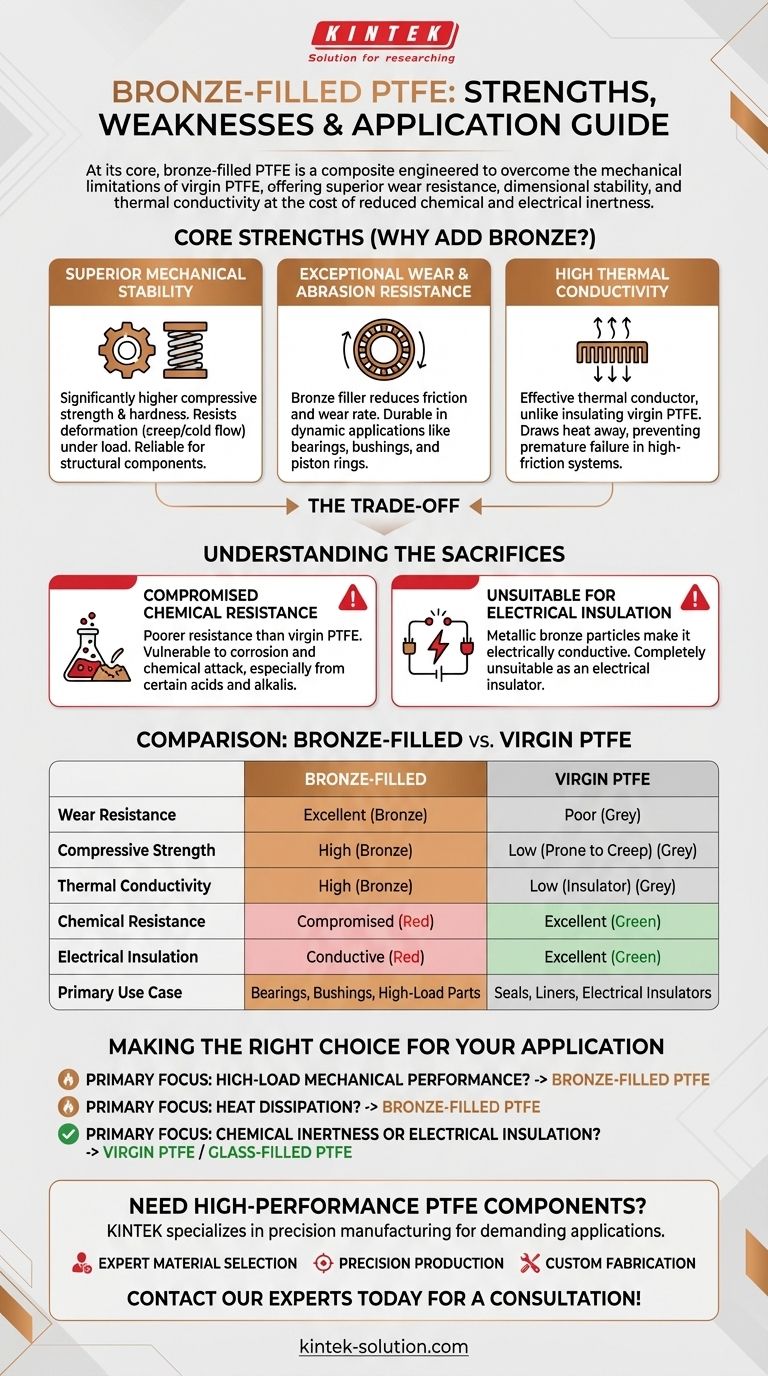
At its core, bronze-filled PTFE is a composite material engineered to overcome the mechanical limitations of virgin PTFE. It offers vastly superior wear resistance, dimensional stability, and thermal conductivity, making it ideal for demanding mechanical applications. However, these enhancements come at the cost of reduced chemical resistance and the loss of PTFE's excellent electrical insulation properties.
The addition of bronze transforms PTFE from a soft, inert insulator into a hard, thermally conductive material. This trade-off is the central principle: you sacrifice chemical and electrical inertness to gain significant mechanical robustness and the ability to dissipate heat.

Why Add Bronze to PTFE? The Core Strengths
The primary reason to specify bronze-filled PTFE is to enhance its performance under mechanical and thermal stress. This is typically achieved by compounding PTFE with 40% to 60% bronze powder.
Superior Mechanical Stability and Strength
Virgin PTFE is susceptible to deforming under load, a phenomenon known as creep or cold flow. Adding bronze particles dramatically improves the material's structural integrity.
This results in significantly higher compressive strength and hardness. The material maintains its shape under pressure, making it a reliable choice for structural components.
Exceptional Wear and Abrasion Resistance
Bronze-filled PTFE is one of the most wear-resistant PTFE variants. The bronze filler acts as a bearing material, reducing the friction and wear rate of the composite.
This makes it exceptionally durable in dynamic applications like plain bearings, bushings, and piston rings where it endures constant rubbing and sliding contact.
High Thermal Conductivity
Unlike virgin PTFE, which is a thermal insulator, bronze-filled PTFE is an effective thermal conductor.
This property is critical in applications that generate heat from friction. The material can draw heat away from the surface, preventing premature failure and maintaining performance stability.
Understanding the Trade-offs: What You Sacrifice
The benefits of adding bronze do not come for free. The filler material fundamentally alters some of PTFE's most well-known properties.
Compromised Chemical Resistance
PTFE is famous for being nearly chemically inert. However, the bronze filler is not.
This blend has poorer chemical resistance than virgin or glass-filled PTFE. It is more vulnerable to corrosion and chemical attack, especially from certain acids and alkalis, which limits its use in highly corrosive environments.
Unsuitability for Electrical Insulation
The most critical limitation is in electrical applications. The metallic bronze particles make the material electrically conductive.
Therefore, bronze-filled PTFE is completely unsuitable for use as an electrical insulator. For applications requiring dielectric strength, other grades like virgin or glass-filled PTFE are the correct choice.
Reduced Non-Stick Properties
While it retains a low coefficient of friction, the inclusion of bronze particles can slightly diminish the exceptional non-stick, low-friction surface that pure PTFE is known for.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right material depends entirely on the primary demands of your design.
- If your primary focus is high-load mechanical performance: Bronze-filled PTFE is an excellent choice for bearings, bushings, and compressor rings due to its high compressive strength and wear resistance.
- If your primary focus is heat dissipation: The material's high thermal conductivity makes it ideal for components in dynamic systems that generate friction and need to manage heat buildup.
- If your primary focus is chemical inertness or electrical insulation: You must avoid bronze-filled PTFE and instead consider virgin PTFE or a grade filled with an inert material like glass.
By understanding this fundamental trade-off between mechanical strength and chemical inertness, you can confidently specify bronze-filled PTFE for applications where its robust properties are paramount.
Summary Table:
| Property | Bronze-Filled PTFE | Virgin PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Wear Resistance | Excellent | Poor |
| Compressive Strength | High | Low (Prone to Creep) |
| Thermal Conductivity | High | Low (Insulator) |
| Chemical Resistance | Compromised | Excellent |
| Electrical Insulation | Conductive | Excellent |
| Primary Use Case | Bearings, Bushings, High-Load Parts | Seals, Liners, Electrical Insulators |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components for Your Application?
Selecting the right material is critical for your project's success. At KINTEK, we specialize in the precision manufacturing of PTFE components, including custom bronze-filled PTFE parts for demanding applications in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We provide:
- Expert Material Selection: Our team will help you determine if bronze-filled PTFE is the ideal choice for your specific requirements, balancing strength, wear resistance, and environmental factors.
- Precision Production: We manufacture components to your exact specifications, ensuring optimal performance and durability.
- Custom Fabrication: From rapid prototypes to high-volume production runs, we deliver quality and consistency.
Let us help you build a better product. Contact our experts today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs



















