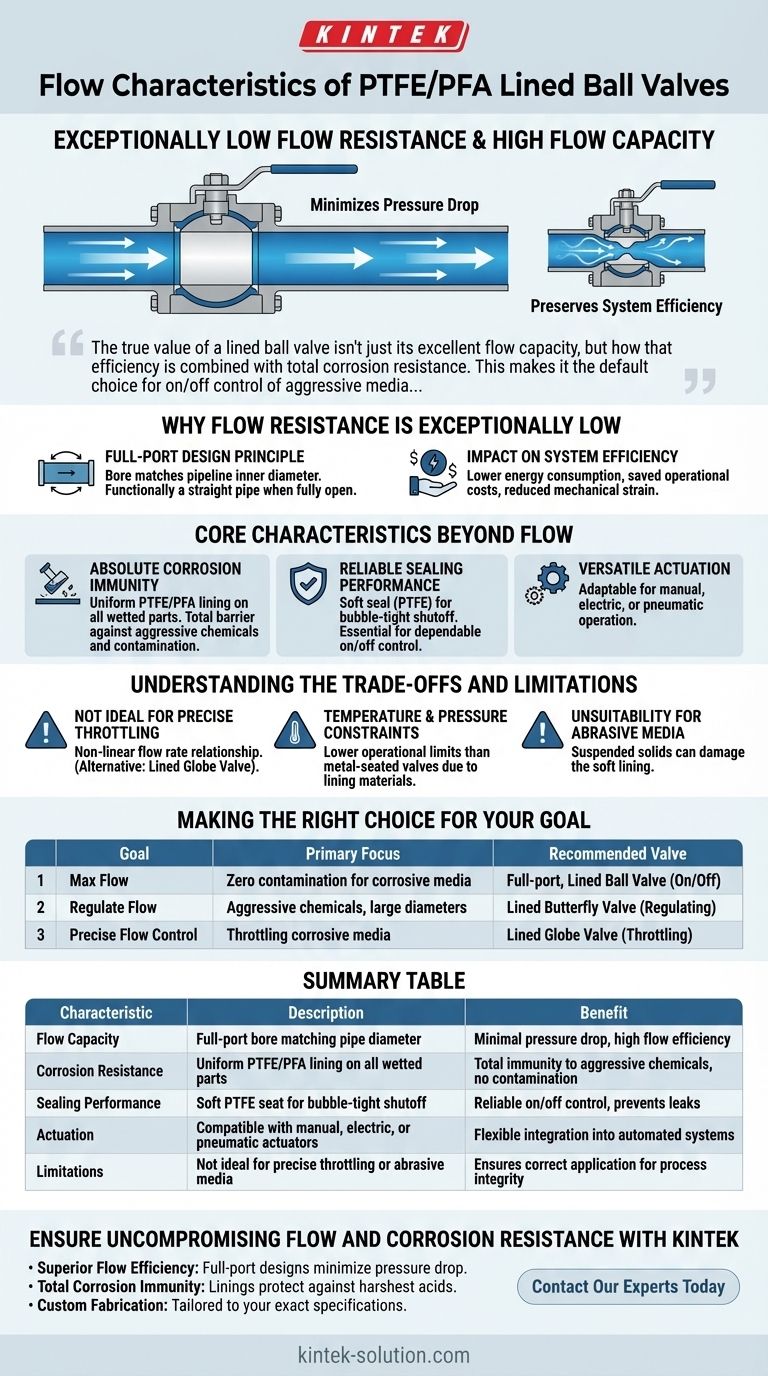
In short, PTFE/PFA lined ball valves are defined by exceptionally low flow resistance and high flow capacity. Their design features a full-port bore that matches the internal diameter of the connecting pipe. This creates a straight, unobstructed path for media when the valve is open, resulting in minimal pressure drop and preserving system efficiency.
The true value of a lined ball valve isn't just its excellent flow capacity, but how that efficiency is combined with total corrosion resistance. This makes it the default choice for on/off control of aggressive media where maintaining system pressure and preventing contamination are paramount.
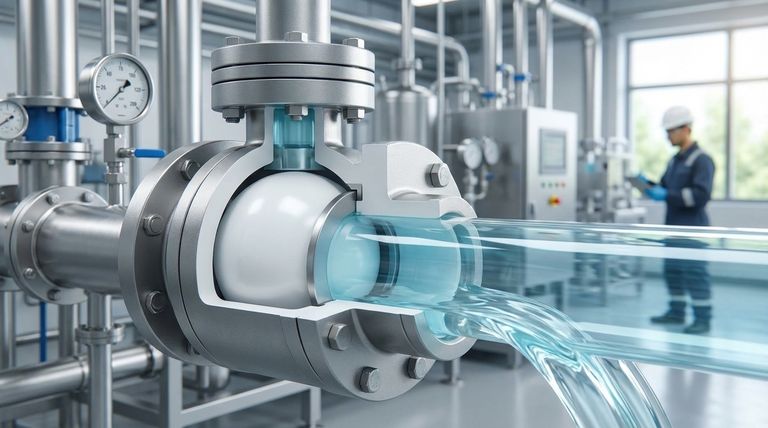

Why Flow Resistance is Exceptionally Low
The superior flow characteristics of these valves are not accidental; they are a direct result of their core mechanical design.
The Full-Port Design Principle
A full-port (or full-bore) design means the hole in the valve's ball is the same size as the pipeline's inner diameter.
When the valve is fully open, it is functionally like a straight piece of pipe. This eliminates the constrictions and turbulence that cause pressure loss in other valve types.
Impact on System Efficiency
This minimal flow resistance directly translates to lower energy consumption. Pumps do not have to work as hard to move fluid through the system, saving operational costs and reducing mechanical strain.
Core Characteristics Beyond Flow
While their flow profile is a key feature, the reason for their widespread use in demanding industries comes from a combination of critical attributes.
Absolute Corrosion Immunity
The defining feature is the uniform PTFE or PFA lining that covers all wetted parts of the valve—the body, ball, and stem.
This inert lining provides a complete barrier against aggressive chemicals, including strong acids, alkalis, and salts, preventing both corrosion of the valve and contamination of the media.
Reliable Sealing Performance
Lined ball valves utilize a soft seal valve seat, typically also made of PTFE. This ensures a bubble-tight shutoff when the valve is closed.
This high level of sealability is essential for applications requiring dependable on/off control to isolate process lines or prevent leaks of hazardous materials.
Versatile Actuation
These valves are highly adaptable to different control schemes. They can be operated with a simple manual lever, a handwheel for higher torque, or integrated into an automated system using electric or pneumatic actuators.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No component is perfect for every situation. Objectivity requires acknowledging where these valves may not be the optimal choice.
Throttling and Control Precision
While they can be used to regulate flow, lined ball valves are not ideal for precise throttling. The relationship between the degree of turn and the flow rate is not linear.
For applications requiring fine-tuned flow control, a lined globe valve is often a more suitable, albeit higher-pressure-drop, alternative.
Temperature and Pressure Constraints
The PTFE/PFA linings and soft seats that provide excellent chemical resistance and sealing also impose operational limits. These materials have a maximum temperature and pressure rating that is lower than that of metal-seated valves.
Unsuitability for Abrasive Media
Lined valves are designed for clean, corrosive liquids and gases. Abrasive slurries or media containing suspended solids can quickly damage the soft lining, leading to valve failure and loss of corrosion resistance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct valve requires matching its characteristics to your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum flow with zero contamination for corrosive media: A full-port, lined ball valve is the ideal choice for on/off service.
- If your primary focus is regulating the flow of aggressive chemicals, especially in large-diameter pipes: A lined butterfly valve often provides a more suitable and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is extremely precise flow control (throttling) of corrosive media: You should consider a lined globe valve, accepting the trade-off of a higher pressure drop.
By understanding these core principles, you can confidently select the valve that ensures both the efficiency and the integrity of your process.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Flow Capacity | Full-port bore matching pipe diameter | Minimal pressure drop, high flow efficiency |
| Corrosion Resistance | Uniform PTFE/PFA lining on all wetted parts | Total immunity to aggressive chemicals, no contamination |
| Sealing Performance | Soft PTFE seat for bubble-tight shutoff | Reliable on/off control, prevents leaks |
| Actuation | Compatible with manual, electric, or pneumatic actuators | Flexible integration into automated systems |
| Limitations | Not ideal for precise throttling or abrasive media | Ensures correct application for process integrity |
Ensure Uncompromising Flow and Corrosion Resistance in Your System
Do you need a reliable, high-flow valve solution for aggressive chemicals in your semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial process? KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of PTFE and PFA components, including custom-lined ball valves.
We deliver:
- Superior Flow Efficiency: Full-port designs that minimize pressure drop and preserve system energy.
- Total Corrosion Immunity: Linings that protect against the harshest acids, alkalis, and solvents.
- Custom Fabrication: From prototype development to high-volume production orders, tailored to your exact specifications.
Let's discuss your application requirements. Contact our experts today to find the perfect valve solution for your critical process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What industries commonly use PTFE balls? Essential for Chemical, Pharma, and Food Processing
- What makes PTFE balls ideal for chemical applications? Unmatched Inertness for Demanding Environments
- What are the tolerances for PTFE balls based on size? Precision vs. Standard Grade Explained
- What are the properties of Teflon balls? Unlock Elite Chemical & Friction Resistance
- What materials are used for PTFE balls? A Guide to Virgin PTFE vs. Filled Composites



















