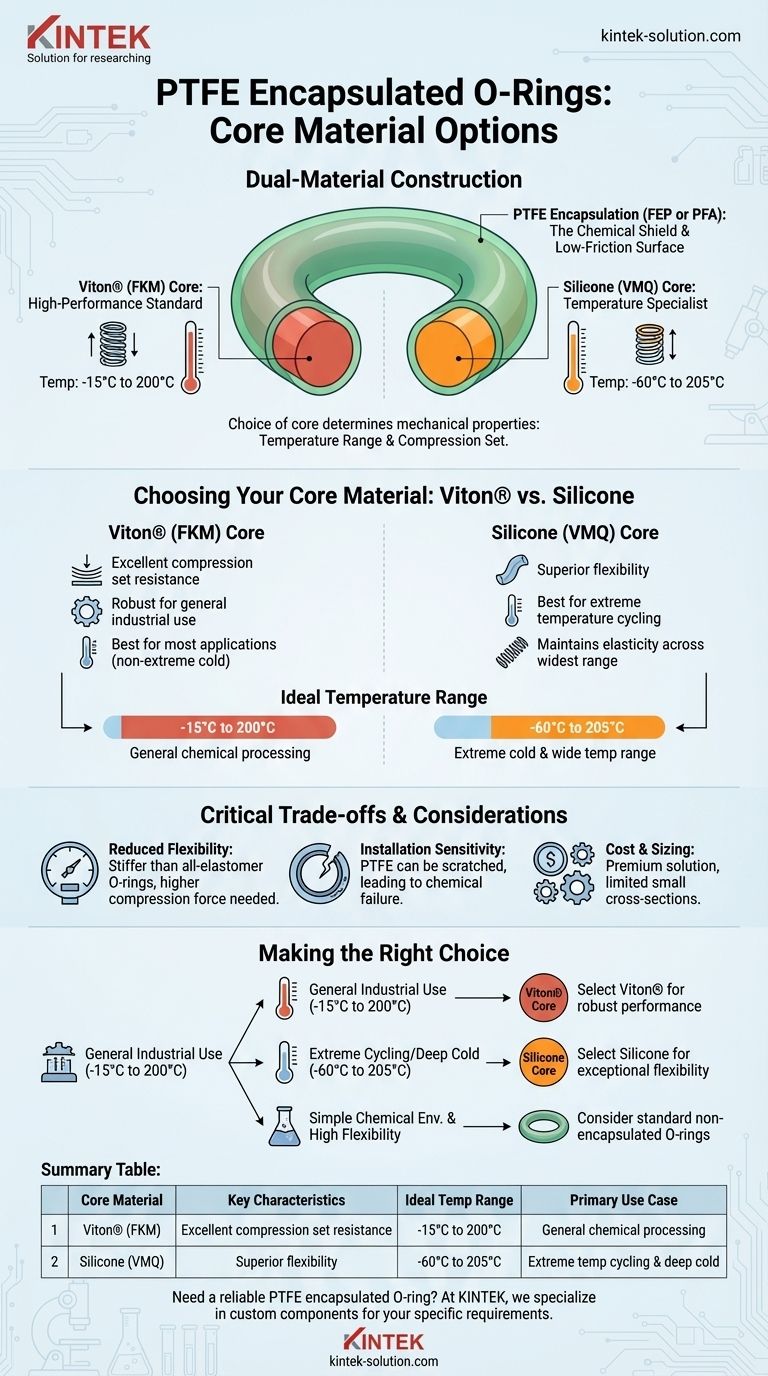
At its core, a PTFE encapsulated O-ring utilizes one of two primary elastomer materials. The choice comes down to either a Viton® (fluoroelastomer) core for general-purpose high performance or a silicone core for applications requiring a wider temperature range.
The rigid PTFE outer jacket provides the universal chemical resistance and low-friction surface. The choice of the softer inner core—Viton® or silicone—is what determines the seal's mechanical properties, specifically its temperature range and compression set.

Understanding the Dual-Material Construction
A PTFE encapsulated O-ring is a composite seal, combining the properties of two distinct materials to achieve performance that neither could alone. Understanding this structure is key to selecting the right one.
The PTFE Encapsulation: The Chemical Shield
The outer jacket is a seamless layer of PTFE (Teflon®), typically FEP or PFA. This encapsulation is the component that contacts the media.
Its primary role is to provide extreme chemical inertness, making the seal suitable for aggressive solvents, acids, and bases.
The PTFE jacket also creates a low-friction, anti-stick surface that is ideal for sanitary applications, preventing contamination and simplifying cleaning.
The Elastomer Core: The Mechanical Spring
While PTFE is chemically robust, it is also a rigid material with poor elastic memory. It cannot function as a seal on its own.
The inner core, made of either Viton® or silicone, acts as the "spring." It provides the energizing force, compressing to create a tight seal and rebounding to maintain it over time.
The properties of this inner core dictate the O-ring's overall flexibility, temperature limits, and ability to resist permanent deformation (compression set).
Choosing Your Core Material: Viton® vs. Silicone
The decision between a Viton® or silicone core is based entirely on the physical demands of your application, not the chemical environment, which is handled by the PTFE jacket.
The Viton® (FKM) Core: The High-Performance Standard
Viton® is the most common core material for encapsulated O-rings. It offers an excellent balance of properties for a wide range of industrial uses.
It provides a very good high-temperature resistance and a superior resistance to compression set compared to silicone in typical operating ranges. This makes it the reliable, go-to choice for most applications that don't involve extreme cold.
The Silicone (VMQ) Core: The Temperature Specialist
Silicone is selected when the primary challenge is temperature, particularly extreme cold. It remains flexible at much lower temperatures than Viton®.
Silicone also offers a slightly higher maximum temperature limit. Its main advantage is maintaining its elasticity and sealing force across the widest possible thermal range.
Critical Trade-offs and Considerations
While highly effective, encapsulated O-rings are a specialized solution with specific limitations that must be understood to prevent seal failure.
Reduced Flexibility
The rigid PTFE jacket makes these seals significantly stiffer than standard all-elastomer O-rings. They require more force to compress and create a seal.
Installation Sensitivity
The PTFE encapsulation can be scratched or damaged during installation if not handled with care. Any breach in the jacket will compromise the seal's chemical resistance and lead to rapid failure.
Cost and Sizing
Encapsulated O-rings are a premium sealing solution and are more expensive than standard O-rings. Due to the manufacturing process, they are also less common in very small or non-standard cross-sections.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct core is a matter of matching the material's mechanical properties to your specific operational environment.
- If your primary focus is general chemical processing and industrial applications (-15°C to 200°C): The Viton® core is the robust, default choice offering excellent compression set resistance.
- If your primary focus is performance in extreme temperature cycling or deep cold (-60°C to 205°C): The silicone core is the superior option due to its exceptional flexibility.
- If your application requires high flexibility and has a simple chemical environment: Consider whether a standard, non-encapsulated Viton® or EPDM O-ring might be a more suitable and cost-effective solution.
By understanding the distinct roles of the jacket and the core, you can confidently select the precise seal for your system's needs.
Summary Table:
| Core Material | Key Characteristics | Ideal Temperature Range | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Viton® (FKM) | Excellent compression set resistance, robust for industrial use | -15°C to 200°C | General chemical processing, high-performance industrial applications |
| Silicone (VMQ) | Superior flexibility, best for extreme temperature cycling | -60°C to 205°C | Applications requiring wide temperature range, extreme cold environments |
Need a reliable PTFE encapsulated O-ring for your application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including custom encapsulated O-rings for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require a Viton® core for robust performance or a silicone core for extreme temperatures, our team provides expert guidance and custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and ensure optimal sealing performance in your system. Get in touch via our contact form for a personalized solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are some important physical property values for PTFE? Master Its Extreme Performance for Demanding Applications
- When and by whom was PTFE discovered? A Tale of Accidental Innovation
- What is the temperature range that PTFE can withstand? From -200°C to +260°C for Demanding Applications
- Why is PTFE considered a significant discovery? A Material That Revolutionized Industry
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications



















