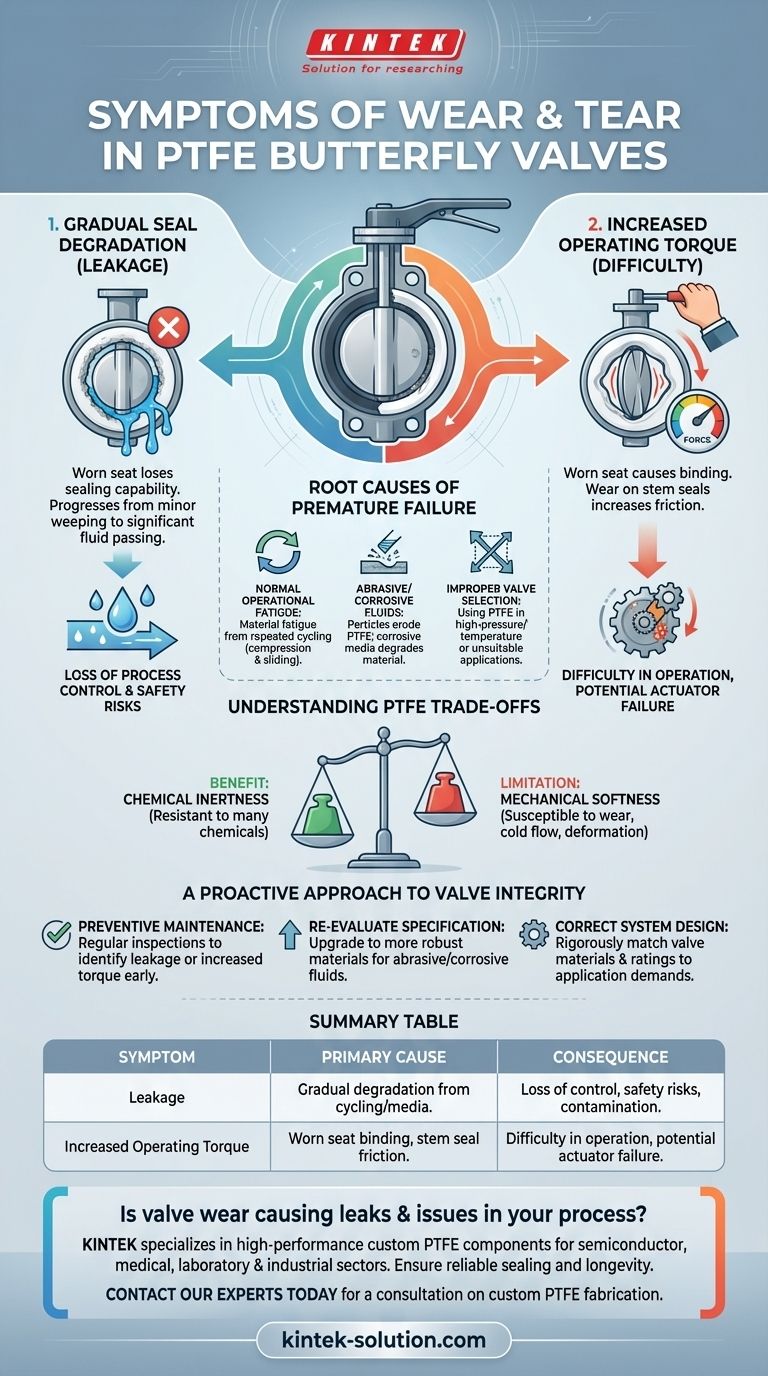
At its core, the two primary symptoms of wear and tear in a PTFE butterfly valve are a loss of sealing capability and increased difficulty in operation. These signs indicate that the valve's internal components, particularly the soft PTFE seat, are degrading and no longer performing as designed.
The visible symptoms of leakage and operational stiffness are lagging indicators of wear. The fundamental challenge is understanding that PTFE, despite its chemical resilience, is a soft material susceptible to mechanical failure, which is often accelerated by the specific conditions of your application.

Diagnosing the Symptoms of Wear
Wear in a PTFE-seated butterfly valve is not typically a sudden event. It is a gradual process that manifests in clear, observable performance changes.
Gradual Seal Degradation (Leakage)
The most critical function of a butterfly valve is to provide a tight shut-off. As the PTFE seat wears down from repeated opening and closing cycles or from the process media, it loses its ability to form a perfect seal around the disc.
This degradation first appears as minor, weeping leaks when the valve is closed and eventually progresses to a significant passing of fluid, compromising process control and safety.
Increased Operating Torque (Difficulty)
You may notice that the valve becomes progressively harder to open or close. This increased torque requirement is often a symptom of two underlying issues.
First, the worn seat can cause the disc to bind or chafe instead of seating smoothly. Second, wear on the stem seals or the intrusion of abrasive media into the stem area can create significant friction, making actuation difficult for both manual and automated valves.
Uncovering the Root Causes of Premature Failure
Recognizing the symptoms is the first step. To prevent recurrence, you must understand what is accelerating the wear process.
Normal Operational Fatigue
Every time a valve is cycled, the disc compresses and slides against the PTFE seat. Over thousands of cycles, this mechanical stress naturally causes the material to fatigue, compress, and wear away, even under ideal conditions.
Abrasive or Corrosive Fluids
This is a primary cause of accelerated failure. If the fluid contains suspended solids or abrasive particles, it will act like sandpaper on the soft PTFE liner, physically eroding it with every cycle.
Similarly, while PTFE is highly resistant to many chemicals, aggressive or corrosive fluids, especially at elevated temperatures, can slowly degrade the material's integrity, making it brittle and prone to cracking.
Improper Valve Selection
A valve that is not correctly specified for the application is destined for a short service life. Using a PTFE-seated valve in a high-pressure, high-temperature, or abrasive service for which it was not designed will cause it to fail rapidly.
Understanding the Trade-offs of PTFE
PTFE is chosen for specific reasons, but those strengths come with inherent limitations that are critical to understanding its wear patterns.
The Benefit: Chemical Inertness
The primary advantage of PTFE is its exceptional resistance to a vast range of chemicals. It is often the only viable choice for liners and seats in highly corrosive applications.
The Limitation: Mechanical Softness
The key trade-off is that PTFE is a relatively soft material. It is susceptible to mechanical wear from abrasion and can be permanently deformed under high pressure or temperature, a phenomenon known as "cold flow," which directly leads to leakage.
A Proactive Approach to Valve Integrity
Instead of reacting to failures, a proactive strategy based on your operational goals is the most effective way to manage valve health.
- If your primary focus is preventing unplanned downtime: Implement a regular inspection and preventive maintenance schedule to identify early signs of leakage or increased torque before they cause a shutdown.
- If your primary focus is handling abrasive or corrosive fluids: Re-evaluate your valve specification; upgrading to a valve with a more robust liner material may be necessary for long-term reliability.
- If your primary focus is designing a new system: Ensure the valve's material, size, and pressure/temperature ratings are rigorously matched to the specific demands of the application from the outset.
By treating these symptoms as valuable data about your process, you can make informed decisions that enhance the safety and reliability of your entire system.
Summary Table:
| Symptom | Primary Cause | Consequence |
|---|---|---|
| Leakage | Gradual degradation of the soft PTFE seat from cycling or media. | Loss of process control, safety risks, and contamination. |
| Increased Operating Torque | Worn seat causing disc binding or friction from damaged stem seals. | Difficulty in manual/automated operation, potential for actuator failure. |
Is valve wear causing leaks and operational issues in your process?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance, custom PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our precision production ensures reliable sealing and longevity, even in demanding applications with abrasive or corrosive media.
Let us provide a solution that enhances your system's integrity and minimizes unplanned downtime. Contact our experts today for a consultation on custom PTFE fabrication, from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What challenges arise when machining PTFE (Teflon)? Overcome Softness, Heat, and Instability
- What are the main applications of PTFE type Teflon? Unlock Its Versatility for Your Industry
- What industrial benefits do PTFE-machined parts offer? Achieve Peak Performance in Demanding Applications
- What finishing techniques are effective for machined Teflon parts? Achieve Functional Performance and Dimensional Stability
- What chemical processing applications involve PTFE-machined parts? Essential Components for Corrosive & High-Purity Systems



















