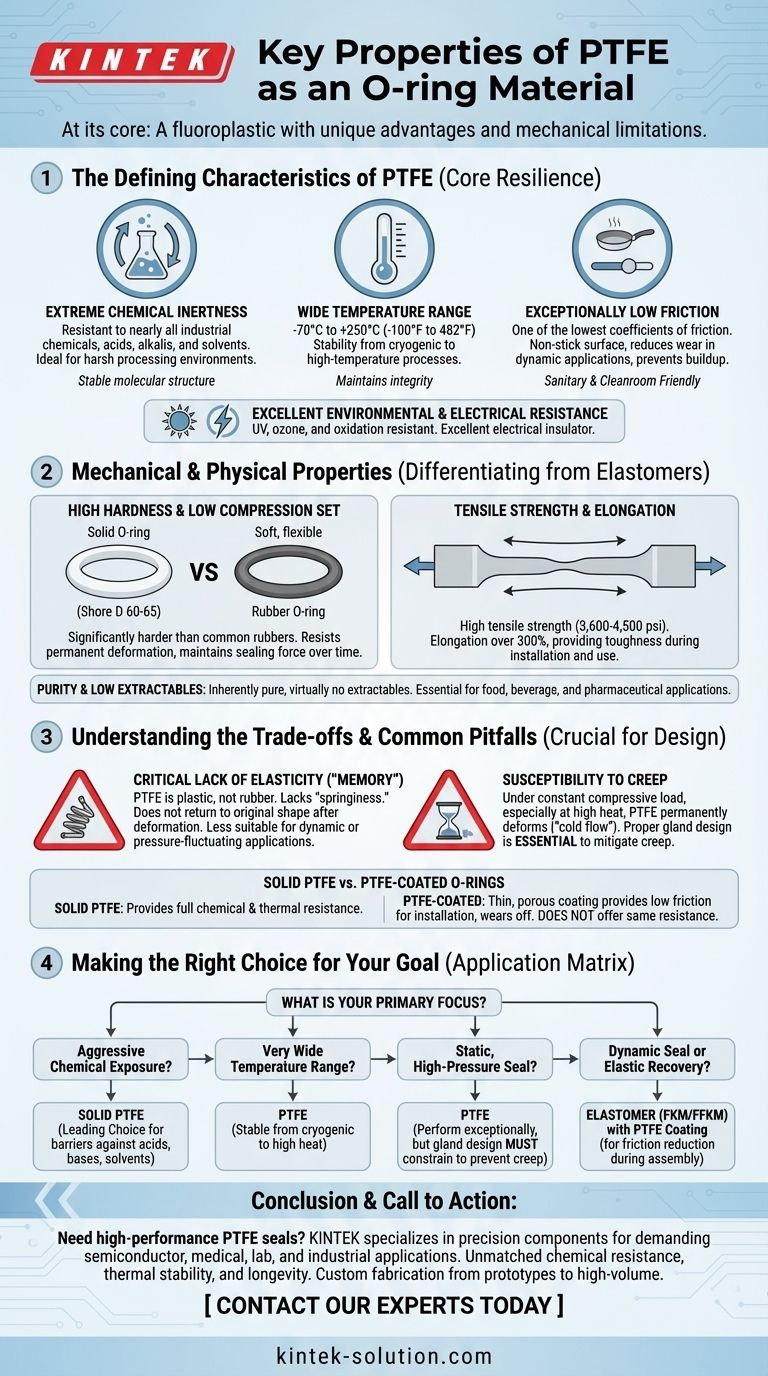
At its core, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is defined as a sealing material by three dominant characteristics: its near-universal chemical inertness, its wide operational temperature range, and its extremely low coefficient of friction. Unlike traditional rubber elastomers, PTFE is a fluoroplastic, giving it unique advantages in harsh environments but also imposing specific mechanical limitations that must be understood for successful application.
While PTFE offers unmatched resistance to chemicals and extreme temperatures, its defining limitation is its nature as a plastic, not a rubber. This results in very low elasticity, which is a critical factor to consider in any sealing design.

The Defining Characteristics of PTFE
PTFE's reputation in demanding industries is built on a foundation of exceptional resilience. These core properties make it a default choice for applications where other materials would quickly fail.
### Extreme Chemical Inertness
PTFE is resistant to nearly all industrial chemicals, including the most aggressive acids, alkalis, and solvents. This makes it an ideal choice for chemical processing, pharmaceutical, and petrochemical industries.
Its molecular structure is incredibly stable, providing a reliable barrier against substances that would degrade conventional elastomers.
### Wide Operational Temperature Range
PTFE maintains its integrity across an exceptionally broad temperature spectrum, typically cited from -70°C to +250°C (-100°F to 482°F).
This stability allows it to be used in applications ranging from cryogenic systems to high-temperature processing without significant loss of material properties.
### Exceptionally Low Friction
With one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, PTFE provides a non-stick surface. This is highly advantageous for reducing wear in dynamic sealing applications and easing installation.
This property also prevents material buildup on the O-ring surface, which is critical in sanitary or cleanroom environments.
### Excellent Environmental and Electrical Resistance
PTFE exhibits outstanding resistance to environmental factors like UV radiation, ozone, and oxidation, ensuring a long service life in exposed conditions.
It is also an excellent electrical insulator, making it suitable for applications where electrical isolation is a key requirement.
Mechanical and Physical Properties
While its resistances are top-tier, the mechanical properties of PTFE are what truly differentiate it from elastomeric seals.
### High Hardness and Low Compression Set
Solid PTFE O-rings typically have a hardness of 60-65 Shore D, which is significantly harder and less flexible than common rubbers like Nitrile or FKM.
However, PTFE has a very low compression set, meaning it resists permanent deformation after being compressed. This allows it to maintain its sealing force over time in the correct applications.
### Tensile Strength and Elongation
PTFE has a high tensile strength, generally in the range of 3,600 to 4,500 psi. This reflects its overall durability and resistance to tearing under tension.
Its ability to stretch before breaking (elongation) is also significant, typically over 300%, providing a degree of toughness during installation and use.
### Purity and Low Extractables
The material is inherently pure and has virtually no extractables, meaning it does not leach chemicals into the media it contacts. This is a non-negotiable requirement for food, beverage, and pharmaceutical applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
The strengths of PTFE are directly linked to its weaknesses as a sealing material. Ignoring these trade-offs is a common source of seal failure.
### Critical Lack of Elasticity ("Memory")
This is the most important limitation of PTFE. As a plastic, it lacks the "springiness" or elastic memory of rubber. Once stretched or deformed, it does not readily return to its original shape.
This makes it less suitable for dynamic applications or sealing situations that experience pressure fluctuations, as it cannot respond and adapt to changing gland dimensions as effectively as an elastomer.
### Susceptibility to Creep
Under a constant compressive load, especially at elevated temperatures, PTFE is susceptible to creep or "cold flow." This is a slow, permanent deformation that can eventually lead to a loss of sealing force.
Proper gland design that fully contains the O-ring is essential to mitigate the effects of creep.
### Solid PTFE vs. PTFE-Coated O-Rings
It is critical to distinguish between a solid PTFE O-ring and an elastomeric O-ring with a PTFE coating.
A coating provides a low-friction surface for installation and can add color identification. However, the coating is thin, porous, and wears off easily. It does not provide the chemical or thermal resistance of a solid PTFE O-ring.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct material requires matching its properties to the primary demands of your application.
- If your primary focus is aggressive chemical exposure: Solid PTFE is an industry-leading choice, providing a nearly impenetrable barrier against acids, bases, and solvents.
- If your primary focus is a very wide temperature range: PTFE's stability from cryogenic lows to high heat makes it one of the most versatile options available.
- If your primary focus is a static, high-pressure seal: PTFE can perform exceptionally well, but ensure your gland design properly constrains the ring to prevent creep.
- If your primary focus is a dynamic seal or requires elastic recovery: You should strongly consider an elastomer like FKM or FFKM, potentially with a PTFE coating for reduced friction during assembly.
Understanding PTFE's unique balance of chemical resilience and plastic-like rigidity is the key to deploying it effectively in demanding sealing applications.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Performance Characteristic | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to nearly all aggressive chemicals, acids, and solvents. | Ideal for chemical processing, pharmaceutical, and petrochemical applications. |
| Temperature Range | Stable from -70°C to +250°C (-100°F to 482°F). | Suitable for cryogenic to high-temperature processes. |
| Friction & Wear | Extremely low coefficient of friction; non-stick. | Reduces wear in dynamic applications; eases installation. |
| Mechanical Nature | High hardness (Shore D 60-65), low compression set, but low elasticity. | Best for static seals; gland design is critical to prevent creep (cold flow). |
| Purity & Safety | Inherently pure with low extractables. | Essential for food, beverage, pharmaceutical, and semiconductor industries. |
Need high-performance PTFE seals that meet your exact specifications?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including O-rings, seals, liners, and custom labware—for the most demanding applications in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures your seals deliver unmatched chemical resistance, thermal stability, and longevity.
We provide custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, guaranteeing the precision and reliability your operations demand.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project and get a quote tailored to your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- How can PTFE be customized for specific applications? Tailor Performance with Fillers & Fabrication
- How is PTFE applied in the medical field? Enhancing Patient Care with Biocompatible Solutions
- How should PTFE-lined valves be maintained for optimal performance? Ensure Long-Term Reliability & Prevent Costly Downtime
- What are the advantages of PTFE Liner in terms of weight and noise reduction? Achieve Quieter, Lighter Systems
- What types of cutting tools are recommended for machining PTFE? Achieve Clean Cuts and Tight Tolerances
- Where are Teflon encapsulated silicone o-rings commonly used? For Superior Sealing in Harsh Environments
- How are PTFE Teflon washers used in the automotive industry? Essential for High-Temp, Corrosive Seals
- How are PTFE sheets utilized in the electrical industry? For Superior Insulation and Signal Integrity



















