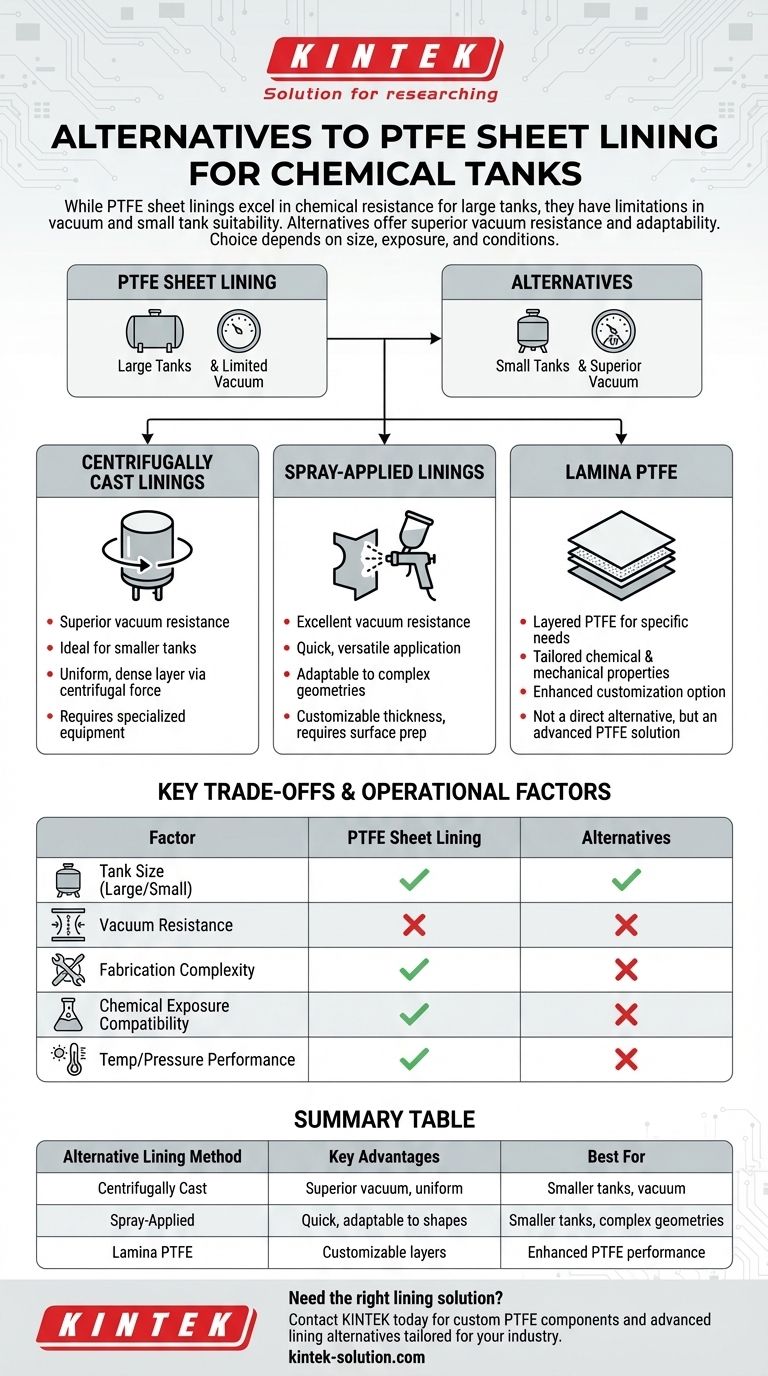
When considering alternatives to PTFE sheet lining for chemical tanks, several options stand out, each with unique advantages depending on the application. PTFE sheet linings are known for their excellent chemical resistance, especially in large tanks, but they have limitations in vacuum resistance and suitability for smaller tanks. Alternatives like centrifugally cast linings and spray-applied linings offer better vacuum resistance and are more adaptable for smaller tanks. The choice depends on factors like tank size, chemical exposure, and operational conditions, with proper design and fabrication being critical for all methods.

Key Points Explained:
-
Centrifugally Cast Linings
- Advantages: These linings provide superior vacuum resistance compared to PTFE sheet linings, making them ideal for applications where vacuum conditions are a concern. They are also more suitable for smaller tanks due to their application process.
- Process: The lining material is applied using centrifugal force, ensuring a uniform and dense layer that adheres well to the tank walls.
- Considerations: Requires specialized equipment and expertise, similar to PTFE sheet linings, but offers better performance in specific scenarios.
-
Spray-Applied Linings
- Advantages: Like centrifugally cast linings, spray-applied linings excel in vacuum resistance and are more versatile for smaller tanks. They can also be applied more quickly and evenly over complex geometries.
- Process: The lining material is sprayed onto the tank surface, allowing for a customizable thickness and coverage.
- Considerations: Proper surface preparation is critical to ensure adhesion, and the process may require multiple layers for optimal performance.
-
- Advantages: While not an alternative, lamina PTFE refers to layered PTFE linings that can be tailored for specific chemical resistance and mechanical properties. It’s worth considering if PTFE is preferred but with enhanced customization.
- Applications: Useful when PTFE’s chemical resistance is needed but with adjustments for specific tank designs or operational requirements.
-
Key Trade-offs
- Tank Size: PTFE sheet linings are better for large tanks, while centrifugally cast and spray-applied linings are more suited for smaller tanks.
- Vacuum Resistance: Alternatives outperform PTFE sheet linings in vacuum conditions.
- Fabrication Complexity: All methods require specialized expertise, but PTFE sheet linings may involve more intricate tank design considerations.
-
Operational and Design Factors
- Chemical Exposure: Ensure the chosen lining material is compatible with the chemicals stored.
- Temperature and Pressure: Consider how the lining will perform under operational temperature and pressure ranges.
- Maintenance and Longevity: Evaluate the expected lifespan and maintenance needs of each lining type.
By weighing these factors, you can select the most appropriate lining method for your chemical tank, balancing performance, cost, and application-specific requirements.
Summary Table:
| Alternative Lining Method | Key Advantages | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Centrifugally Cast Linings | Superior vacuum resistance, uniform application | Smaller tanks, vacuum conditions |
| Spray-Applied Linings | Quick application, adaptable to complex shapes | Smaller tanks, versatile geometries |
| Lamina PTFE | Customizable PTFE layers for specific needs | Enhanced PTFE performance |
Need the right lining solution for your chemical tank? Contact KINTEK today to discuss custom PTFE components and advanced lining alternatives tailored for your industry. Whether you're in semiconductor, medical, or industrial sectors, our precision fabrication ensures durability and performance. Get a quote now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Are PTFE O-rings safe for use in food processing equipment? Ensure Compliance and Safety
- How do PTFE bearing pads contribute to structural safety and efficiency? Enhance Structural Integrity with Low-Friction Support
- In what industries are PTFE instrumentation tube fittings commonly used? Ensuring Purity and Chemical Resistance
- How do PTFE rotary shaft seals perform in high-speed applications? Master High-Speed Sealing with Low Friction
- What are the key benefits of PTFE energized seals for the aerospace industry? Unmatched Reliability in Extreme Environments
- How does PTFE's low friction coefficient benefit impeller performance? Boost Efficiency & Lifespan
- In which industries are Teflon backup rings commonly used? Prevent Seal Failure in High-Pressure Systems
- What are the benefits of using a PTFE coating thrust washer in a fishing reel? Smoother Drag, Longer Reel Life



















