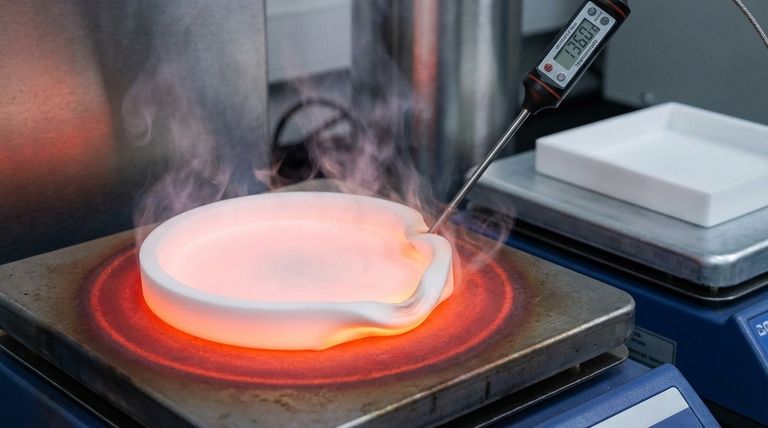
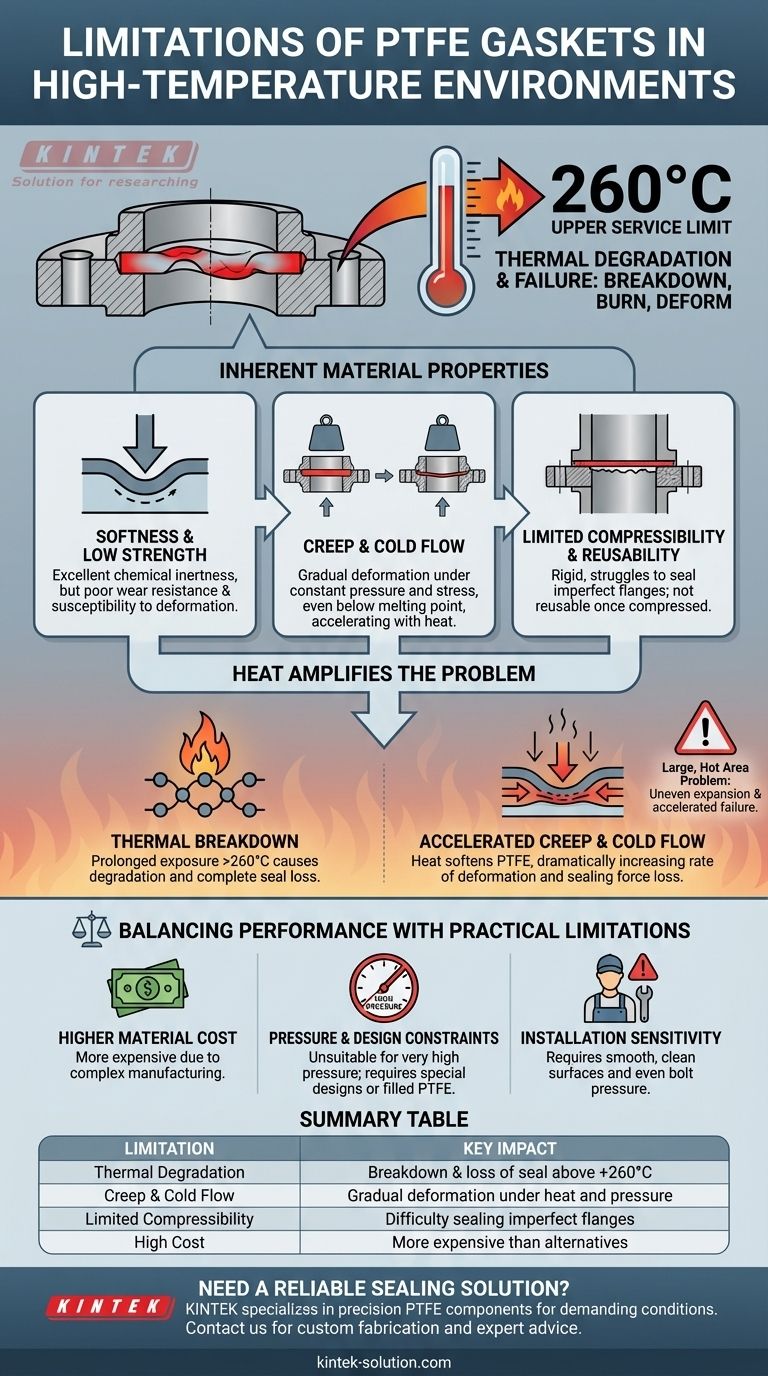
The primary limitation of PTFE gaskets in high-temperature environments is their tendency to break down, burn, and deform. While pure PTFE has an impressive upper service limit of around +260°C, prolonged exposure near this temperature—especially over large surfaces—can cause thermal degradation, leading to a loss of sealing integrity and eventual failure.
The core issue with PTFE is not just its temperature ceiling, but its inherent softness. This softness leads to mechanical weaknesses like creep and cold flow, which are significantly worsened by heat and pressure, causing the gasket to lose its seal over time.

Understanding PTFE's Inherent Material Properties
To grasp why PTFE struggles under certain conditions, we must first look at its fundamental characteristics. Its strengths in chemical resistance are directly tied to its weaknesses in mechanical stability.
Softness and Low Mechanical Strength: The Root Cause
PTFE is a relatively soft polymer. This property gives it excellent chemical inertness but also results in poor wear resistance and a susceptibility to deformation under load.
Creep: The Slow Deformation Under Stress
Creep is the gradual deformation of a material under constant, long-term stress. For a PTFE gasket, this means that even if the bolts are torqued correctly, the gasket material can slowly thin out, reducing the sealing pressure and potentially causing a leak.
Cold Flow: The Tendency to Deform
A related concept, cold flow, describes the material's tendency to deform under pressure, even at elevated temperatures below its melting point. This is a critical factor in high-temperature applications, as it accelerates the loss of the gasket's shape and effectiveness.
Limited Compressibility and Reusability
Unlike more pliable materials, PTFE gaskets are quite rigid. This limited compressibility makes it difficult for them to conform to scratched or imperfect flange surfaces, requiring consistent pressure to achieve a proper seal. Once compressed and used, they are not reusable.
How High Temperatures Magnify the Problem
Heat acts as a catalyst, amplifying the inherent mechanical weaknesses of pure PTFE and introducing the risk of thermal breakdown.
Thermal Degradation and Breakdown
The most direct limitation is thermal failure. When exposed to temperatures beyond its +260°C limit or subjected to prolonged heat stress near this point, the PTFE polymer can begin to degrade and burn, compromising the seal entirely.
Amplifying Creep and Cold Flow
Elevated temperatures make the PTFE material even softer and more prone to deformation. This means the rate of creep and cold flow increases dramatically, causing the gasket to lose its sealing force much faster than it would at room temperature.
The "Large, Hot Area" Problem
Large, heated surfaces pose a unique challenge. They can cause uneven thermal expansion and create inconsistent stress across the gasket, finding the weakest points and accelerating failure through a combination of thermal breakdown and cold flow.
Balancing Performance with Practical Limitations
While PTFE offers elite performance in specific areas, it's crucial to acknowledge its practical and economic trade-offs.
Higher Material Cost
PTFE gaskets are significantly more expensive than many traditional sealing materials, such as rubber gaskets. This is due to the complex manufacturing process of the PTFE polymer.
Pressure and Design Constraints
The softness and tendency to creep make pure PTFE unsuitable for very high-pressure applications. In such cases, special designs or filled PTFE (which incorporates materials like glass or carbon) are necessary to enhance mechanical strength.
Installation Sensitivity
Achieving a reliable seal with PTFE requires careful installation. The flange surfaces must be smooth and clean, and the bolt pressure must be applied evenly to compensate for the material's limited compressibility.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right gasket depends entirely on the specific demands of your system.
- If your primary focus is unmatched chemical inertness in temperatures below 260°C: Pure PTFE is an excellent choice, provided system pressures are moderate and flanges are in good condition.
- If your primary focus is high-pressure sealing or temperatures approaching the 260°C limit: You should strongly consider filled or reinforced PTFE gaskets to mitigate creep and improve mechanical stability.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for a standard application with imperfect flanges: A more compressible and forgiving material, such as a suitable elastomer, might be a more practical solution.
Understanding these material trade-offs is the key to ensuring long-term sealing reliability.
Summary Table:
| Limitation | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| Thermal Degradation | Breakdown and loss of seal above +260°C |
| Creep & Cold Flow | Gradual deformation under heat and pressure |
| Limited Compressibility | Difficulty sealing imperfect flanges |
| High Cost | More expensive than many alternative materials |
Need a reliable sealing solution for demanding conditions?
PTFE's limitations in high-temperature or high-pressure applications can compromise your system's integrity. At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We prioritize precision production and offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring your components meet the exact demands of your application.
Let us help you achieve a perfect, long-lasting seal. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
People Also Ask
- When and by whom was PTFE discovered? A Tale of Accidental Innovation
- What are some applications of CNC machined PTFE parts? Critical Components for Medical, Electrical & Food Industries
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What is the temperature range that PTFE can withstand? From -200°C to +260°C for Demanding Applications
- What are some important physical property values for PTFE? Master Its Extreme Performance for Demanding Applications



















