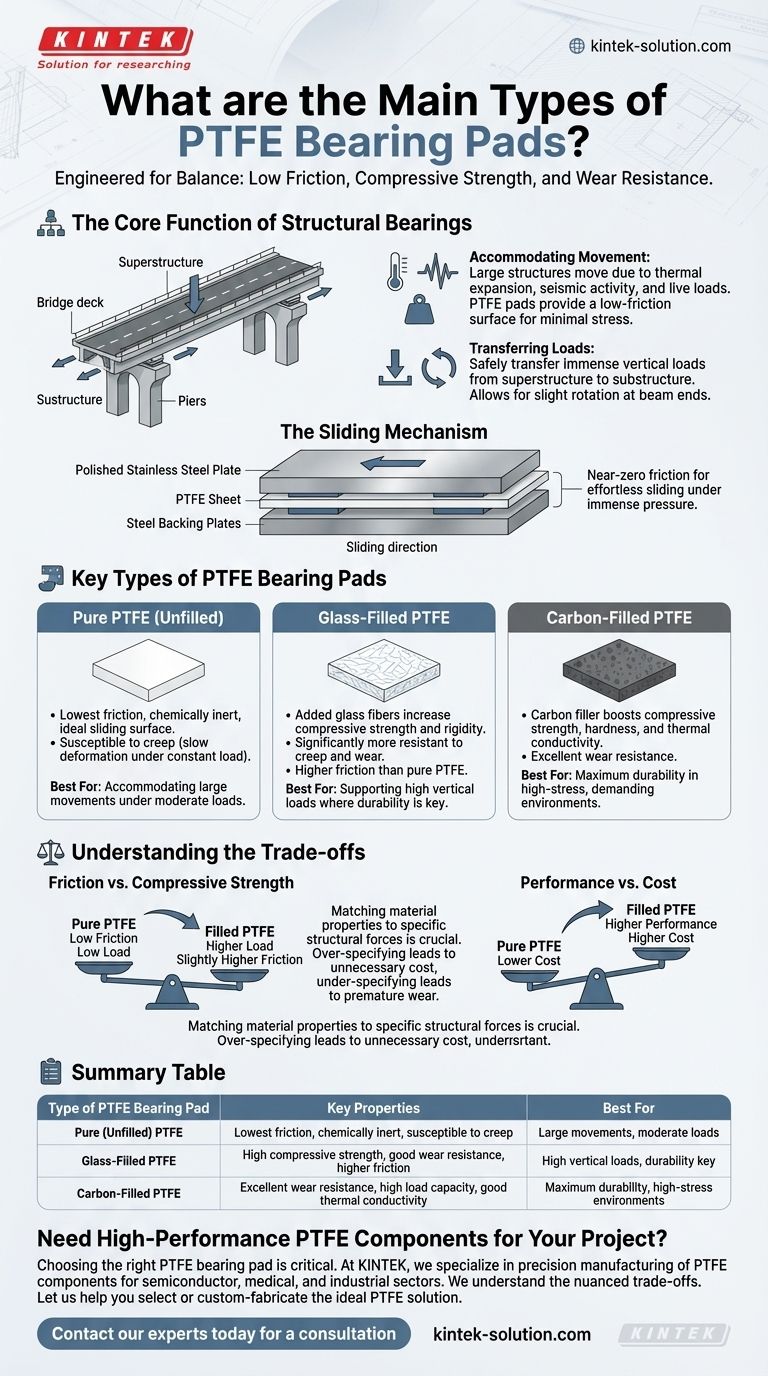
The primary types of PTFE bearing pads are pure (unfilled) PTFE, glass-filled PTFE, and carbon-filled PTFE. Each formulation is engineered to provide a specific balance of low friction, compressive strength, and wear resistance tailored to different structural demands.
The choice between PTFE bearing types is not about finding the "best" material, but about matching the specific properties of the filler material to the unique load, movement, and environmental demands of the structure.
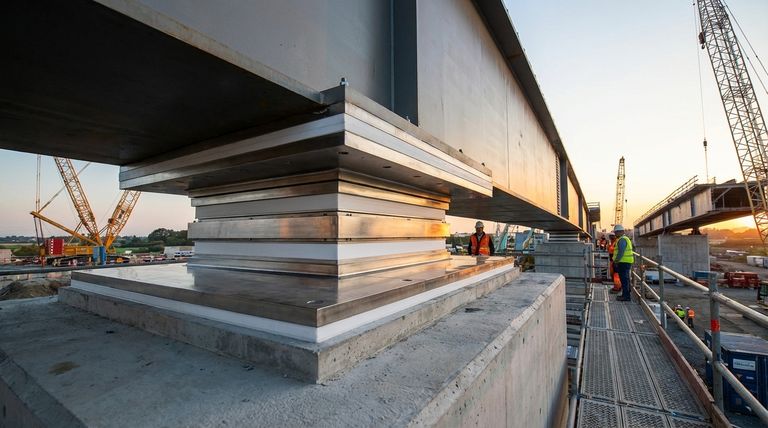

The Core Function of Structural Bearings
A structural bearing is a critical component that creates a manageable interface between a structure's substructure (like a pier) and its superstructure (like a bridge deck). Its job is to safely transfer loads while accommodating movement.
Accommodating Movement
Large structures are not static; they move due to thermal expansion and contraction, seismic activity, and live loads. PTFE pads provide an exceptionally low-friction surface, allowing these movements to occur with minimal stress on the structural elements.
Transferring Loads
The bearing must transfer immense vertical loads from the superstructure to the substructure. It also handles horizontal forces and allows for slight rotation at the beam ends, which is crucial for structural integrity.
The Sliding Mechanism
A typical PTFE sliding bearing consists of two main elements. A lower element holds a sheet of PTFE, often recessed into a steel backing plate. An upper element consists of a highly polished stainless steel plate, also attached to a backing plate. The near-zero friction between the PTFE and polished steel allows for effortless sliding under immense pressure.
Key Types of PTFE Bearing Pads
While all PTFE pads offer low friction, adding fillers dramatically changes their mechanical properties.
Pure PTFE (Unfilled)
This is the most basic form, offering the lowest coefficient of friction of any solid material. It is chemically inert and highly effective at providing a sliding surface.
However, pure PTFE is relatively soft and can be susceptible to "creep," which is slow deformation when under a constant load.
Glass-Filled PTFE
By adding glass fibers to the PTFE matrix, the material's compressive strength and rigidity are significantly increased. This makes it far more resistant to creep and wear.
This is a common choice for applications with higher contact pressures where durability is a primary concern, even if it results in a marginally higher friction coefficient than pure PTFE.
Carbon-Filled PTFE
Adding carbon as a filler also boosts compressive strength and hardness, similar to glass. Carbon provides excellent wear resistance and can also improve the material's thermal conductivity.
This formulation is often specified for highly demanding applications that require a combination of high load capacity and long-term durability.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting the right material requires balancing competing priorities. Making the wrong choice can lead to premature wear or unnecessary expense.
Friction vs. Compressive Strength
Pure PTFE provides the absolute lowest friction but has the lowest load-bearing capacity. Adding fillers like glass or carbon increases the load capacity and wear resistance but introduces a slightly higher coefficient of friction.
Performance vs. Cost
Filled PTFE variants are more expensive to produce than pure PTFE. Over-specifying a bearing pad with a high-performance filled material for a low-load application leads to unnecessary project costs.
The Importance of the System
The PTFE pad is only half of the equation. The performance of the entire bearing assembly depends on the quality and finish of the mating stainless steel plate. Any contamination or corrosion on the steel surface will drastically increase friction and accelerate wear on the PTFE.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final selection should be driven by the specific engineering requirements of your project.
- If your primary focus is accommodating large movements under moderate loads: Pure PTFE is often the most effective and economical choice due to its exceptionally low friction.
- If your primary focus is supporting high vertical loads with significant wear resistance: Glass-filled PTFE provides the necessary compressive strength to prevent creep and ensure durability.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability in a high-stress environment: Carbon-filled PTFE offers an excellent balance of high load capacity and superior wear characteristics for the most demanding applications.
Ultimately, a successful design hinges on correctly matching the material's properties to the specific structural forces at play.
Summary Table:
| Type of PTFE Bearing Pad | Key Properties | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Pure (Unfilled) PTFE | Lowest friction, chemically inert, susceptible to creep | Accommodating large movements under moderate loads |
| Glass-Filled PTFE | High compressive strength, good wear resistance, higher friction than pure | Supporting high vertical loads where durability is key |
| Carbon-Filled PTFE | Excellent wear resistance, high load capacity, good thermal conductivity | Maximum durability in high-stress, demanding environments |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components for Your Project?
Choosing the right PTFE bearing pad is critical for your structure's safety and longevity. At KINTEK, we specialize in the precision manufacturing of PTFE components, including seals, liners, labware, and custom bearing pads for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We understand the nuanced trade-offs between friction, strength, and durability. Our team can help you select or custom-fabricate the ideal PTFE solution—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensuring it meets your exact engineering specifications.
Let's discuss how we can support your project. Contact our experts today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature range for PTFE expansion bellows? From -200°C to 260°C for Extreme Applications
- What are the available sizes and thicknesses for PTFE sheets? A Guide for Engineers & Designers
- What techniques help minimize material smearing during Teflon machining? Achieve Clean, Precise PTFE Parts
- What are the limitations of PTFE gaskets in high-pressure applications? Overcoming Cold Flow & Creep Issues
- What industries commonly use CNC machined Teflon parts? Key Sectors Relying on PTFE's Performance
- What are the benefits of using PTFE for seals and gaskets? Unlock Superior Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the different types of PTFE seals and their applications? Match the Right Seal to Your Application
- How do PTFE properties benefit butterfly valve performance? Enhance Durability & Efficiency



















