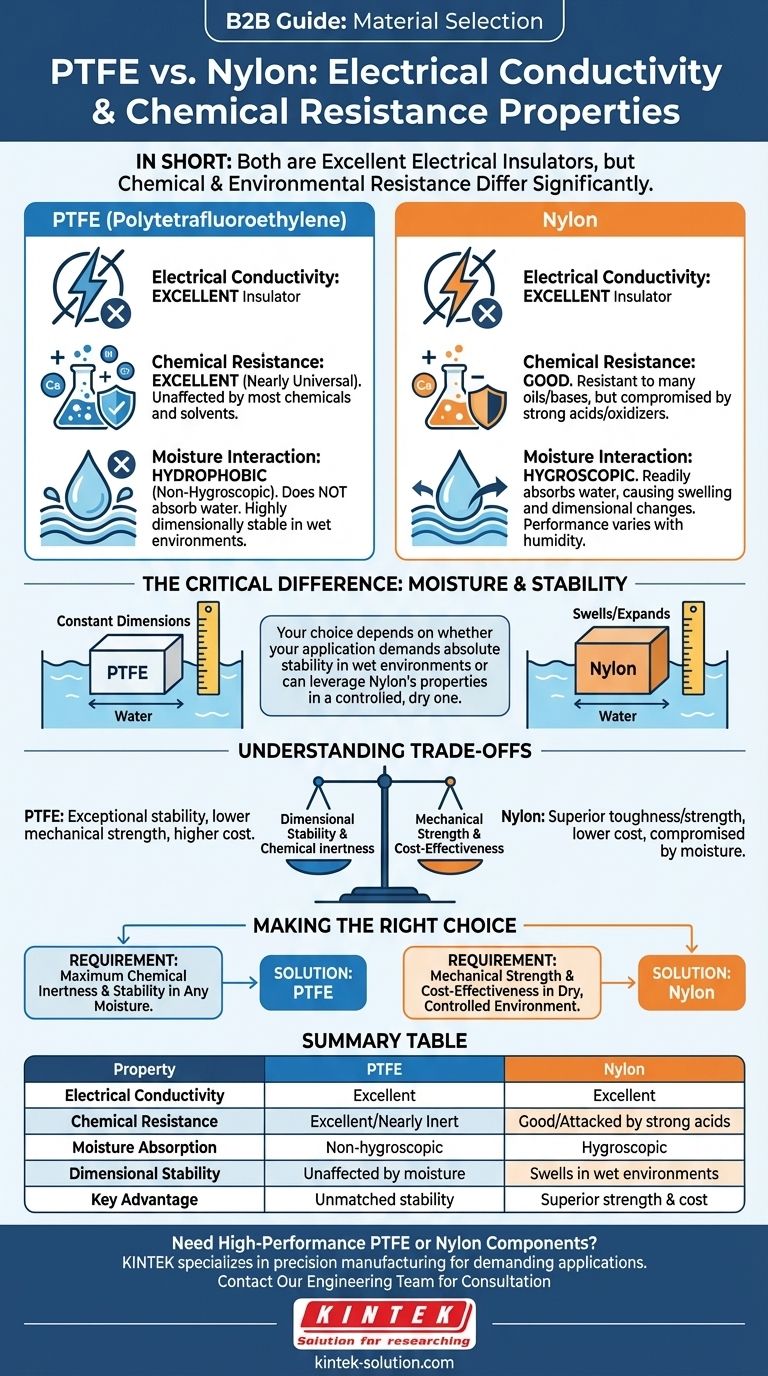
In short, both PTFE and nylon are excellent electrical insulators. However, their chemical and environmental resistances differ significantly. PTFE offers near-universal chemical resistance and is completely unaffected by moisture, while nylon provides good resistance but can be compromised by certain chemicals and will absorb water, affecting its dimensional stability.
The critical distinction between PTFE and nylon is not just their chemical resistance, but how they interact with moisture. Your choice will ultimately depend on whether your application demands absolute dimensional stability in a wet environment or can leverage nylon's properties in a controlled, dry one.

A Head-to-Head Comparison of Core Properties
Understanding the fundamental differences in electrical and chemical behavior is the first step in selecting the correct material for your specific engineering challenge.
Electrical Conductivity: Both Are Excellent Insulators
Both PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) and nylon exhibit very low electrical conductivity.
Functionally, this means both materials are highly effective electrical insulators, suitable for preventing the flow of electric current in a wide range of applications.
Chemical Resistance: The Difference Between "Good" and "Excellent"
PTFE is renowned for its excellent chemical resistance. It is one of the most chemically inert polymers, resisting nearly all industrial chemicals and solvents.
Nylon has good chemical resistance but is more limited. It performs well against many oils and alkaline substances but can be attacked by strong acids, oxidizing agents, and certain solvents.
The Critical Factor: Interaction with Moisture
The most significant practical difference between these two materials is their response to water and humidity. This single factor often dictates which material is suitable for an application.
PTFE: Fundamentally Hydrophobic
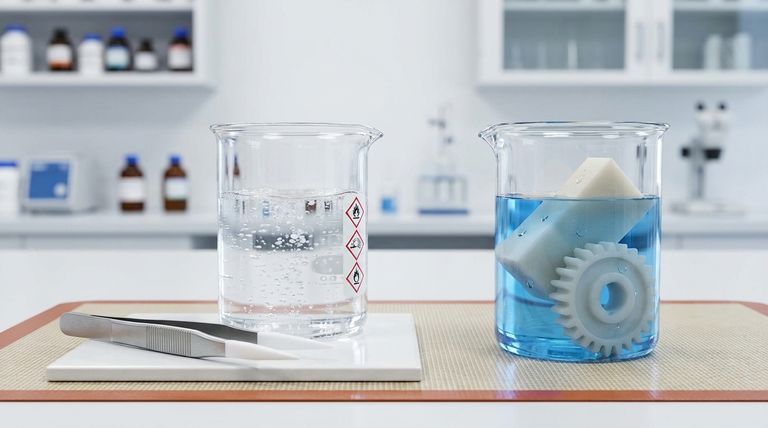
PTFE is non-hygroscopic, or hydrophobic, meaning it does not absorb water. Its properties remain constant regardless of humidity or submersion.
This makes it the ideal choice for applications requiring high dimensional stability in high-moisture environments, as it experiences little to no swelling or changes in shape.
Nylon: Inherently Hygroscopic
Nylon is hygroscopic, meaning it readily absorbs water from its environment. This absorption can cause the material to swell.
This change in dimension must be accounted for in any design with tight tolerances. While it can be a stable material in dry conditions, its performance can vary significantly with changes in humidity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Material selection is never about finding a "perfect" material, but the right material for a specific context. The choice between PTFE and nylon involves balancing key performance characteristics.
Dimensional Stability vs. Mechanical Properties
PTFE's primary advantage is its exceptional stability across chemical and moisture environments. However, it is a softer material with lower mechanical strength and wear resistance compared to nylon.
Nylon typically offers superior toughness, wear resistance, and tensile strength. This mechanical advantage, however, is compromised in the presence of moisture, which can alter its properties.
Environmental Inertness vs. Cost
PTFE's unparalleled chemical and moisture resistance comes at a higher material cost.
Nylon is generally a more cost-effective polymer, making it an attractive option for high-volume applications where the environment can be controlled or its hygroscopic nature is not a critical design flaw.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be based on the non-negotiable requirements of your project's operating environment.
- If your primary focus is maximum chemical inertness and dimensional stability in any moisture condition: PTFE is the definitive choice due to its hydrophobic and nearly inert nature.
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength and cost-effectiveness in a controlled, dry environment: Nylon is often the superior option, providing excellent durability for its price point.
Ultimately, a clear understanding of your application's environment is the key to successful material selection.
Summary Table:
| Property | PTFE (Teflon™) | Nylon |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | Excellent Insulator | Excellent Insulator |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (Nearly inert) | Good (Attacked by strong acids, oxidizers) |
| Moisture Absorption | Non-hygroscopic (Hydrophobic) | Hygroscopic (Absorbs water) |
| Dimensional Stability | Unaffected by moisture | Swells in humid/wet environments |
| Key Advantage | Unmatched chemical/environmental stability | Superior mechanical strength & cost-effectiveness |
Need High-Performance PTFE or Nylon Components?
Choosing the right material is critical for the success of your project. KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of PTFE components (seals, liners, labware) and other high-performance polymers for demanding applications in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We provide:
- Expert Material Selection Guidance: Leverage our expertise to choose the optimal polymer for your specific environment and performance requirements.
- Precision Production: From custom prototypes to high-volume orders, we ensure every part meets your exact specifications for reliability and performance.
Let us help you build a better product. Contact our engineering team today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials



















