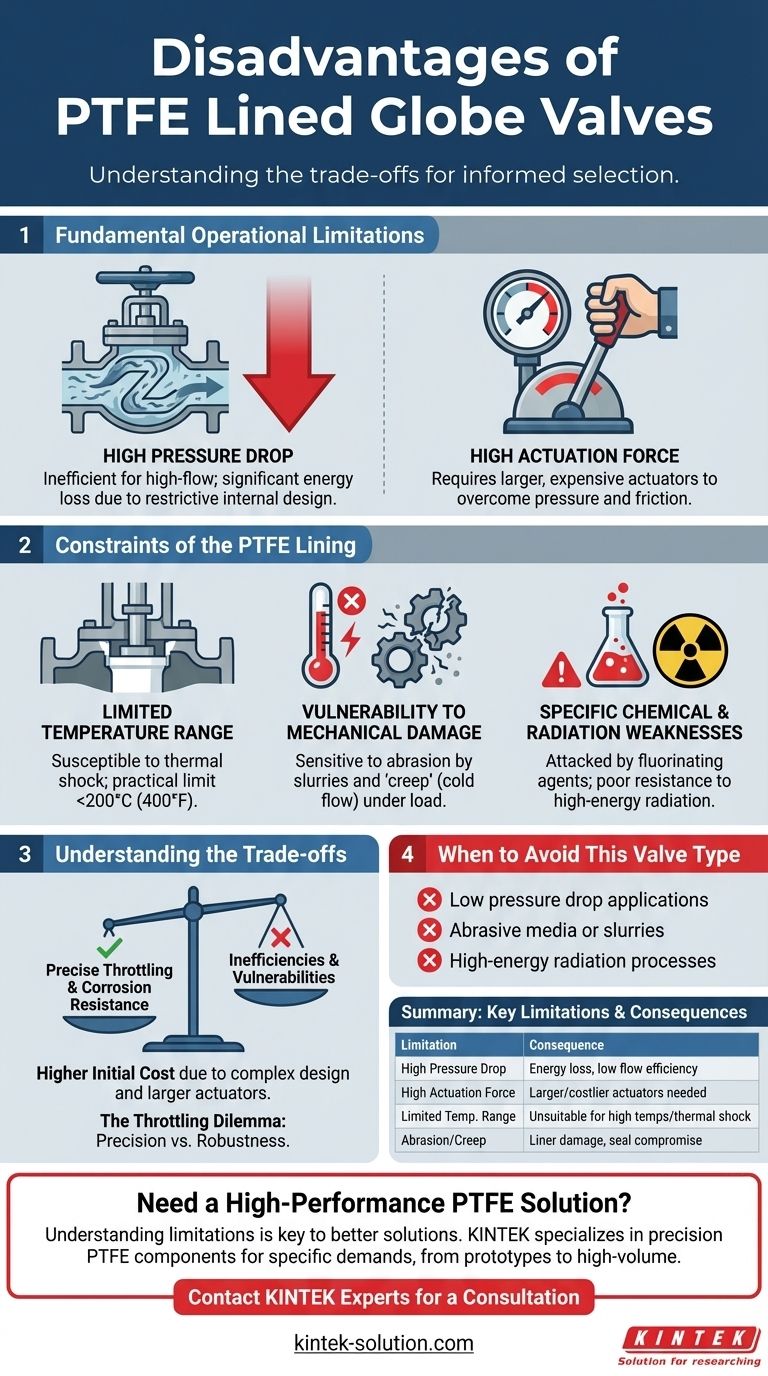
The primary disadvantages of a PTFE lined globe valve are its unfavorable performance under high pressure drops and the significant force required to achieve shut-off. This is a direct consequence of its internal design, which prioritizes precise flow control (throttling) over high-flow efficiency.
While unmatched for throttling corrosive fluids, a PTFE lined globe valve's specialization introduces distinct limitations. Understanding these trade-offs, which center on operational pressure, temperature range, and mechanical robustness, is critical to avoiding misapplication.
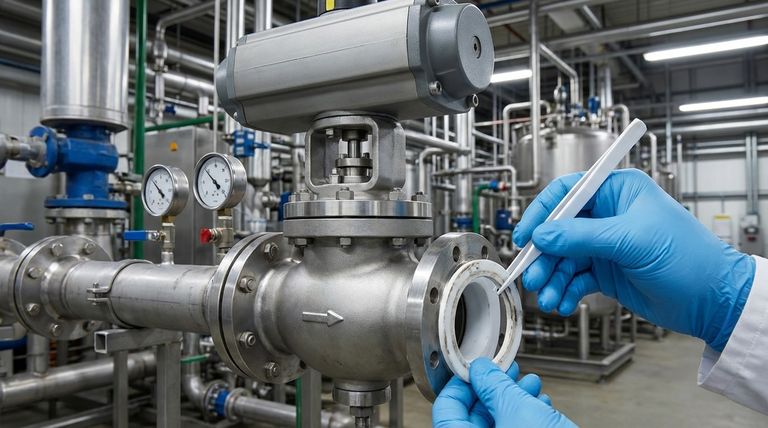

Fundamental Operational Limitations
A globe valve's core function—precise flow regulation—is also the source of its main operational drawbacks. The internal geometry required for throttling inherently creates resistance and demands high operating forces.
High Pressure Drop and Flow Restriction
A globe valve forces media through a tortuous, Z-shaped path. This design is excellent for gradual control but creates significant turbulence and resistance.
The result is a much higher pressure drop across the valve compared to straight-path valves like ball or gate valves. This makes it inefficient for applications where maximizing flow and minimizing energy loss is the goal.
High Actuation Force Requirements
To close a globe valve, the disc must be pushed firmly against the flow of media and seated tightly. This requires overcoming the line pressure acting on the disc.
This inherent design, combined with the friction of the PTFE components, means a high actuation force is necessary. This often necessitates larger, more expensive actuators (whether manual or automated) compared to quarter-turn valves.
The Constraints of the PTFE Lining
The PTFE liner provides outstanding chemical resistance but also introduces its own set of material-specific vulnerabilities that define the valve's operating envelope.
Limited Temperature Range
PTFE has a definitive upper temperature limit, with a melting point around 326°C (620°F). In practice, its useful service temperature is lower, as the material begins to soften and lose mechanical strength well below this point.
It is also susceptible to damage from rapid, extreme temperature changes, known as thermal shock.
Vulnerability to Mechanical Damage
While chemically robust, PTFE is a relatively soft material. It is sensitive to abrasion from slurries or media containing solid particulates, which can quickly erode the liner and cause failure.
Furthermore, PTFE is subject to creep, or "cold flow," where the material slowly deforms over time when subjected to a constant load, such as the compressive force of the valve seat. This can eventually compromise the integrity of the seal.
Specific Chemical and Radiation Weaknesses
While resistant to most chemicals, PTFE is not invincible. It can be attacked by highly reactive chemicals like elementary fluorine, chlorine trifluoride, and other strong fluorinating agents, especially at high temperatures.
It also has poor resistance to high-energy radiation, which can break down its molecular structure and cause it to become brittle.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a PTFE lined globe valve means accepting a series of compromises. The benefits of its precise control and corrosion resistance must be weighed against its inherent inefficiencies and vulnerabilities.
Higher Initial Cost
The combination of a complex globe valve body and a specialized PTFE lining process makes these valves more expensive than simpler alternatives like unlined valves or even other lined valve types like butterfly valves. The need for larger actuators further adds to the total cost.
The Throttling Dilemma: Precision vs. Robustness
The very features that make a globe valve an excellent throttling device—its restrictive flow path and perpendicular disc seating—are what create the high pressure drop and require high actuation force. You cannot have one without the other.
When to Avoid This Valve Type
You should look for alternatives if your application requires low pressure drop, is sensitive to cost, or involves abrasive media. Similarly, if the process involves high-energy radiation or the few specific chemicals that attack PTFE, this valve is an unsuitable choice.
Making the Right Choice for Your System
Selecting the correct valve is about aligning its capabilities with your primary operational goal. Use these points as a guide.
- If your primary focus is precise throttling of highly corrosive media: A PTFE lined globe valve is an excellent choice, and its inherent trade-offs are likely acceptable.
- If your primary focus is high flow capacity and low energy loss: Consider a PTFE lined ball, plug, or butterfly valve as a more efficient alternative.
- If your system involves abrasive slurries or high mechanical stress: The soft PTFE lining is a significant risk; investigate valves with hardened metal or ceramic trim.
- If your operating temperatures exceed the practical limits of PTFE (around 200°C / 400°F): You must specify a valve made from a suitable metal alloy.
Ultimately, proper valve selection requires matching the tool directly to the technical demands of the job.
Summary Table:
| Limitation | Key Consequence |
|---|---|
| High Pressure Drop | Inefficient for high-flow applications; significant energy loss. |
| High Actuation Force | Requires larger, more expensive manual or automated actuators. |
| Limited Temperature Range | Unsuitable for high-temperature processes; susceptible to thermal shock. |
| Vulnerability to Abrasion | PTFE lining can be damaged by slurries or solid particulates. |
| Susceptible to Creep (Cold Flow) | Liner can deform over time under constant load, compromising the seal. |
Need a High-Performance PTFE Solution?
Understanding the limitations of standard components is the first step toward finding a better solution. At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including custom seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We prioritize precision production and offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring your components are engineered to meet the specific demands of your application, avoiding the common pitfalls of off-the-shelf parts.
Let's engineer a solution that works for you. Contact our experts today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
People Also Ask
- What temperature range can PTFE sheets withstand? From -200°C to +260°C for Extreme Applications
- Why are PTFE seals suitable for high-velocity applications? Superior Performance at Extreme Speeds
- How is Teflon used in bearing pads for different load requirements? Matching PTFE Type to Load
- How is PTFE used in filtration applications? Essential for Corrosive & High-Temp Environments
- What types of PTFE components are used in the gas and oil industry? Enhance Reliability in Extreme Conditions
- What are the overall advantages of using PTFE bellows? Superior Chemical Resistance & Purity
- What are the application advantages of PTFE backup rings? Boost System Reliability in Extreme Conditions
- What are the key considerations when designing a PTFE PCB? Master High-Frequency Performance



















