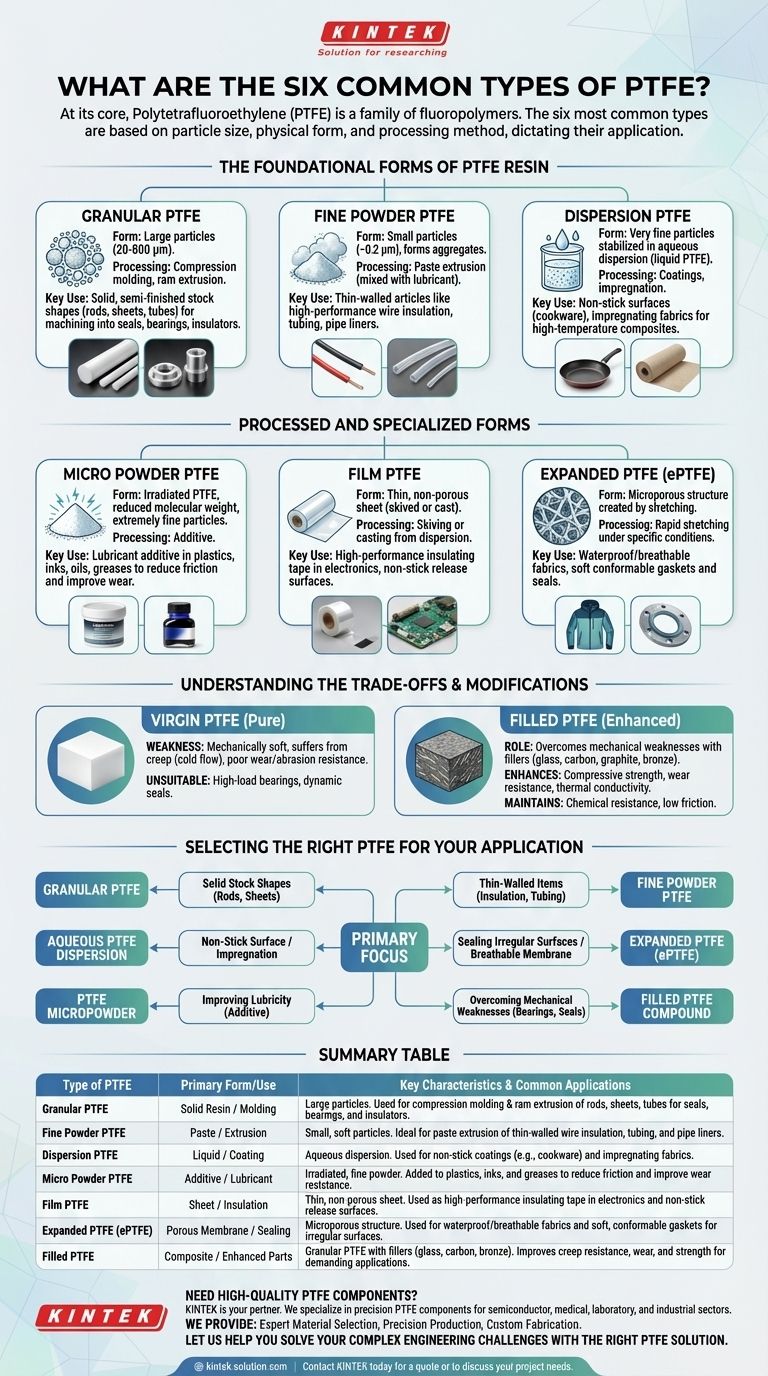
At its core, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is not a single material but a family of related fluoropolymers. The six most common types are Granular PTFE, Fine Powder PTFE, Dispersion PTFE, Micro Powder PTFE, Film PTFE, and Expanded PTFE. These classifications are not arbitrary; they are based on the polymer's particle size and physical form, which directly dictate the processing method and final application.
The key to understanding PTFE is to see it not as one substance, but as a system of raw materials and processed forms. Your choice depends entirely on whether you are molding a solid part, extruding a thin-walled tube, applying a coating, or using it as an additive.
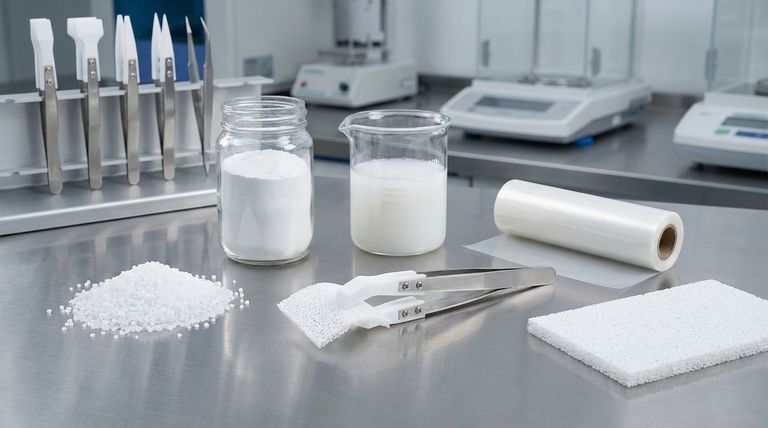

The Foundational Forms of PTFE Resin
The primary forms of PTFE are essentially raw materials used in different manufacturing processes. The distinction between them comes down to particle size and how they are handled.
Granular PTFE
Granular PTFE consists of relatively large particles (20-800 micrometers). It is designed to be processed using techniques similar to those for metals, such as compression molding and ram extrusion.
This is the foundational material for creating solid, semi-finished stock shapes. Think of it as the starting block for machining parts. Common products include rods, sheets, and tubes that are later cut into finished components like bearings, seals, or insulators.
Fine Powder PTFE
Fine Powder PTFE is made of much smaller, softer particles (around 0.2 micrometers) that form aggregates. This type is not free-flowing like granular resin.
Its unique structure makes it ideal for paste extrusion. In this process, the powder is mixed with a lubricant (like naphtha) to form a paste, which is then extruded under high pressure to create thin-walled articles. This is the method used for making high-performance wire insulation, tubing, and pipe liners.
Dispersion PTFE
This form consists of very fine PTFE particles stabilized in water, creating an aqueous dispersion. It is essentially liquid PTFE.
Dispersions are used for coatings and impregnation. The most famous application is creating the non-stick surfaces on cookware. It is also used to impregnate fiberglass cloth to create high-temperature, chemically resistant composite materials.
Processed and Specialized Forms
These types of PTFE are often derived from the foundational forms or are processed in a unique way to create materials with distinct properties and uses.
Micro Powder PTFE
Also known as lubricant powder, this is PTFE that has been irradiated to break down its molecular weight, resulting in extremely fine particles.
Unlike fine powder (for extrusion) or granular resin (for molding), micropowder is not meant to be used on its own. It is an additive mixed into other materials—such as plastics, inks, oils, and greases—to reduce their coefficient of friction and improve wear resistance.
Film PTFE
PTFE film is a thin, non-porous sheet created from PTFE resin. It can be manufactured by skiving a molded billet of granular PTFE or by casting from a dispersion.
This form is prized for its exceptional dielectric properties and chemical inertness. It is widely used in electronics as a high-performance insulating tape and in industrial settings as a non-stick release surface.
Expanded PTFE (ePTFE)
Expanded PTFE is a remarkable material created by rapidly stretching PTFE under specific conditions. This process creates a microporous structure of nodes interconnected by fibrils.
This structure makes ePTFE both waterproof and breathable, famously used in high-performance fabrics. Industrially, its soft, conformable nature makes it an excellent material for gaskets and seals, especially for sealing damaged or irregular flange surfaces.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Modifications
While PTFE is known for its incredible chemical resistance and low friction, its "virgin" or pure form has significant mechanical limitations.
The Weakness of Virgin PTFE
Pure PTFE is mechanically soft. It suffers from creep, or cold flow, meaning it deforms permanently under sustained load. It also has relatively poor wear and abrasion resistance compared to other engineering plastics.
These limitations make virgin PTFE unsuitable for many demanding mechanical applications, such as high-load bearings or dynamic seals.
The Role of Filled PTFE
To overcome these mechanical weaknesses, fillers are added to granular PTFE resin before molding. These filled PTFE compounds offer vastly improved performance characteristics.
Common fillers include glass fiber, carbon, graphite, and bronze. Each filler imparts different properties, enhancing attributes like compressive strength, wear resistance, and thermal conductivity while generally maintaining PTFE's excellent chemical resistance and low friction.
Selecting the Right PTFE for Your Application
Choosing the correct type of PTFE is a critical engineering decision based on the final product and manufacturing process.
- If your primary focus is creating solid stock shapes (rods, sheets) for machining: Your starting point is Granular PTFE.
- If your primary focus is producing thin-walled items like wire insulation or tubing: Fine Powder PTFE for paste extrusion is the required material.
- If your primary focus is applying a non-stick surface or impregnating a fabric: You must use an aqueous PTFE Dispersion.
- If your primary focus is sealing irregular surfaces or creating a breathable membrane: The microporous structure of Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) is necessary.
- If your primary focus is improving the lubricity of another material: PTFE Micropowder serves as a high-performance additive.
- If your primary focus is overcoming the mechanical weaknesses of pure PTFE for bearings or seals: A Filled PTFE compound is the correct choice.
Understanding these fundamental types transforms PTFE from a single material into a versatile toolkit for solving complex engineering challenges.
Summary Table:
| Type of PTFE | Primary Form/Use | Key Characteristics & Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Granular PTFE | Solid Resin / Molding | Large particles. Used for compression molding & ram extrusion of rods, sheets, tubes for seals, bearings, and insulators. |
| Fine Powder PTFE | Paste / Extrusion | Small, soft particles. Ideal for paste extrusion of thin-walled wire insulation, tubing, and pipe liners. |
| Dispersion PTFE | Liquid / Coating | Aqueous dispersion. Used for non-stick coatings (e.g., cookware) and impregnating fabrics. |
| Micro Powder PTFE | Additive / Lubricant | Irradiated, fine powder. Added to plastics, inks, and greases to reduce friction and improve wear resistance. |
| Film PTFE | Sheet / Insulation | Thin, non-porous sheet. Used as high-performance insulating tape in electronics and non-stick release surfaces. |
| Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) | Porous Membrane / Sealing | Microporous structure. Used for waterproof/breathable fabrics and soft, conformable gaskets for irregular surfaces. |
| Filled PTFE | Composite / Enhanced Parts | Granular PTFE with fillers (glass, carbon, bronze). Improves creep resistance, wear, and strength for demanding applications. |
Need High-Quality PTFE Components?
Navigating the different types of PTFE is the first step. KINTEK is your partner for the next one. We specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—from seals and liners to custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We provide:
- Expert Material Selection: Guidance on choosing the right PTFE type (Granular, Fine Powder, ePTFE, etc.) or filled compound for your specific performance requirements.
- Precision Production: Advanced processing techniques to transform raw PTFE into high-tolerance parts.
- Custom Fabrication: Full support from prototype development to high-volume production runs.
Let us help you solve your complex engineering challenges with the right PTFE solution.
Contact KINTEK today for a quote or to discuss your project needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What challenges arise when machining PTFE (Teflon)? Overcome Softness, Heat, and Instability
- What chemical processing applications involve PTFE-machined parts? Essential Components for Corrosive & High-Purity Systems
- What industrial benefits do PTFE-machined parts offer? Achieve Peak Performance in Demanding Applications
- What are the main applications of PTFE type Teflon? Unlock Its Versatility for Your Industry
- What finishing techniques are effective for machined Teflon parts? Achieve Functional Performance and Dimensional Stability



















