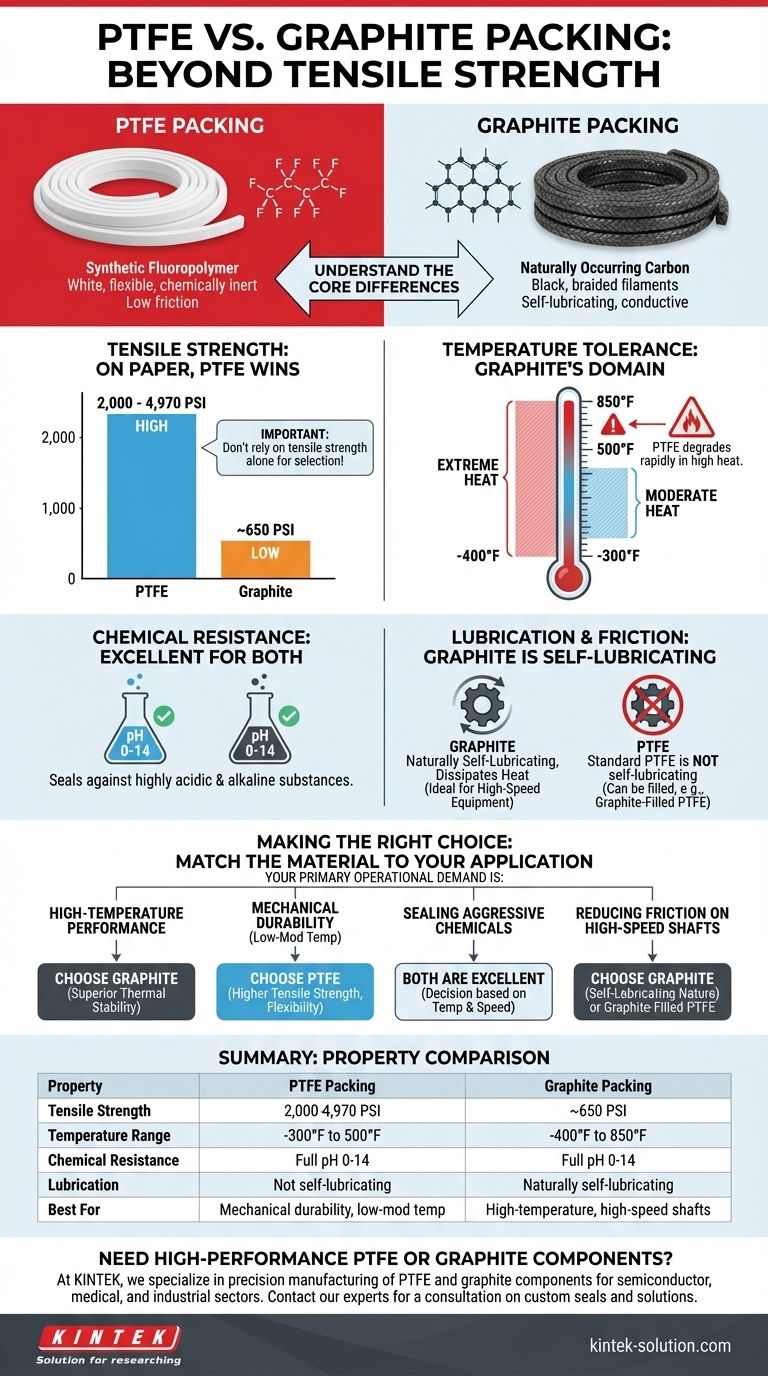
On paper, PTFE packing has a significantly higher tensile strength, with values ranging from 2,000 to nearly 5,000 PSI. Graphite packing, by contrast, has a tensile strength of approximately 650 PSI. However, this single metric is often misleading when selecting the right material for an industrial application.
The choice between PTFE and graphite packing is rarely about tensile strength alone. The decision must be driven by the specific operational conditions of your application, particularly temperature, shaft speed, and chemical environment.

A Deeper Look at Material Properties
Understanding the fundamental differences between these two materials is the key to making an informed decision. They originate from different sources and, as a result, possess distinct performance characteristics.
Composition and Origin
PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) is a synthetic fluoropolymer, known for its chemical inertness and low friction. It is typically a white, flexible material.
Graphite is a naturally occurring, inorganic form of pure carbon. For packing, it is often formed into braided filaments, giving it a characteristic black appearance.
Tensile Strength Explained
Tensile strength measures a material's resistance to being pulled apart. PTFE's polymer structure gives it a clear advantage here, with a strength of 2,000 - 4,970 PSI.
Graphite's braided carbon structure is less resistant to direct pulling forces, resulting in a lower tensile strength of 650 PSI.
Temperature Tolerance
This is one of the most critical differentiators. Graphite excels in extreme temperatures, operating effectively from -400°F to 850°F.
PTFE has a much narrower operating window, suitable for applications from -300°F to 500°F. It will degrade rapidly in high-temperature environments where graphite thrives.
Chemical Resistance
Both materials offer exceptional resistance to chemical attack. They are both rated for a full pH range of 0-14, making them suitable for sealing against highly acidic and alkaline substances.
Lubrication and Friction
Graphite is naturally self-lubricating and thermally conductive, allowing it to dissipate heat effectively. This makes it a superior choice for high-speed rotating equipment.
Standard PTFE is not self-lubricating but can be manufactured with lubricants to enhance performance. A common hybrid, graphite-filled PTFE, combines PTFE's strength with graphite's low friction and wear resistance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Focusing solely on a single specification can lead to incorrect material selection and premature failure. You must weigh the pros and cons within the context of your specific needs.
When High Tensile Strength is Not Enough
While PTFE is technically "stronger" in terms of tensile strength, this property is irrelevant if the application's temperature exceeds 500°F. In a high-temperature steam valve, for instance, PTFE would fail where graphite would perform reliably.
Brittleness vs. Flexibility
Graphite's lower tensile strength can make it more brittle and require more careful handling and installation than the more pliable PTFE packing.
Matching Material to the Machine
For a high-speed pump shaft, heat dissipation and low friction are paramount. Graphite's self-lubricating and conductive properties are far more valuable here than PTFE's higher tensile strength. Conversely, for a slow-moving valve stem in a room-temperature chemical line, PTFE's durability and flexibility might be the better choice.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use your primary operational demand to guide your selection.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature performance: Graphite is the definitive choice due to its superior thermal stability.
- If your primary focus is mechanical durability in a low-to-moderate temperature system: PTFE's higher tensile strength and flexibility offer a distinct advantage.
- If your primary focus is sealing against aggressive chemicals: Both are excellent, so the decision should be based on temperature and equipment speed.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction on high-speed shafts: Graphite's self-lubricating nature is ideal, with graphite-filled PTFE serving as a strong alternative.
Ultimately, choosing the right packing material requires matching its complete performance profile to the unique demands of your equipment.
Summary Table:
| Property | PTFE Packing | Graphite Packing |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 2,000 - 4,970 PSI | ~650 PSI |
| Temperature Range | -300°F to 500°F | -400°F to 850°F |
| Chemical Resistance | Full pH 0-14 | Full pH 0-14 |
| Lubrication | Not self-lubricating (can be filled) | Naturally self-lubricating |
| Best For | Mechanical durability, low-mod temp | High-temperature, high-speed shafts |
Need High-Performance PTFE or Graphite Components?
Choosing the right sealing material is critical to your equipment's performance and longevity. At KINTEK, we specialize in the precision manufacturing of PTFE and graphite components—including custom seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We understand that your application's unique demands for temperature, chemical resistance, and mechanical stress require a tailored solution. Whether you need the high tensile strength of PTFE or the extreme temperature tolerance of graphite, our team can provide custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Let us help you optimize your application. Contact our experts today for a consultation on the ideal material and component design for your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- How is PTFE used in industrial processes? Maximize Safety and Efficiency
- What are some important physical property values for PTFE? Master Its Extreme Performance for Demanding Applications
- What is the temperature range that PTFE can withstand? From -200°C to +260°C for Demanding Applications
- Why is PTFE considered a significant discovery? A Material That Revolutionized Industry
- What are some applications of CNC machined PTFE parts? Critical Components for Medical, Electrical & Food Industries



















