillers to create Filled PTFE is a direct trade-off. While mechanical strength and wear resistance are gained, there can be a slight reduction in overall chemical resistance or dielectric strength compared to Virgin PTFE.
The filler material itself dictates which properties are compromised and which are enhanced.
Environmental Vulnerabilities
Despite its robustness, PTFE in all its forms exhibits poor resistance to high-energy radiation. This exposure can cause the polymer's molecular structure to break down, leading to material failure.
Specific Chemical Weaknesses
While resistant to most chemicals, PTFE is not invincible. It can be attacked by highly reactive substances like chlorine trifluoride, elementary fluorine gas, and molten alkali metals, particularly at elevated temperatures and pressures.
How to Select the Right PTFE for Your Application
Choosing the correct PTFE variant is essential for project success. Base your decision on the primary performance demand of the component.
- If your primary focus is maximum chemical purity and electrical insulation: Virgin PTFE is the definitive choice for applications like laboratory equipment or high-voltage components.
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength and wear resistance: Filled PTFE provides the necessary durability for dynamic parts like bearings, piston rings, and valve seats.
- If your primary focus is sealing irregular or damaged surfaces: Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) offers the required conformability and sealing effectiveness, especially in gasketing for industrial piping.
Choosing the correct type transforms PTFE from a simple material into a precisely engineered solution.
Summary Table:
| PTFE Type | Key Characteristics | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Virgin PTFE | 100% pure, chemically inert, low friction, excellent electrical insulator | Food & pharmaceutical processing, labware, high-voltage insulation |
| Filled PTFE | Enhanced with additives (glass, carbon, etc.) for wear/creep resistance | Bearings, piston rings, valve seats, components under load |
| Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) | Microporous, soft, highly conformable, seals irregular surfaces | Gaskets for worn/damaged flanges, low bolt load sealing applications |
Need Precision PTFE Components for Your Project?
Understanding the nuances of PTFE is just the first step. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We deliver the precision you require, whether you need prototypes or high-volume production runs.
Let us help you select the perfect PTFE material and fabricate a solution that meets your exact specifications.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What standards define the dielectric strengths of PTFE products? A Guide to ASTM Standards & Performance
- Why is PTFE considered safe for food and beverage applications? Ensuring Product Purity and Operational Safety
- How can waste from PTFE manufacturing be reused? Transform Scrap into High-Performance Micropowder
- What are the main properties of Teflon material? Unrivaled Chemical Resistance & Non-Stick Performance
- What are the disadvantages of PTFE? Key Limitations in High-Performance Applications
- What are the key characteristics of PTFE's molecular structure? Unlock the Power of the Fluorine Sheath
- Is PTFE coating safe to use? A Guide to Safe Temperatures and Applications
- What are the key features of PTFE laminated fabric? Unmatched Protection & Breathability



















