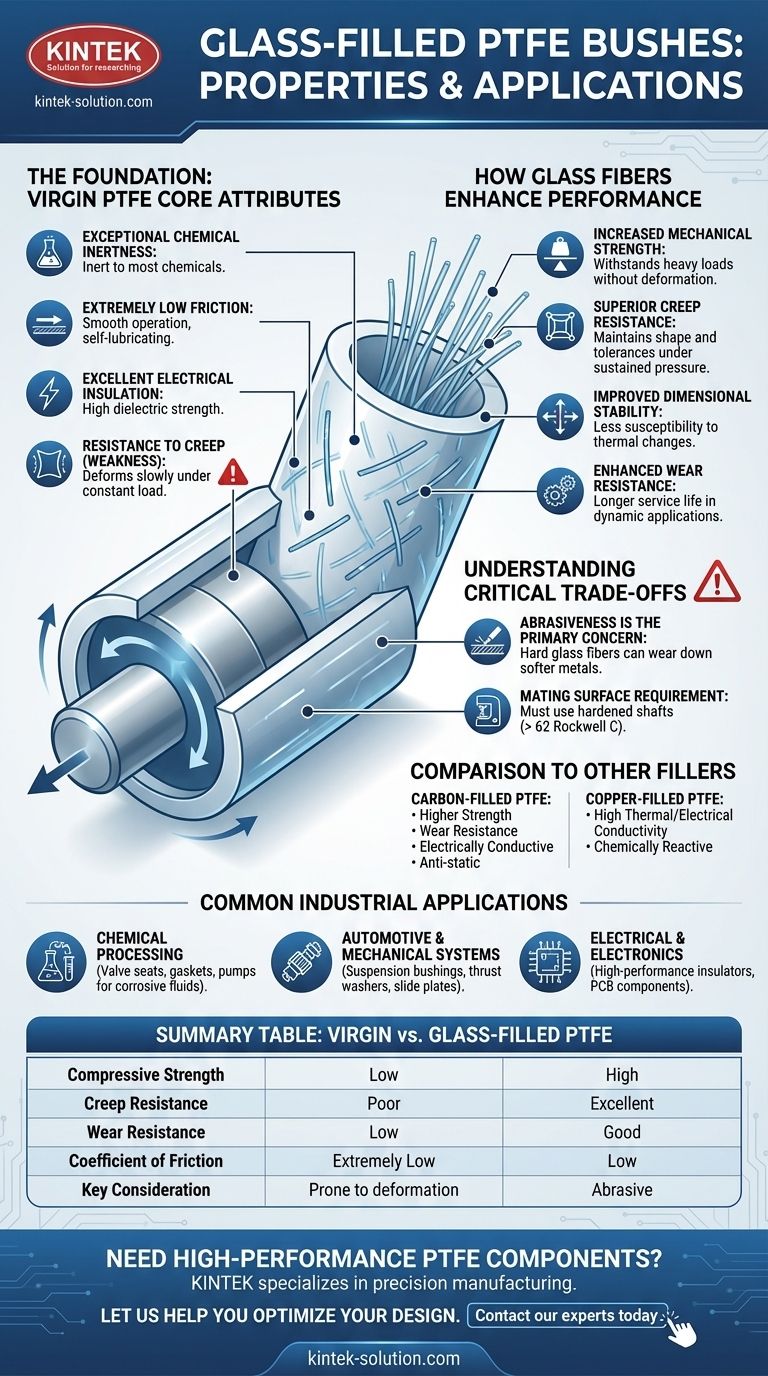
Glass-filled PTFE bushes are high-performance polymer components designed to enhance the natural properties of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). By incorporating glass fibers, typically at a 25% concentration, these bushes gain significant mechanical strength, stiffness, and resistance to deformation under load, while retaining PTFE’s excellent low-friction and chemical-resistant characteristics. They are primarily used in applications requiring self-lubricating, durable moving parts in demanding industrial environments.
The central takeaway is that adding glass fibers to PTFE creates a mechanically superior material for bushes operating under higher loads and temperatures. This improvement, however, introduces a critical trade-off: the material becomes abrasive, demanding the use of hardened mating surfaces to prevent premature wear.

The Foundation: Virgin PTFE's Core Attributes
To understand the role of glass fill, we must first appreciate the baseline properties of pure Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), from which these bushes are made.
Exceptional Chemical Inertness
PTFE is virtually inert to almost all industrial chemicals and solvents. This makes it a default choice for components used in aggressive chemical processing environments.
Extremely Low Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, which is why it is famous for non-stick surfaces. This allows PTFE bushes to operate smoothly without external lubrication.
Excellent Electrical Insulation
As a material with high dielectric strength, PTFE is an outstanding electrical insulator, making it suitable for applications where electrical isolation is critical.
Resistance to Creep
A key weakness of virgin PTFE is "creep," or the tendency to slowly deform under a constant load. While this can be useful for seals, it is a significant drawback for structural components like bushes.
How Glass Fibers Enhance Performance
The introduction of glass fibers fundamentally changes the mechanical behavior of PTFE, turning a soft, pliable material into a robust engineering plastic.
Increased Mechanical Strength
Glass fibers act as a reinforcement, dramatically increasing the compressive strength and stiffness of the PTFE. This allows the bushes to withstand heavy loads without deforming.
Superior Creep Resistance
The rigid structure provided by the glass fibers significantly reduces the material's tendency to creep. This ensures the bush maintains its shape and tolerances over time, even under sustained pressure.
Improved Dimensional Stability
The addition of glass makes the composite less susceptible to thermal expansion and contraction. This dimensional stability is crucial for maintaining tight clearances in precision assemblies.
Enhanced Wear Resistance
Glass-filled PTFE offers much better resistance to wear compared to its unfilled counterpart, leading to a longer service life in dynamic applications with sliding or rotating parts.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
While the benefits are significant, choosing glass-filled PTFE requires a clear understanding of its limitations and how it compares to other filled grades.
Abrasiveness is the Primary Concern
The key drawback of glass-filled PTFE is its abrasive nature. The hard glass fibers can wear down softer metals.
It is strongly recommended that glass-filled PTFE bushes only be used with mating shafts that have a surface hardness greater than 62 Rockwell C. Using them on soft shafts will lead to rapid failure of the shaft itself.
Comparison to Other Fillers
Glass is not the only option for reinforcing PTFE. Understanding the alternatives provides critical context for material selection.
- Carbon-Filled PTFE: Offers higher compressive strength and wear resistance than glass-filled variants. Crucially, it is also electrically conductive, making it ideal for anti-static applications.
- Copper-Filled PTFE: Significantly increases thermal and electrical conductivity. However, it is more chemically reactive and can be prone to corrosion in certain environments.
Common Industrial Applications
The unique balance of properties in glass-filled PTFE makes it a solution for specific engineering challenges across several industries.
Chemical Processing
Because it retains PTFE's chemical inertness while adding strength, it is used for valve seats, gaskets, and pump parts that handle corrosive fluids under pressure.
Automotive and Mechanical Systems
The material's strength and wear resistance make it ideal for suspension bushings, thrust washers, and slide plates that operate under heavy, dynamic loads.
Electrical and Electronics
In applications requiring both structural integrity and electrical insulation, glass-filled PTFE is used for high-performance insulators and components in printed circuit boards (PCBs).
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct PTFE variant is crucial for the success and longevity of your application.
- If your primary focus is high mechanical loads with a hardened steel shaft: Glass-filled PTFE is an excellent and cost-effective choice for its strength and creep resistance.
- If your primary focus is static dissipation or you need better wear resistance with a hard shaft: Carbon-filled PTFE is the superior option.
- If your primary focus is maximum chemical inertness on a soft or unhardened shaft: You must use unfilled (virgin) PTFE to avoid abrasion.
- If your primary focus is heat dissipation: Copper-filled PTFE should be considered, provided its chemical reactivity is not a concern for your environment.
Ultimately, selecting glass-filled PTFE is a calculated engineering decision that balances its powerful mechanical enhancements against the critical requirement of material compatibility.
Summary Table:
| Property | Glass-Filled PTFE (Typical 25% Glass) | Virgin PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Compressive Strength | High | Low |
| Creep Resistance | Excellent | Poor |
| Wear Resistance | Good | Low |
| Coefficient of Friction | Low | Extremely Low |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (Retained from PTFE) | Excellent |
| Key Consideration | Abrasive to soft metals | Prone to deformation under load |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components for Your Application?
Choosing the right material is critical for the longevity and efficiency of your equipment. The decision between virgin, glass-filled, carbon-filled, or copper-filled PTFE depends entirely on your specific requirements for load, environment, and mating surfaces.
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of PTFE components, including custom bushes, seals, liners, and labware. We serve the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors, offering expert guidance on material selection and custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Let us help you optimize your design. Contact our experts today to discuss your project and discover how our PTFE solutions can enhance your product's performance and durability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability



















