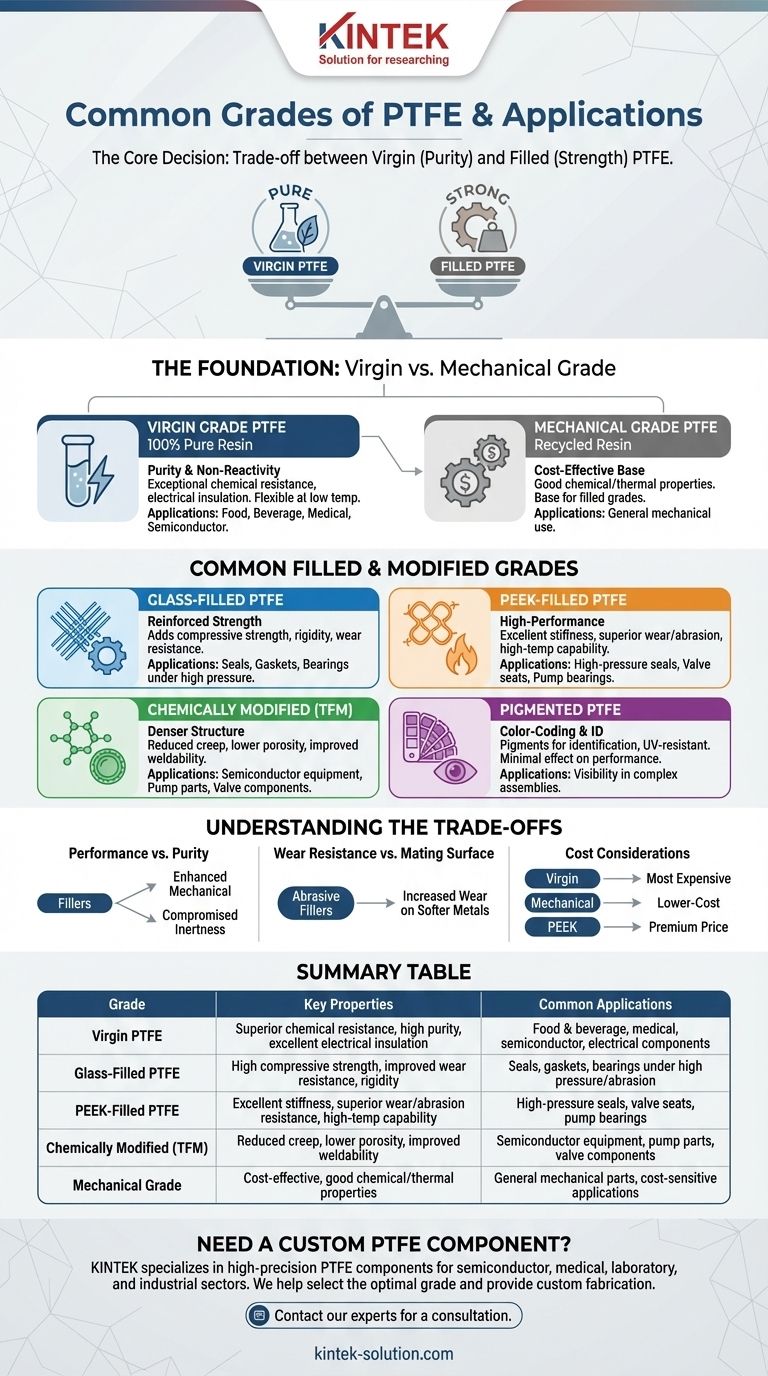
The most common grades of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) are Virgin (pure) PTFE and a variety of filled grades designed to enhance specific mechanical properties. Virgin PTFE is prized for its unparalleled chemical resistance and electrical insulation. Filled grades, such as glass-filled or PEEK-filled PTFE, add reinforcing materials to improve characteristics like compressive strength, wear resistance, and dimensional stability for more demanding mechanical applications.
The core decision in selecting a PTFE grade is a direct trade-off. You must choose between the exceptional chemical inertness and purity of virgin PTFE and the superior mechanical strength and wear resistance offered by filled PTFE composites.
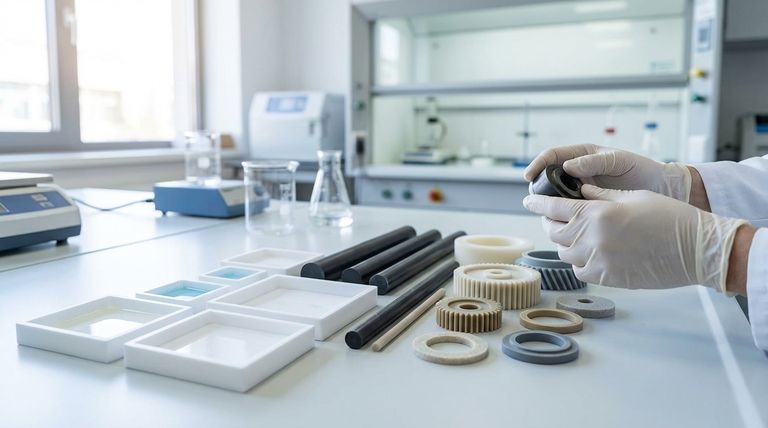

The Foundation: Virgin vs. Mechanical Grade
Before considering fillers, it's crucial to understand the base resin. The two primary starting points for any PTFE component are virgin and mechanical grade resin.
Virgin Grade PTFE
Virgin PTFE is made from 100% pure, new PTFE resin without any additives or recycled material. This is the highest quality grade available.
Its primary strengths are its exceptional chemical resistance across a wide range of substances and its excellent electrical insulation properties. It also retains flexibility at very low temperatures.
This grade is the standard for applications in the food, beverage, medical, and semiconductor industries, where purity and non-reactivity are critical.
Mechanical Grade PTFE
Mechanical grade PTFE is produced using reprocessed or recycled PTFE resin. This makes it a more cost-effective option.
While it retains good chemical and thermal properties, its overall physical performance may be slightly less than virgin grade.
However, mechanical grade resin is often the base material used for creating filled PTFE grades, where its properties are then enhanced by specific additives.
Common Filled and Modified Grades
Fillers are added to PTFE to overcome its inherent softness and tendency to deform under load (a phenomenon known as "creep"). Each filler imparts a unique set of properties.
Glass-Filled PTFE
This is one of the most common filled grades, typically reinforced with glass fibers.
Adding glass significantly increases compressive strength and rigidity. It dramatically improves wear resistance compared to virgin PTFE.
It is frequently used for seals, gaskets, and bearings that must operate under high pressure or abrasive conditions.
PEEK-Filled PTFE
This grade combines PTFE with Polyetheretherketone (PEEK), a high-performance polymer.
The addition of PEEK results in a material with excellent stiffness, superior wear and abrasion resistance, and high-temperature capabilities.
PEEK-filled PTFE is ideal for highly demanding environments like high-pressure seals, valve seats, and bearings in pumps and other industrial equipment.
Chemically Modified PTFE
Also known as TFM, this grade is a second-generation PTFE that has been chemically modified at the molecular level.
This modification results in a denser polymer structure, which reduces creep, lowers porosity, and improves the weldability of the material.
It's often used in semiconductor equipment, pump parts, and valve components where purity and improved mechanical integrity are required.
Pigmented PTFE
In this grade, pigments are added to the PTFE resin, most commonly for color-coding and identification.
The pigments are typically UV-resistant, which helps with visibility in outdoor applications or complex assemblies.
This modification is for practical identification and has a minimal effect on the material's core performance properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a filled grade is not a universal upgrade. You must consider the potential downsides to make an informed decision.
Performance vs. Purity
The primary trade-off is purity. While fillers enhance mechanical properties, they can compromise the extreme chemical inertness of virgin PTFE.
For applications involving highly aggressive chemicals or requiring FDA compliance for food contact, virgin PTFE is almost always the correct choice.
Wear Resistance vs. Mating Surface
Highly abrasive fillers like glass can increase the wear on the mating surface, especially softer metals like aluminum or stainless steel.
When designing with glass-filled PTFE, it is critical to consider the hardness of the opposing component to prevent premature failure of the system.
Cost Considerations
Virgin PTFE is typically the most expensive base resin due to its purity. Mechanical grade offers a lower-cost alternative.
Filled grades have varying costs depending on the type and percentage of the filler material, with high-performance fillers like PEEK commanding a premium price.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your specific goal will determine the optimal PTFE grade.
- If your primary focus is chemical purity, food safety, or electrical insulation: Choose Virgin PTFE for its unparalleled inertness and dielectric properties.
- If your primary focus is high load capacity and wear resistance: Choose Glass-Filled or PEEK-Filled PTFE, depending on the severity of the wear and temperature.
- If your primary focus is reduced deformation and lower porosity: Choose Chemically Modified PTFE (TFM) for a more stable and less permeable material.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for general mechanical use: A Mechanical Grade composite with an appropriate filler is often the most practical solution.
Ultimately, selecting the correct PTFE grade requires matching your specific operational demands with the unique properties each material offers.
Summary Table:
| Grade | Key Properties | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Virgin PTFE | Superior chemical resistance, high purity, excellent electrical insulation | Food & beverage, medical, semiconductor, electrical components |
| Glass-Filled PTFE | High compressive strength, improved wear resistance, rigidity | Seals, gaskets, bearings under high pressure/abrasion |
| PEEK-Filled PTFE | Excellent stiffness, superior wear/abrasion resistance, high-temp capability | High-pressure seals, valve seats, pump bearings |
| Chemically Modified (TFM) | Reduced creep, lower porosity, improved weldability | Semiconductor equipment, pump parts, valve components |
| Mechanical Grade | Cost-effective, good chemical/thermal properties | General mechanical parts, cost-sensitive applications |
Need a Custom PTFE Component?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We help you select the optimal PTFE grade and provide custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume production, ensuring your parts meet exact performance and purity requirements.
Contact our experts today for a consultation on your specific application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Customizable PTFE Crucibles for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What properties make Teflon ideal for medical applications? Discover Its Critical Role in Safety & Performance
- What are the common uses of Teflon? A Guide to PTFE's Versatile Applications
- How was PTFE discovered and by whom? A Serendipitous Breakthrough in Material Science
- How does PTFE function as a lubricant? Master Low-Friction Performance in Harsh Environments
- What makes Teflon suitable for electret manufacturing? Achieve Unmatched Charge Stability for Your Devices
- What industrial applications utilize expanded PTFE? Sealing, Filtration & Insulation Solutions
- How does PTFE's temperature resistance benefit its applications? Ensure Reliability from -200°C to +260°C
- How does Teflon perform in harsh chemical environments? Unmatched Chemical Resistance for Demanding Applications



















