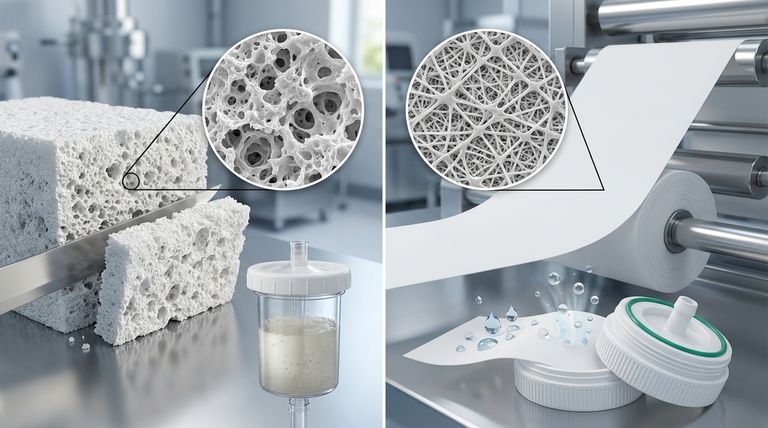
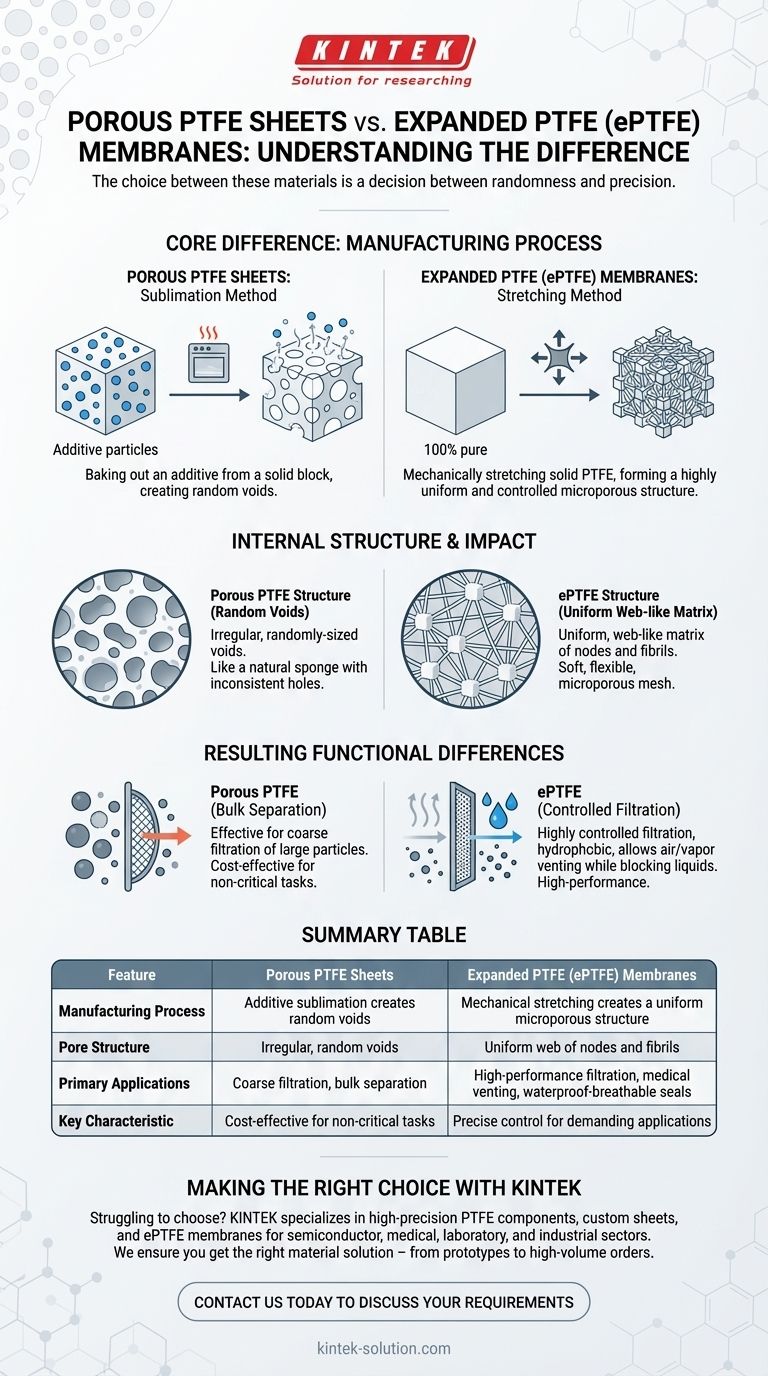
At their core, the difference between porous PTFE sheets and expanded PTFE (ePTFE) membranes lies in their manufacturing process. Porous sheets are made by baking out an additive from a solid block, creating random voids, whereas ePTFE membranes are created by mechanically stretching solid PTFE, which forms a highly uniform and controlled microporous structure.
The choice between these materials is a decision between randomness and precision. Porous PTFE sheets are suited for simple, coarse separation, while the precisely controlled structure of ePTFE membranes makes them the definitive choice for high-performance filtration, venting, and sealing applications.

How They Are Made: The Origin of Porosity
The fundamental differences in performance between these two materials begin with their distinct manufacturing methods. Each process creates a fundamentally different internal architecture.
Porous PTFE Sheets: The Sublimation Method
Porous PTFE sheets are created by mixing a solid PTFE resin with a filler material or additive. This mixture is then molded and sintered (heated).
During the heating process, the additive sublimates—it turns from a solid directly into a gas—leaving behind voids or pores. This process results in a random and non-uniform pore structure with less control over the final pore size and distribution.
Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) Membranes: The Stretching Method
Expanded PTFE is made from 100% pure PTFE without any additives. The process involves the mechanical stretching of solid PTFE material under very specific conditions of temperature and rate.
This stretching action pulls the material's molecular structure apart. It creates a highly intricate and uniform network of solid PTFE nodes interconnected by extremely thin fibrils. The spaces between these nodes and fibrils form the material's micropores.
The Critical Difference: Pore Structure and Its Impact
The manufacturing method directly dictates the material's internal structure, which in turn defines its function and ideal applications.
Structure of Porous PTFE
The internal structure of a porous PTFE sheet is best described as a collection of irregular, randomly-sized voids. Think of it like a natural sponge, where the holes are inconsistent in size and shape.
Structure of ePTFE
The structure of an ePTFE membrane is a uniform, web-like matrix. This microscopic mesh gives the material a soft, flexible, and almost spongey texture, while maintaining the strength of the underlying PTFE polymer.
Resulting Functional Differences
The structural contrast leads to clear performance differences. The random voids in porous PTFE are effective for bulk separation, such as filtering large solid particles from a liquid.
The precise, microporous web of ePTFE allows for highly controlled filtration. It is naturally hydrophobic (water-repellent), so its pores can be engineered to be small enough to block liquid water while still being large enough to allow gases and water vapor to pass through freely.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Applications
While both materials share the exceptional chemical and thermal resistance of PTFE, their applications rarely overlap due to their structural differences.
When to Use Porous PTFE Sheets
Porous PTFE is the appropriate choice for less demanding applications where cost is a primary driver and absolute precision is not required.
It is typically used for general-purpose, coarse filtration tasks. An example would be separating large contaminants from a chemical bath where the exact particle size being filtered is not critical.
When to Use Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) Membranes
Expanded PTFE is the superior material for any application that demands high reliability, precision, and specific performance characteristics.
Its controlled porosity is essential for waterproof-breathable textiles, medical venting, high-purity filters, and advanced industrial seals. The ability to allow air to vent while preventing liquid and contaminant ingress is its defining feature.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct material requires a clear understanding of your engineering goal and the level of precision your system demands.
- If your primary focus is coarse, bulk separation: Porous PTFE sheets offer a cost-effective solution where exact pore size is not a critical factor.
- If your primary focus is controlled filtration or venting: Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) membranes provide the precise, uniform microporous structure necessary for high-performance applications.
- If your primary focus is flexibility and sealing: The unique, soft texture and compliant nature of ePTFE make it ideal for creating high-integrity gaskets and seals.
Understanding the fundamental difference in their creation—sublimation versus expansion—is the key to selecting the correct material for your specific engineering challenge.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Porous PTFE Sheets | Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) Membranes |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Additive sublimation creates random voids | Mechanical stretching creates a uniform microporous structure |
| Pore Structure | Irregular, random voids | Uniform web of nodes and fibrils |
| Primary Applications | Coarse filtration, bulk separation | High-performance filtration, medical venting, waterproof-breathable seals |
| Key Characteristic | Cost-effective for non-critical tasks | Precise control for demanding applications |
Struggling to choose between porous PTFE and ePTFE for your project? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including custom porous sheets and expanded PTFE membranes, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures you get the right material solution—from prototypes to high-volume orders—optimized for your specific filtration, venting, or sealing needs. Contact us today to discuss your requirements and leverage our precision production capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What is a PTFE lined valve? A Cost-Effective Solution for Corrosive & High-Purity Fluids
- How do PTFE lip seals compare to traditional elastomer lip seals? A Guide to High-Performance Sealing
- What material is replacing carbon in seals and piston rings, and why? PTFE's Superior Durability & Lifespan
- How does the flexibility of the lip design in Teflon rotary shaft seals enhance performance? Boost Reliability & Extend Equipment Life
- What are the key advantages of using PTFE gaskets and sheets? Superior Sealing for Harsh Environments
- What are the advantages of using a Teflon sheet for heat press? Protect Your Projects & Achieve Flawless Results
- What are the two main types of lip seals? PTFE Metal-Cased vs. All-Polymer Seals Explained
- How does chemical resistance benefit PTFE Teflon washers? Ensure Leak-Free Seals in Harsh Environments



















