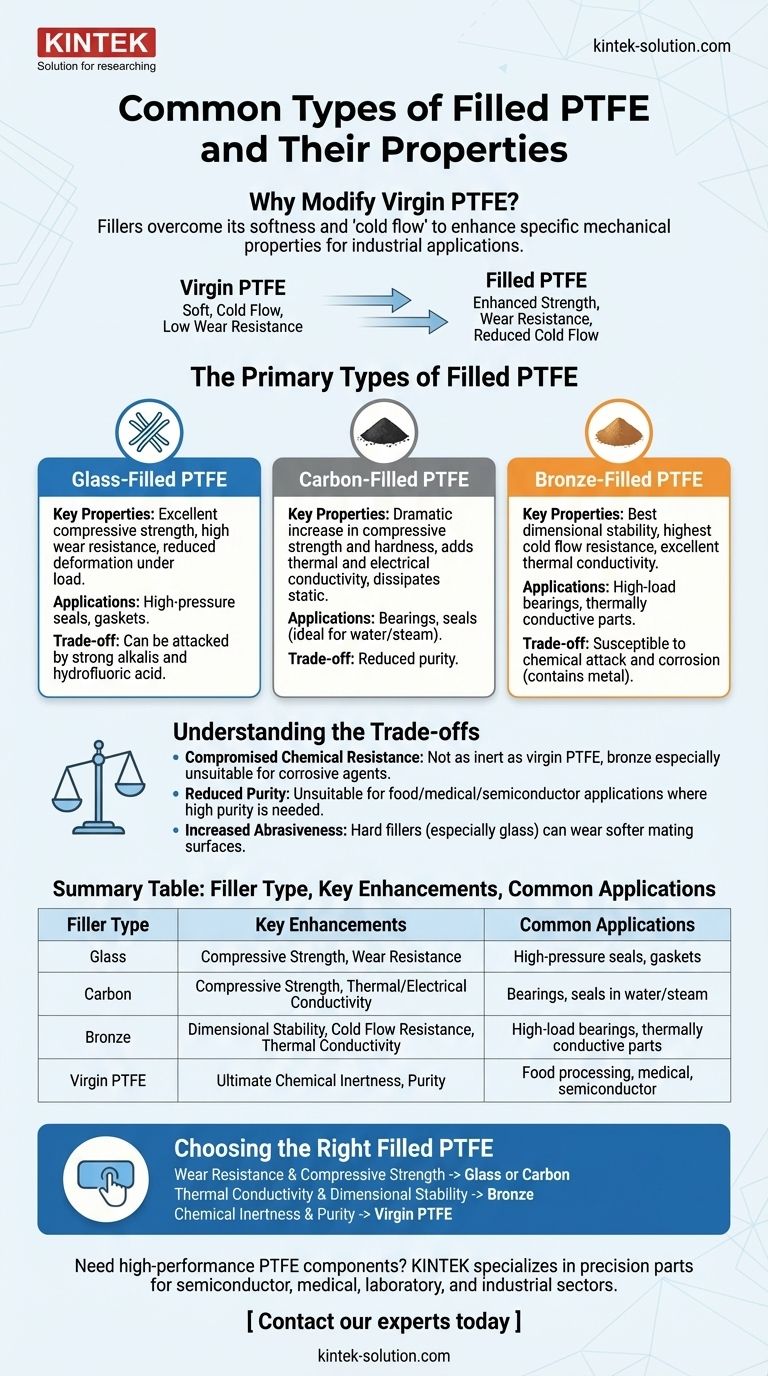
To put it simply, the most common types of filled PTFE are modified with glass, carbon, or bronze to enhance specific mechanical properties. These fillers are added to virgin Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), also known by the brand name Teflon®, to overcome its inherent softness and tendency to deform under load, a phenomenon known as "cold flow." Each filler imparts a unique set of characteristics, making the resulting material suitable for demanding industrial applications.
The core principle to understand is that fillers are used to solve PTFE's mechanical weaknesses—primarily its low wear resistance and poor compressive strength. This enhancement comes with trade-offs, often slightly reducing the material's exceptional chemical inertness or purity.

Why Modify a Near-Perfect Material? The Purpose of Fillers
Virgin PTFE is renowned for its nearly universal chemical resistance, extremely low coefficient of friction, and high-temperature tolerance. However, it is a relatively soft material.
The Problem of "Cold Flow"
Under sustained pressure, especially at elevated temperatures, virgin PTFE can deform permanently. This "creep" or cold flow makes it unsuitable for high-load structural or sealing applications.
Poor Wear Resistance
The low-friction surface of PTFE is not inherently durable against abrasion. In dynamic applications like bearings or seals, virgin PTFE wears away quickly. Fillers create a composite material that is far more resilient.
The Primary Types of Filled PTFE
Choosing a filler is about targeting a specific performance improvement. While many fillers exist, a few have become industry standards due to their effectiveness and predictable results.
Glass-Filled PTFE
This is one of the most common and cost-effective variants. Adding glass fibers significantly boosts the material's durability.
Glass-filled PTFE offers excellent compressive strength and wear resistance. It also lowers the material's tendency to deform under load, making it ideal for high-pressure seals and gaskets. While it retains good chemical resistance, it can be attacked by strong alkalis and hydrofluoric acid.
Carbon-Filled PTFE
Carbon, often added in powder or fiber form, provides a balanced set of enhancements. It is a preferred choice for dynamic applications involving water and steam.
This formulation dramatically increases compressive strength and hardness. Crucially, carbon also adds thermal and electrical conductivity, helping to dissipate static charge and heat in bearings and seals.
Bronze-Filled PTFE
Adding bronze powder creates the strongest and most wear-resistant PTFE composite, but with specific trade-offs.
Bronze-filled PTFE has the best dimensional stability and the highest resistance to cold flow. It also boasts excellent thermal conductivity. However, the presence of metal makes it more susceptible to chemical attack and corrosion compared to other filled grades.
Other Notable Fillers
While less common, other materials are used for specialized needs.
Graphite is often used in combination with other fillers (like carbon) to lower the coefficient of friction and improve wear properties. Molybdenum disulfide ("Moly") is another additive that enhances self-lubrication and heat resistance, particularly in vacuum applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs of Filled PTFE
Introducing a second material into pure PTFE is a balancing act. The gains in mechanical strength come at a cost that must be considered for your specific application.
Compromised Chemical Resistance
While most filled grades are still highly resistant, they do not match the near-total inertness of virgin PTFE. Bronze-filled PTFE, for example, is unsuitable for use with strong acids or corrosive agents that would attack the metal filler.
Reduced Purity
Fillers make the material unsuitable for applications requiring the highest purity, such as in food processing, medical devices, or semiconductor manufacturing. In these cases, virgin PTFE remains the standard.
Increased Abrasiveness
Hard fillers, particularly glass fibers, can be abrasive to softer mating surfaces like steel or aluminum shafts. This must be factored into the overall system design to prevent premature wear on other components.
Choosing the Right Filled PTFE for Your Application
Your final selection depends entirely on the primary challenge you need the material to overcome.
- If your primary focus is wear resistance and compressive strength: Glass-filled PTFE is an excellent general-purpose choice, while carbon-filled PTFE offers a superior balance of properties for dynamic applications.
- If your primary focus is thermal conductivity and dimensional stability: Bronze-filled PTFE provides the best performance against cold flow and for dissipating heat, provided chemical compatibility is not an issue.
- If your primary focus is chemical inertness and purity at all costs: Stick with virgin PTFE and design your system to accommodate its mechanical limitations.
By understanding the distinct role of each filler, you can select a material precisely engineered to meet the demands of your application.
Summary Table:
| Filler Type | Key Property Enhancements | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Glass | Compressive Strength, Wear Resistance | High-pressure seals, gaskets |
| Carbon | Compressive Strength, Thermal/Electrical Conductivity | Bearings, seals in water/steam |
| Bronze | Dimensional Stability, Cold Flow Resistance, Thermal Conductivity | High-load bearings, thermally conductive parts |
| Virgin PTFE | Ultimate Chemical Inertness, Purity | Food processing, medical, semiconductor |
Need a high-performance PTFE component tailored to your specific application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you need a custom prototype or a high-volume order, our expertise in material selection and fabrication ensures your parts meet the highest standards for durability and performance.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer Conductive Glass Substrate Cleaning Rack
People Also Ask
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers



















