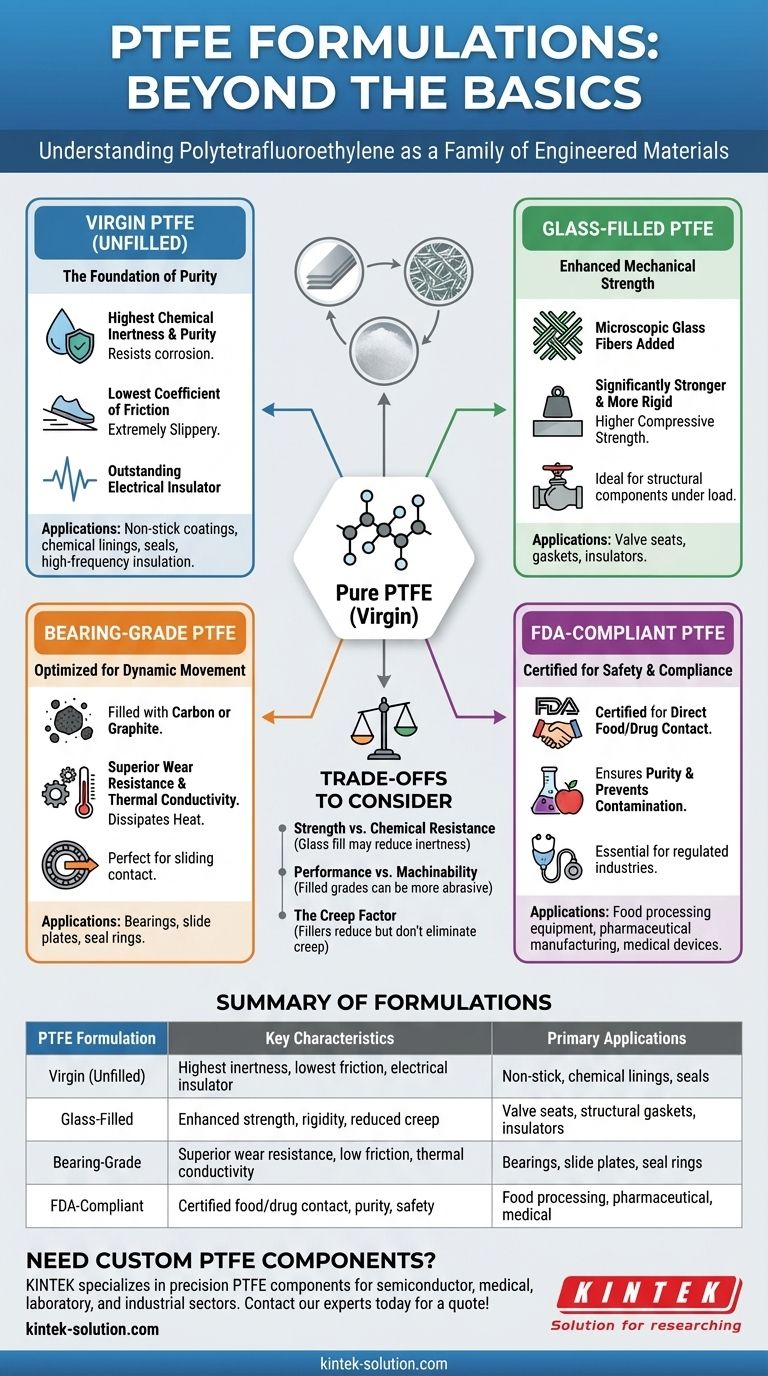
In short, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is not a single material but a family of formulations. The most common types include unfilled (virgin) PTFE, glass-filled PTFE for enhanced strength, specialized bearing grades for low friction under load, and FDA-compliant grades for regulated industries. Each formulation starts with the remarkable properties of pure PTFE and modifies them to solve specific engineering challenges.
While virgin PTFE offers an unparalleled combination of chemical inertness and low friction, its true power in modern applications is unlocked through specialized formulations. These additives enhance properties like mechanical strength and wear resistance, transforming a versatile polymer into a precise solution for demanding environments.

The Foundation: Understanding Virgin PTFE
Virgin, or unfilled, PTFE is the base polymer in its purest form. Its unique molecular structure gives it a set of core characteristics that make it valuable in a wide range of applications where it isn't subjected to high mechanical loads.
Core Properties
The fundamental properties of virgin PTFE are exceptional. It possesses the lowest coefficient of friction of any known solid, making it incredibly slippery.
It is also almost completely chemically inert, resisting even the most corrosive acids and bases. This is combined with excellent performance across a wide temperature range, from cryogenic lows to a high melting point of around 347°C.
Finally, it is an outstanding electrical insulator, with high dielectric strength, making it ideal for high-frequency applications.
Typical Applications
These core properties make virgin PTFE the default choice for many uses. It is the basis for non-stick coatings on cookware, chemically resistant linings for pipes and containers, high-performance seals and gaskets, and insulation for specialized wiring like coaxial cables.
Enhanced Formulations for Mechanical Demands
The primary limitation of virgin PTFE is its relative softness and tendency to deform, or "creep," under sustained pressure. To overcome this, fillers are added to create composite materials with enhanced mechanical properties.
Glass-Filled PTFE
By adding microscopic glass fibers to the PTFE matrix, the resulting material becomes significantly stronger and more rigid. Glass-filled PTFE exhibits much higher compressive strength and better wear resistance than its virgin counterpart.
This formulation is ideal for components that require structural integrity, such as valve seats, gaskets, and insulators that must withstand significant clamping force without deforming.
Bearing-Grade PTFE
Bearing grades are specifically engineered for dynamic applications involving sliding contact under load. These formulations are typically filled with materials like carbon or graphite.
These additives dramatically increase wear resistance and thermal conductivity, which helps dissipate frictional heat. This makes bearing-grade PTFE perfect for slide plates, bearings, and seal rings where low friction must be maintained over millions of cycles.
Specialized Grades for Regulated Environments
In many industries, material performance is secondary to safety and compliance. Specialized PTFE formulations exist to meet these strict requirements.
FDA-Compliant PTFE
This designation does not refer to a single formulation, but rather to any PTFE grade (virgin or filled) made from resins and additives that are certified by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for direct contact with food.
These materials are essential for equipment used in food processing, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and medical devices, ensuring purity and preventing contamination.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a PTFE formulation is an exercise in balancing engineering priorities. Enhancing one property often comes at the expense of another.
Strength vs. Chemical Resistance
While adding glass fibers boosts mechanical strength, it can slightly reduce the material's overall chemical resistance, as the fibers themselves may not be as inert as the PTFE matrix. For the most aggressive chemical environments, virgin PTFE often remains the superior choice.
Performance vs. Machinability
Filled PTFE grades are more abrasive than virgin PTFE. This can lead to faster tool wear during machining operations, potentially increasing manufacturing costs and complexity for intricate parts.
The Creep Factor
It is critical to remember that while fillers significantly reduce creep, they do not eliminate it entirely. For applications involving high, constant loads, the potential for slow deformation over time must always be a key design consideration.
Choosing the Right PTFE Formulation
Your final choice depends entirely on the primary demand of your application.
- If your primary focus is ultimate chemical inertness and purity: Virgin or an FDA-compliant grade of virgin PTFE is the correct choice for labware, chemical linings, or food-contact surfaces.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity under load: Glass-filled PTFE provides the necessary compressive strength and rigidity for components like valve seats and structural insulators.
- If your primary focus is low-friction movement and high wear resistance: A bearing-grade formulation with carbon or graphite is specifically engineered for dynamic parts like bearings and slide plates.
- If your primary focus is superior electrical insulation: Virgin PTFE offers the best dielectric properties for high-frequency connectors and critical cable insulation.
By understanding these distinct formulations, you can select the precise material engineered to solve your specific problem.
Summary Table:
| PTFE Formulation | Key Characteristics | Primary Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Virgin (Unfilled) | Highest chemical inertness, lowest friction, excellent electrical insulator | Non-stick coatings, chemical linings, seals, high-frequency insulation |
| Glass-Filled | Enhanced compressive strength, rigidity, reduced creep | Valve seats, structural gaskets, insulators under load |
| Bearing-Grade | Superior wear resistance, low friction under load, good thermal conductivity | Bearings, slide plates, seal rings in dynamic applications |
| FDA-Compliant | Certified for direct food/drug contact; purity and safety | Food processing equipment, pharmaceutical manufacturing, medical devices |
Need a custom PTFE component for your industry?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you need a prototype or a high-volume order, we can help you select the perfect formulation and deliver a part that meets your exact specifications.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable PTFE Crucibles for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
People Also Ask
- What is PTFE and what are its general properties? A Guide to the Ultimate High-Performance Polymer
- How does Teflon perform in outdoor applications? Unmatched Durability Against Weather and UV
- Why is PTFE valuable in automotive and aerospace industries? The Ultimate Material for Extreme Environments
- Why is PTFE considered safe for food and pharmaceutical applications? Ensuring Product Purity and Compliance
- What are the different types of Teflon coatings and their features? Choose the Right Fluoropolymer for Your Application
- What are the key properties of PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene)? Unlock Superior Performance in Harsh Environments
- What are the key takeaways about PTFE and expanded PTFE? Choosing the Right High-Performance Polymer
- What makes PTFE suitable for chemical and pharmaceutical industries? Ensuring Purity and Performance in Critical Applications



















