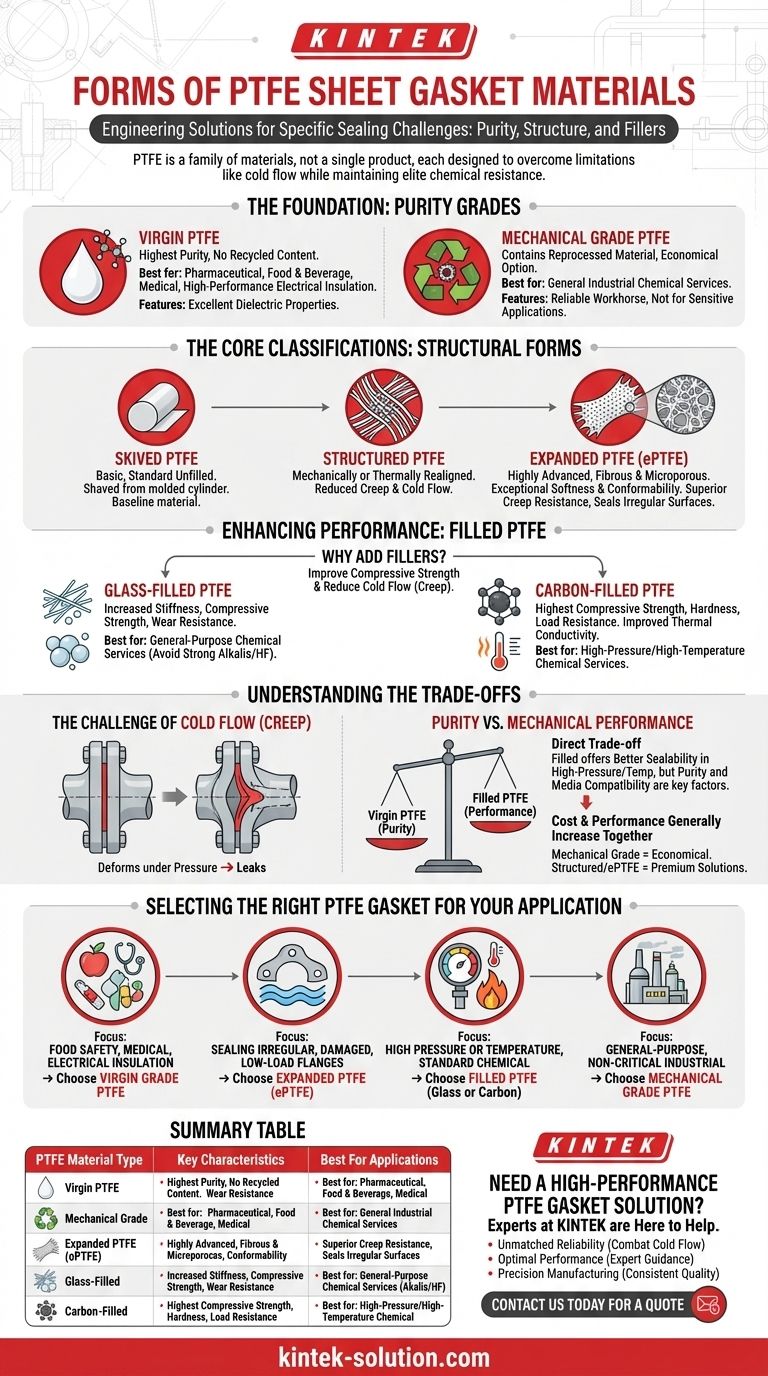
When selecting a PTFE gasket material, it's crucial to understand that it is not a single product but a family of materials, each engineered for specific conditions. The main forms are categorized by their purity (virgin vs. mechanical), their physical structure (skived, structured, or expanded), and by the addition of fillers like glass or carbon to enhance mechanical properties.
The most important takeaway is that while all PTFE offers elite chemical resistance, pure PTFE has mechanical weaknesses. The different forms—especially filled and expanded PTFE—are specifically designed to overcome these limitations, such as the tendency to deform under pressure.
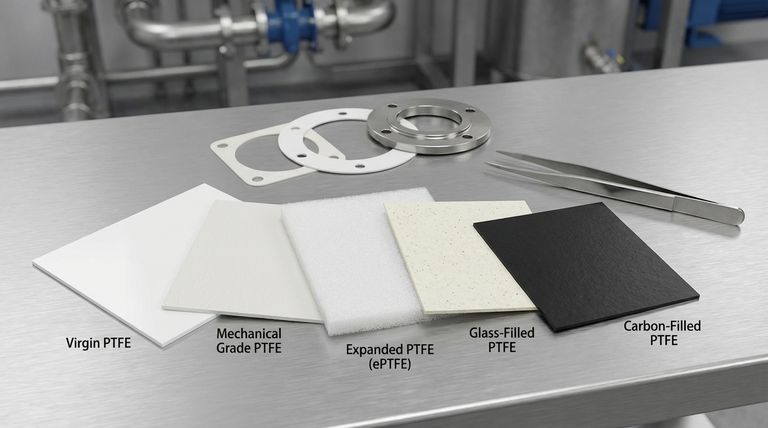

The Foundation: Purity Grades
The purity of the base PTFE resin is the first point of differentiation, primarily separating materials for general use from those for sensitive applications.
Virgin PTFE
This is the highest purity grade, made directly from virgin PTFE resin without any recycled content.
It is specified for the most demanding applications where purity is paramount, such as in the pharmaceutical, food and beverage, and medical industries. Its excellent dielectric properties also make it the default choice for high-performance electrical insulators.
Mechanical Grade PTFE
This grade contains a percentage of reprocessed PTFE material, making it a more economical option.
While its performance is nearly identical to virgin PTFE for most mechanical purposes, it is not used in food, medical, or electrical applications. It is a reliable workhorse for general industrial chemical services.
The Core Classifications: Structural Forms
Beyond purity, PTFE sheets are manufactured into different physical structures that dictate their mechanical behavior and suitability for various sealing challenges.
Skived PTFE
This is the most basic form of PTFE sheeting, created by "skiving" or shaving a thin layer from a large, molded cylinder of PTFE.
It represents standard, unfilled PTFE and serves as the baseline material before other modifications are made.
Structured PTFE
This term refers to PTFE that has been mechanically or thermally processed to realign its molecular structure.
This restructuring improves key mechanical properties, most notably reducing the material's tendency to creep or cold flow under load, which is a common failure point for basic PTFE gaskets.
Expanded PTFE (ePTFE)
Expanded PTFE is a highly advanced form created by rapidly stretching PTFE under specific conditions. This process creates a strong, fibrous, and microporous material.
ePTFE is exceptionally soft and conformable, allowing it to create a tight seal on irregular, damaged, or wavy flange surfaces, even with low bolt loads. It also offers dramatically improved creep resistance compared to skived PTFE.
Enhancing Performance: Filled PTFE
To overcome the inherent softness and tendency to creep, pure PTFE is often blended with filler materials. This creates a composite material with significantly enhanced mechanical properties.
Why Add Fillers to PTFE?
The primary reason to add fillers is to improve compressive strength and reduce cold flow. Pure PTFE can deform under constant pressure, leading to a loss of seal over time. Fillers provide a rigid internal structure to resist this.
Common Filler: Glass
Adding glass fibers or spheres is a common way to increase the stiffness and compressive strength of PTFE. It also improves wear resistance.
Glass-filled PTFE is an excellent general-purpose gasket material for many chemical services, but it is not suitable for strong alkalis or hydrofluoric acid.
Common Filler: Carbon
Carbon provides one of the best improvements in compressive strength, hardness, and load resistance. It gives the material a distinctive black color.
Carbon-filled PTFE also has improved thermal conductivity, helping to dissipate heat, and it maintains excellent chemical resistance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right PTFE involves balancing its exceptional chemical inertness against its mechanical limitations and cost.
The Challenge of Cold Flow (Creep)
This is the single most important limitation of pure, unfilled PTFE. Under the compressive load of a bolted flange, the material can slowly "flow" or squeeze out from the joint, reducing sealing stress and eventually causing a leak.
Expanded and filled PTFE are the direct engineering solutions to this fundamental problem.
Purity vs. Mechanical Performance
There is a direct trade-off between the absolute purity of virgin PTFE and the superior mechanical performance of filled PTFE.
While filled PTFE offers better sealability in high-pressure or high-temperature applications, the filler itself may not be compatible with the process media or meet regulatory standards for food and pharma.
Cost and Application
As a general rule, cost and performance increase together. Mechanical grade skived PTFE is the most economical, while highly engineered structured or expanded PTFE gaskets are a premium option for solving difficult sealing problems.
Selecting the Right PTFE Gasket for Your Application
Your choice should be dictated by the specific demands of the service environment.
- If your primary focus is food safety, medical use, or electrical insulation: Choose Virgin Grade PTFE for its unmatched purity and dielectric properties.
- If your primary focus is sealing irregular, damaged, or low-load flanges: Choose Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) for its superior conformability and excellent creep resistance.
- If your primary focus is high pressure or temperature in a standard chemical service: Choose a Filled PTFE (like glass or carbon-filled) to gain the necessary compressive strength and resistance to cold flow.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose, non-critical industrial applications: Mechanical Grade PTFE offers a cost-effective solution with robust chemical resistance.
By matching the specific form of PTFE to your operational demands, you ensure a reliable, long-lasting seal.
Summary Table:
| PTFE Material Type | Key Characteristics | Best For Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Virgin PTFE | Highest purity, excellent chemical resistance, superior dielectric properties | Pharmaceutical, food & beverage, medical, high-performance electrical insulation |
| Mechanical Grade PTFE | Economical, robust chemical resistance (no recycled content for sensitive uses) | General industrial chemical services (non-critical) |
| Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) | Superior conformability, excellent creep resistance, seals irregular surfaces | Low bolt load flanges, damaged or wavy flanges, applications requiring high creep resistance |
| Glass-Filled PTFE | Increased stiffness, compressive strength, and wear resistance | General-purpose chemical services (avoid strong alkalis/hydrofluoric acid) |
| Carbon-Filled PTFE | Highest compressive strength, improved thermal conductivity, excellent load resistance | High-pressure/high-temperature chemical services, applications needing heat dissipation |
Need a High-Performance PTFE Gasket Solution?
Selecting the right PTFE material is critical for seal reliability, safety, and cost-efficiency. The experts at KINTEK are here to help.
We specialize in the precision manufacturing of PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require a standard material or a custom-fabricated solution from prototype to high-volume production, we ensure your gaskets meet the exact demands of your application.
Let us provide you with a PTFE gasket that delivers:
- Unmatched Reliability: Perfect material selection to combat cold flow and ensure a long-lasting seal.
- Optimal Performance: Expert guidance to match PTFE type to your specific pressure, temperature, and chemical environment.
- Precision Manufacturing: High-quality production for consistent performance and fit.
Contact us today to discuss your project requirements and get a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech



















