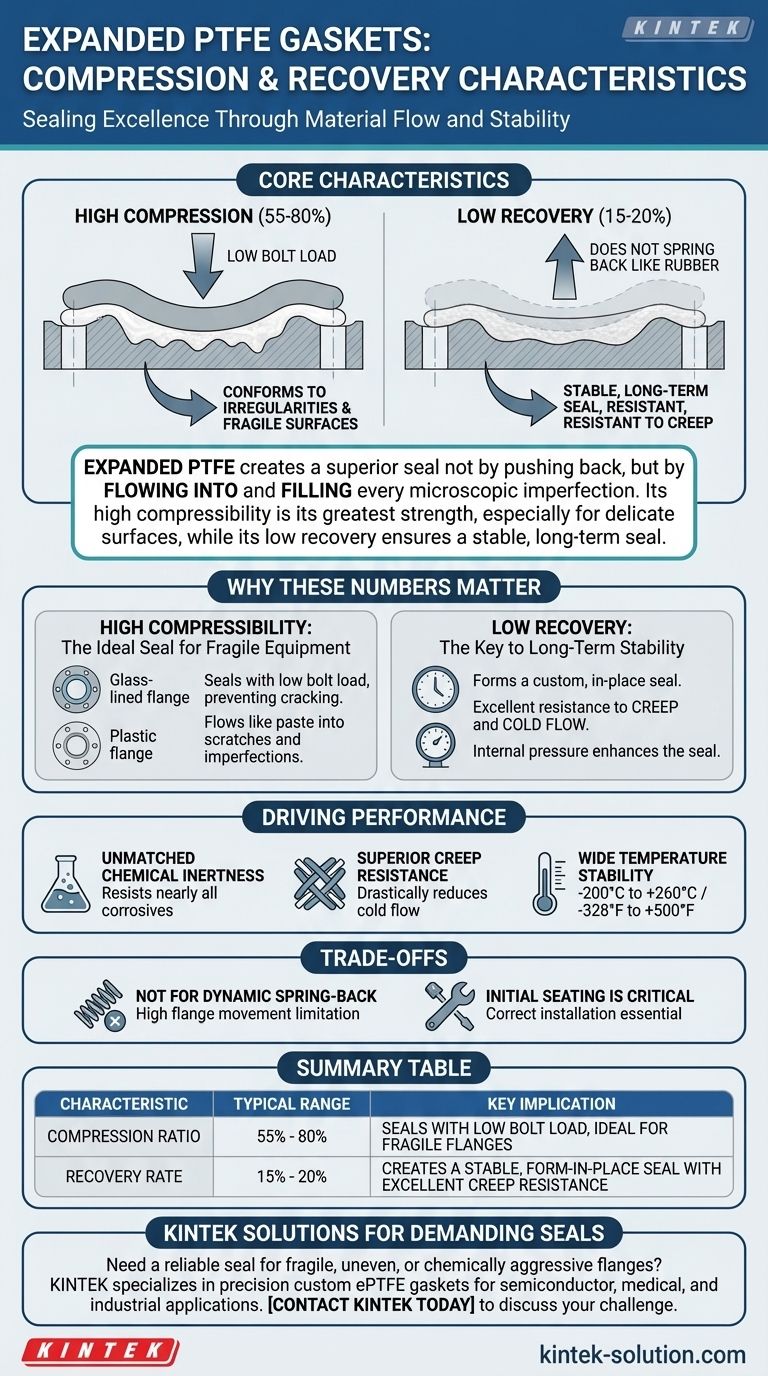
At its core, expanded PTFE (ePTFE) is defined by extreme compressibility and low elastic recovery. An ePTFE gasket has a typical compression ratio between 55% and 80%, allowing it to conform perfectly to surface irregularities. However, its recovery rate is only 15% to 20%, meaning it does not "spring back" like a traditional rubber elastomer.
The central takeaway is that expanded PTFE creates a superior seal not by pushing back against flanges, but by flowing into and filling every microscopic imperfection. Its high compressibility is its greatest strength, especially for delicate or uneven surfaces, while its low recovery ensures a stable, long-term seal resistant to creep.

Deconstructing the Numbers: High Compression, Low Recovery
The unique characteristics of expanded PTFE gaskets stem directly from their compression and recovery values. Understanding these figures is key to understanding where and why this material excels.
What High Compressibility (55-80%) Means for Sealing
The ability to compress by such a large margin means the soft, flexible material can be seated with very low bolt load.
This allows the ePTFE to flow like a thick paste into every scratch, pit, and waviness on a flange face. The result is an exceptionally tight seal that can compensate for damaged or imperfect surfaces where other gaskets would fail.
This property makes it the ideal choice for fragile equipment, such as glass-lined steel, PVC, or fiberglass flanges, which would crack under the high bolt torque required for other gasket types.
The Role of Low Recovery (15-20%)
Unlike a rubber O-ring that relies on its "springiness" to maintain a seal, expanded PTFE functions differently. Its low recovery means it essentially forms a custom, in-place seal that holds its shape.
This is a feature, not a flaw. This resistance to springing back is directly linked to its excellent resistance to creep and cold flow.
Once compressed, the gasket material doesn't squeeze out from under the load over time, ensuring the seal remains tight and stable for a long service life.
How Internal Pressure Enhances the Seal
The slight elasticity that ePTFE does possess works to its advantage. As internal system pressure increases, it pushes against the gasket.
This pressure further forces the material into the flange surfaces, effectively increasing the sealing force and strengthening the integrity of the connection when it's needed most.
The Core Properties Driving Performance
The compression and recovery characteristics are supported by a unique combination of material properties that make ePTFE a premier sealing solution in demanding environments.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
Expanded PTFE consists entirely of carbon and fluorine, making it one of the most chemically resistant materials known. It is unaffected by nearly all corrosive liquids, vapors, and gases.
Superior Creep Resistance
While standard PTFE is known for cold flow, the expanded multi-directional fibrous structure of ePTFE locks together under pressure. This drastically reduces creep and ensures the gasket maintains its shape and sealing capability over time.
Wide Temperature Stability
Expanded PTFE performs reliably from cryogenic temperatures up to +260°C (500°F). This broad operational range makes it suitable for processes with significant thermal cycling without becoming brittle or degrading.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the unique properties of ePTFE mean it isn't a universal solution. Its behavior is distinct from elastomeric or metallic gaskets.
Not Designed for Dynamic "Spring-Back"
If your application involves significant flange movement, heavy vibration, or requires frequent disassembly and reassembly, the low recovery of ePTFE may be a limitation. It is designed to create a static, form-in-place seal.
Initial Seating is Critical
Because the material "sets" into place, the initial installation is the most critical step. Achieving the correct initial compression with the proper bolt-tightening sequence is essential for long-term performance, as the gasket will not recover to compensate for a poor initial fit.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct gasket requires matching the material's properties to the application's demands.
- If your primary focus is sealing fragile or damaged flanges: Expanded PTFE is the ideal choice, as its high compressibility creates a perfect seal with minimal, non-damaging bolt load.
- If your primary focus is aggressive chemical service: Its near-universal chemical inertness provides an exceptionally reliable and long-lasting seal where other materials would quickly fail.
- If your primary focus is maintaining a long-term, stable seal: Its excellent resistance to creep and cold flow ensures the connection remains tight and leak-free for extended periods without re-torquing.
By understanding these unique compression and recovery properties, you can leverage expanded PTFE to create exceptionally reliable seals in your most demanding applications.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | Typical Range | Key Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Compression Ratio | 55% - 80% | Seals with low bolt load, ideal for fragile or damaged flanges |
| Recovery Rate | 15% - 20% | Creates a stable, form-in-place seal with excellent creep resistance |
Need a reliable seal for fragile, uneven, or chemically aggressive flanges?
The unique properties of expanded PTFE (ePTFE) make it the ideal choice for demanding applications in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including custom ePTFE gaskets tailored to your specific requirements—from prototypes to high-volume production.
Our expertise ensures you get a component that delivers superior sealing performance, chemical inertness, and long-term stability.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your sealing challenge and let our experts provide a solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What challenges arise when machining PTFE (Teflon)? Overcome Softness, Heat, and Instability
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? The 3 Pillars Driving Demand for High-Performance Parts
- What chemical processing applications involve PTFE-machined parts? Essential Components for Corrosive & High-Purity Systems
- What finishing techniques are effective for machined Teflon parts? Achieve Functional Performance and Dimensional Stability
- What fabrication services are available for PTFE? Shearing, Stamping, Laser Cutting, Molding & Machining



















