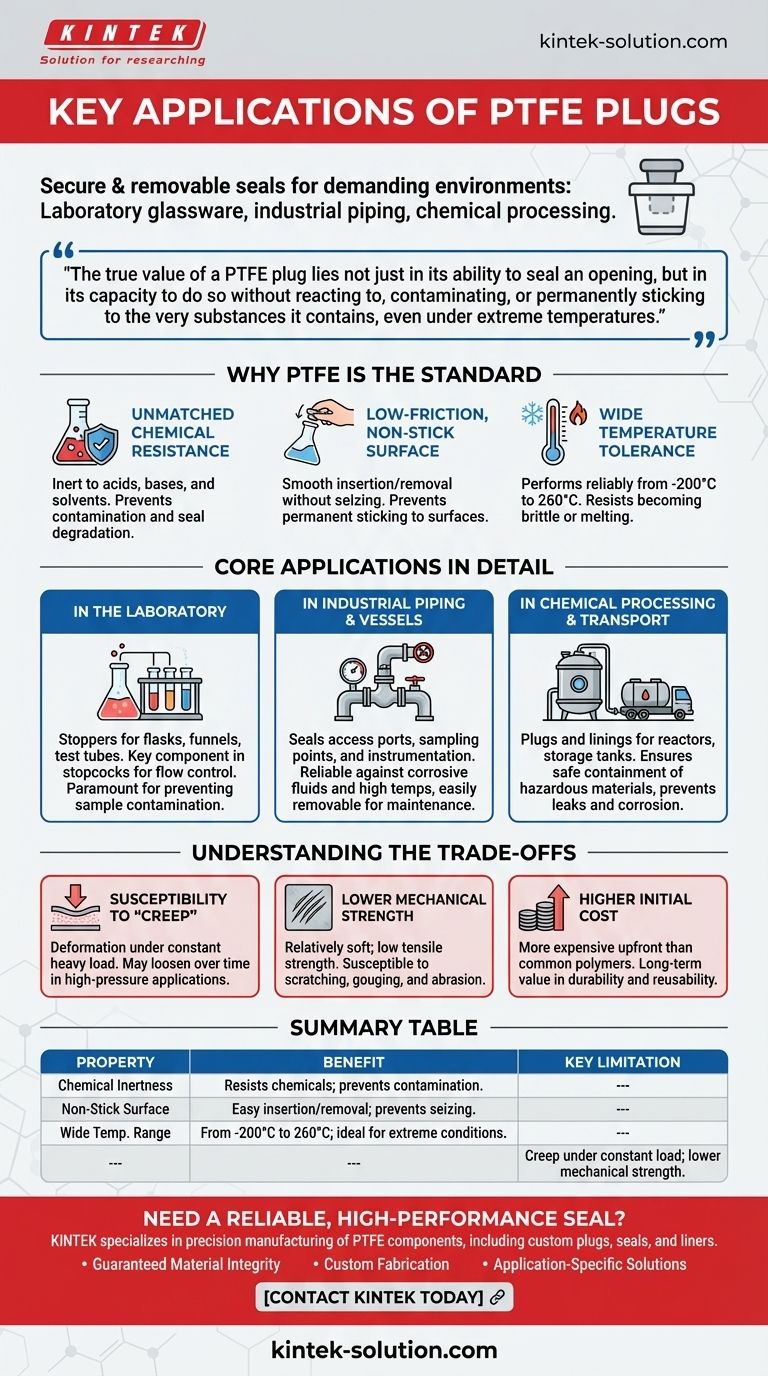
In short, PTFE plugs are primarily used to create a secure and removable seal in highly demanding environments, most notably in laboratory glassware, industrial piping systems, and chemical processing equipment. Their use is dictated by the unique properties of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), which allow them to perform where other materials would fail.
The true value of a PTFE plug lies not just in its ability to seal an opening, but in its capacity to do so without reacting to, contaminating, or permanently sticking to the very substances it contains, even under extreme temperatures.

Why PTFE is the Standard for Sealing Applications
The selection of a material for a plug or stopper is determined by the environment it must withstand. PTFE's molecular structure gives it a combination of properties that make it uniquely suited for sealing applications in science and industry.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
PTFE is almost entirely inert, meaning it does not react with the vast majority of chemicals, including aggressive acids, bases, and organic solvents.
This non-reactive nature is critical in applications where the purity of a substance must be maintained or where a corrosive material would destroy a lesser plug. This prevents both contamination of the product and degradation of the seal itself.
Low-Friction, Non-Stick Surface
Famously used for non-stick cookware, PTFE's extremely low coefficient of friction is also a major advantage for plugs.
This property ensures the plug can be inserted and removed smoothly without binding or seizing, even after long-term use or temperature fluctuations. It prevents the plug from permanently sticking to glass or metal surfaces, ensuring reusability.
Wide Temperature Tolerance
PTFE maintains its integrity and properties across an exceptionally broad temperature range, from cryogenic lows of around -200°C (-328°F) to highs of 260°C (500°F).
This allows PTFE plugs to be used reliably in processes involving extreme heating or cooling, where materials like rubber or other plastics would become brittle, melt, or deform.
Core Applications in Detail
While the principle is simple—to plug a hole—the context in which PTFE plugs are used is what makes them so essential.
In the Laboratory
In a lab setting, PTFE plugs are used as stoppers for flasks, test tubes, and funnels. They are also the key component in stopcocks, which are the valves that control the flow of liquid in burettes and separatory funnels.
Their chemical inertness is paramount here, as it guarantees that a sensitive reaction or a pure chemical sample will not be contaminated by the stopper itself.
In Industrial Piping and Vessels
Across chemical, oil and gas, and even food production plants, pipes and vessels have ports for access, sampling, or instrumentation. PTFE plugs are used to seal these openings.
They provide a reliable seal that can withstand corrosive process fluids and high temperatures while still being easily removable for maintenance or access. Their function is very similar to that of PTFE gaskets and O-rings, which seal connections between components.
In Chemical Processing and Transport
Reactors, storage tanks, and containers used to process or transport highly reactive chemicals rely on PTFE components, including plugs and linings.
Here, the plug ensures a safe and secure containment of hazardous materials, preventing leaks and protecting the integrity of the container from corrosion.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, PTFE is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it correctly.
Susceptibility to "Creep"
PTFE can be subject to "creep" or "cold flow," where the material slowly deforms over time when placed under a constant, heavy load. In very high-pressure sealing applications, this means the seal may loosen over time unless it is part of a reinforced assembly.
Lower Mechanical Strength
Compared to metals, PTFE is a relatively soft material. It has low tensile strength and can be easily scratched or gouged. It cannot be used as a structural component and must be protected from significant mechanical stress or abrasion.
Higher Initial Cost
The manufacturing process for PTFE makes it more expensive upfront than common polymers like polypropylene or elastomers like rubber. Its long-term value comes from its durability and reusability in environments where cheaper materials would quickly fail.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right sealing solution requires matching the material's properties to the technical demands of the task.
- If your primary focus is handling aggressive chemicals or ensuring sample purity: PTFE is the unparalleled choice due to its extreme chemical inertness.
- If your primary focus is creating a removable seal in a high-temperature or cryogenic environment: PTFE's wide operating temperature range makes it a reliable and safe option.
- If your primary focus is a simple, low-cost stopper for non-reactive substances at ambient temperature: A less expensive material like rubber, silicone, or glass may be a more practical and cost-effective choice.
Ultimately, understanding these core properties allows you to select a PTFE plug not just for what it is, but for the specific problem it is engineered to solve.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit for Sealing Applications |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists virtually all acids, bases, and solvents; prevents contamination. |
| Non-Stick Surface | Ensures easy insertion and removal; prevents seizing. |
| Wide Temp. Range | Performs from -200°C to 260°C, ideal for extreme heating/cooling. |
| Key Limitation | Susceptible to creep under constant heavy load; not for high structural stress. |
Need a reliable, high-performance seal for your application?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of PTFE components, including custom plugs, seals, and liners. Our expertise ensures your components meet the exact demands of your environment, whether you're in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sector.
We deliver:
- Guaranteed Material Integrity: Chemically inert and temperature-resistant PTFE.
- Custom Fabrication: From prototypes to high-volume production runs.
- Application-Specific Solutions: Designed to solve your unique sealing challenges.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project requirements and get a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- PTFE Chemical Solvent Sampling Spoon
People Also Ask
- What are some important physical property values for PTFE? Master Its Extreme Performance for Demanding Applications
- How is PTFE used in industrial processes? Maximize Safety and Efficiency
- What is the hardness range of PTFE on the Shore D scale? Leveraging Its Softness for Superior Performance
- When and by whom was PTFE discovered? A Tale of Accidental Innovation
- Why is dimensional stability a concern when machining PTFE? Ensure Accurate, Stable PTFE Components



















