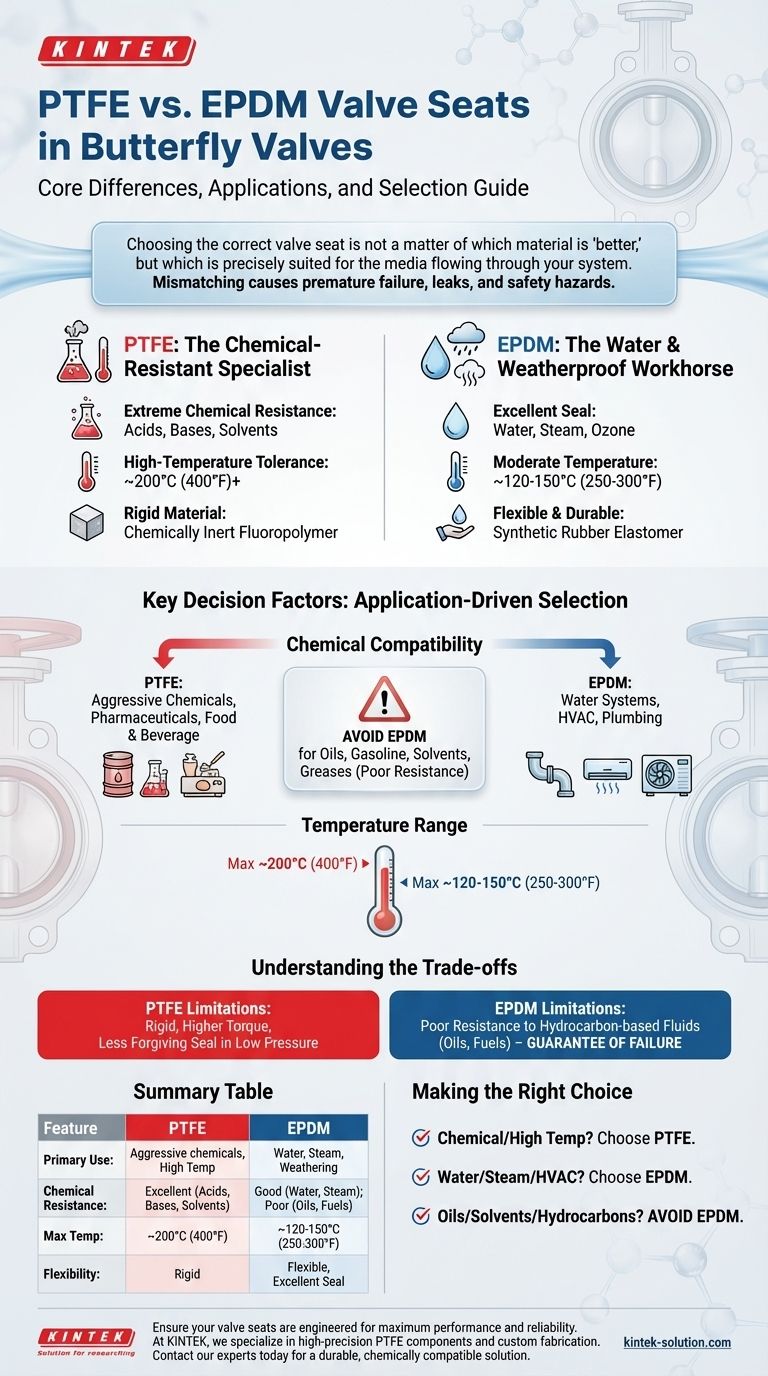
The primary difference between PTFE and EPDM valve seats lies in their core chemical compatibility and ideal operating conditions. PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) is engineered for exceptional resistance to aggressive chemicals and high temperatures. In contrast, EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer) is the standard for applications involving water, steam, and weathering, where its flexibility and durability are paramount.
Choosing the correct valve seat is not a matter of which material is "better," but which is precisely suited for the media flowing through your system. Mismatching the material to the application is a direct path to premature valve failure, leaks, and potential safety hazards.

Understanding the Core Materials
To make an informed decision, you must first understand the fundamental properties that define each material's performance. They are engineered for fundamentally different environments.
PTFE: The Chemical-Resistant Specialist
PTFE is a fluoropolymer renowned for being one of the most chemically inert substances known. This makes it the default choice for harsh processing environments.
Its key characteristics include extreme chemical resistance to a wide range of acids, bases, and solvents. It also offers a high-temperature tolerance, maintaining its integrity in conditions where other elastomers would degrade.
EPDM: The Water & Weatherproof Workhorse
EPDM is a synthetic rubber valued for its excellent durability and flexibility across a wide range of temperatures. Its molecular structure makes it exceptionally resistant to degradation from water, steam, and ozone.
This material provides an outstanding seal in water-based systems, including potable water, wastewater, and HVAC applications. Its flexibility allows it to conform well to the valve disc, ensuring a tight, reliable shutoff.
Key Decision Factors: Application-Driven Selection
Your choice should be guided by a clear analysis of your specific operational requirements. The media, temperature, and sealing demands are the most critical factors.
Chemical Compatibility: The Deciding Factor
This is the most important consideration. Using a material that is not compatible with the media will cause the seat to swell, harden, or dissolve, leading to catastrophic failure.
PTFE is required for applications involving aggressive chemicals, such as those found in chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and food and beverage production where sanitizing agents are used.
EPDM is the superior choice for water-based media. This includes water treatment systems, commercial plumbing, HVAC chilled water loops, and steam applications within its temperature limits.
Temperature Range: Defining Operational Limits
Each material has a distinct effective temperature range that dictates its suitability for a given system.
PTFE excels in high-temperature environments, often performing reliably in continuous service up to 200°C (400°F) or higher, depending on the specific grade and valve design.
EPDM has a more moderate temperature range, typically suitable for service up to approximately 120-150°C (250-300°F). It is excellent for most water and steam applications but is not intended for high-heat chemical processes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect for every situation. Acknowledging the limitations of each option is crucial for ensuring system reliability and avoiding costly mistakes.
The Limitations of PTFE
While chemically robust, PTFE is a relatively rigid material. This can sometimes result in higher torque requirements to actuate the valve and may not provide as forgiving a seal as a flexible elastomer in certain low-pressure applications.
The Limitations of EPDM
The primary weakness of EPDM is its poor resistance to hydrocarbon-based fluids. It will degrade rapidly when exposed to oils, gasoline, solvents, and greases. Using an EPDM seat in one of these applications is a guarantee of failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct seat material is a critical engineering decision. Base your choice on the specific, non-negotiable demands of your system to ensure safety and longevity.
- If your primary focus is chemical processing or high-temperature service: Choose PTFE for its unmatched chemical inertness and thermal stability.
- If your primary focus is water, steam, or HVAC systems: Choose EPDM for its proven durability, excellent sealing performance, and cost-effectiveness in these environments.
- If your media involves any oils, solvents, or hydrocarbon fuels: You must avoid EPDM, as it is chemically incompatible and will fail.
Matching the valve seat material to your specific media is the single most important factor in ensuring long-term valve reliability and system safety.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PTFE | EPDM |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Aggressive chemicals, high temperatures | Water, steam, weathering |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (acids, bases, solvents) | Good (water, steam); Poor (oils, fuels) |
| Max Temp (Continuous) | ~200°C (400°F) | ~120-150°C (250-300°F) |
| Flexibility | Rigid | Flexible, excellent seal |
Ensure your valve seats are engineered for maximum performance and reliability.
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including custom valve seats, seals, and liners. Whether you're in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sector, our expertise in custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensures you get a solution perfectly matched to your media and operating conditions.
Don't risk premature failure. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and get a durable, chemically compatible solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments



















