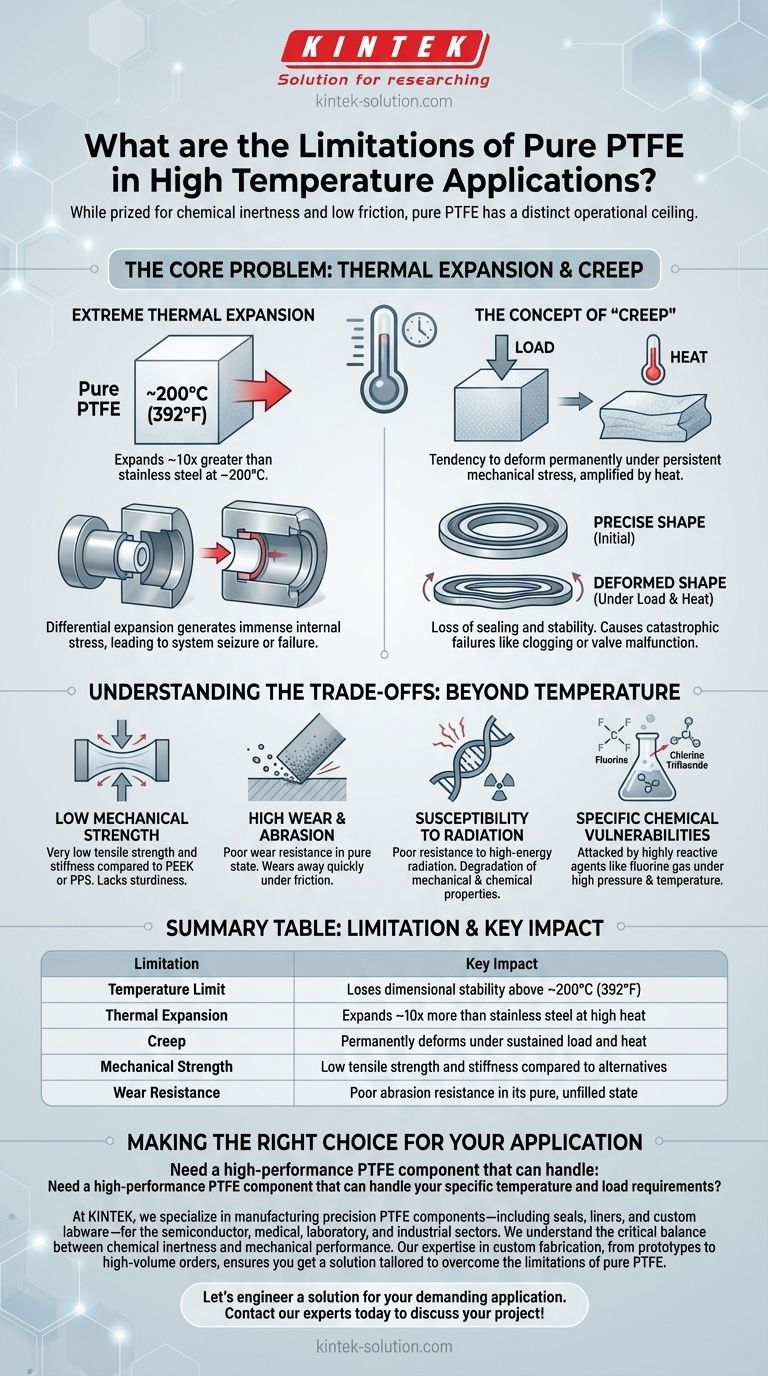
While prized for its chemical inertness and low friction, pure Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) has a distinct operational ceiling for high-temperature applications. Its practical temperature resistance ends around 200°C (392°F). Beyond this point, it does not simply melt but undergoes rapid mechanical failure due to extreme thermal expansion and a phenomenon known as creep, causing permanent deformation.
The critical limitation of pure PTFE at high temperatures is not a sudden melting point but a rapid loss of dimensional and mechanical stability. This behavior makes it unsuitable for precision components or high-load applications that approach or exceed 200°C (392°F).

The Core Problem: Thermal Expansion and Creep
The term "temperature limit" can be misleading. For PTFE, the failure is a physical, not just a thermal, event. It's a loss of the very properties that make it useful in a mechanical system.
Extreme Thermal Expansion
At temperatures approaching 210°C (410°F), PTFE expands at a rate roughly 10 times greater than stainless steel.
In a constrained assembly, such as a seal within a metal valve, this differential expansion generates immense internal stress. The PTFE component will push against its housing, which can lead to system seizure or failure.
The Concept of "Creep"
Creep is the tendency of a solid material to deform permanently under the influence of persistent mechanical stress. Pure PTFE is highly susceptible to creep, a weakness that is significantly amplified by heat.
When a PTFE component like a gasket or bearing is under load at an elevated temperature, it will slowly and irreversibly change its shape. The seal will no longer seal, and the bearing will lose its tolerance.
The Consequence: Loss of Sealing and Stability
The combined effects of thermal expansion and creep mean that pure PTFE components lose their precisely engineered shape.
This leads directly to catastrophic failures in many applications. A common example is the clogging or failure of valve mechanisms, where a deformed PTFE seat can no longer regulate flow correctly.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Beyond Temperature
The challenges with PTFE in demanding applications extend beyond just heat. Understanding these weaknesses is crucial for proper material selection.
Low Mechanical Strength
Compared to other high-performance polymers like PEEK or PPS, pure PTFE has very low tensile strength and stiffness. It is a "soft" material that lacks sturdiness under significant load pressure.
This inherent softness makes it unsuitable for applications requiring high structural integrity or resistance to deformation from direct force.
High Wear and Abrasion
In its pure, unfilled state, PTFE exhibits poor wear resistance. When subjected to friction or abrasive forces, it wears away quickly.
This is why many high-performance PTFE applications use "filled" grades, where materials like glass, carbon, or bronze are added to improve mechanical strength and wear resistance.
Susceptibility to Radiation
PTFE has poor resistance to high-energy radiation. Exposure can cause the polymer's long molecular chains to break down, degrading its mechanical and chemical properties.
This makes it a poor choice for many nuclear and aerospace applications where radiation exposure is a known factor.
Specific Chemical Vulnerabilities
While famous for its chemical inertness, PTFE is not invincible. It can be attacked by highly reactive chemical agents.
Substances like elementary fluorine gas, chlorine trifluoride, and other exotic fluorinating agents can react with PTFE, especially under high pressure and temperature.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right material requires aligning its properties with your primary operational goal. Pure PTFE is an excellent choice for many low-temperature, low-load applications, but you must consider alternatives when conditions become more demanding.
- If your primary focus is operating near its temperature limit (up to 200°C): You must design your system to accommodate significant thermal expansion and the potential for creep under load.
- If your primary focus is mechanical durability under load: Pure PTFE is likely the wrong choice; investigate filled PTFE grades or alternative polymers like PEEK.
- If your primary focus is use in a high-radiation environment: Pure PTFE should be avoided, as it will degrade. Verify any potential replacement material for its specific radiation resistance.
Understanding these limitations allows you to leverage PTFE's unique strengths while avoiding its critical failure points.
Summary Table:
| Limitation | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| Temperature Limit | Loses dimensional stability above ~200°C (392°F) |
| Thermal Expansion | Expands ~10x more than stainless steel at high heat |
| Creep | Permanently deforms under sustained load and heat |
| Mechanical Strength | Low tensile strength and stiffness compared to alternatives |
| Wear Resistance | Poor abrasion resistance in its pure, unfilled state |
Need a high-performance PTFE component that can handle your specific temperature and load requirements?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We understand the critical balance between chemical inertness and mechanical performance. Our expertise in custom fabrication, from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensures you get a solution tailored to overcome the limitations of pure PTFE.
Let's engineer a solution for your demanding application. Contact our experts today to discuss your project!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer PTFE Magnetic Stirring Bar
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer PTFE Cleaning Rack
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What makes PTFE versatile for various industrial uses? Discover the Key Properties Driving Its Success
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of filled PTFE? An Engineering Trade-Off Guide
- Why is water used in PTFE polymerization? The Essential Role of Water in Creating High-Performance PTFE
- What aerospace applications use Teflon? Unlock Reliability in Extreme Environments
- What are the advantages of PTFE's low friction properties? Boost Efficiency & Extend Component Life
- What are the challenges in processing PTFE? Overcoming High Melt Viscosity and Machining Difficulties
- What are the medical applications of PTFE? Critical Uses in Implants and Instruments
- What is the temperature range that PTFE can withstand? From -200°C to +260°C for Demanding Applications



















