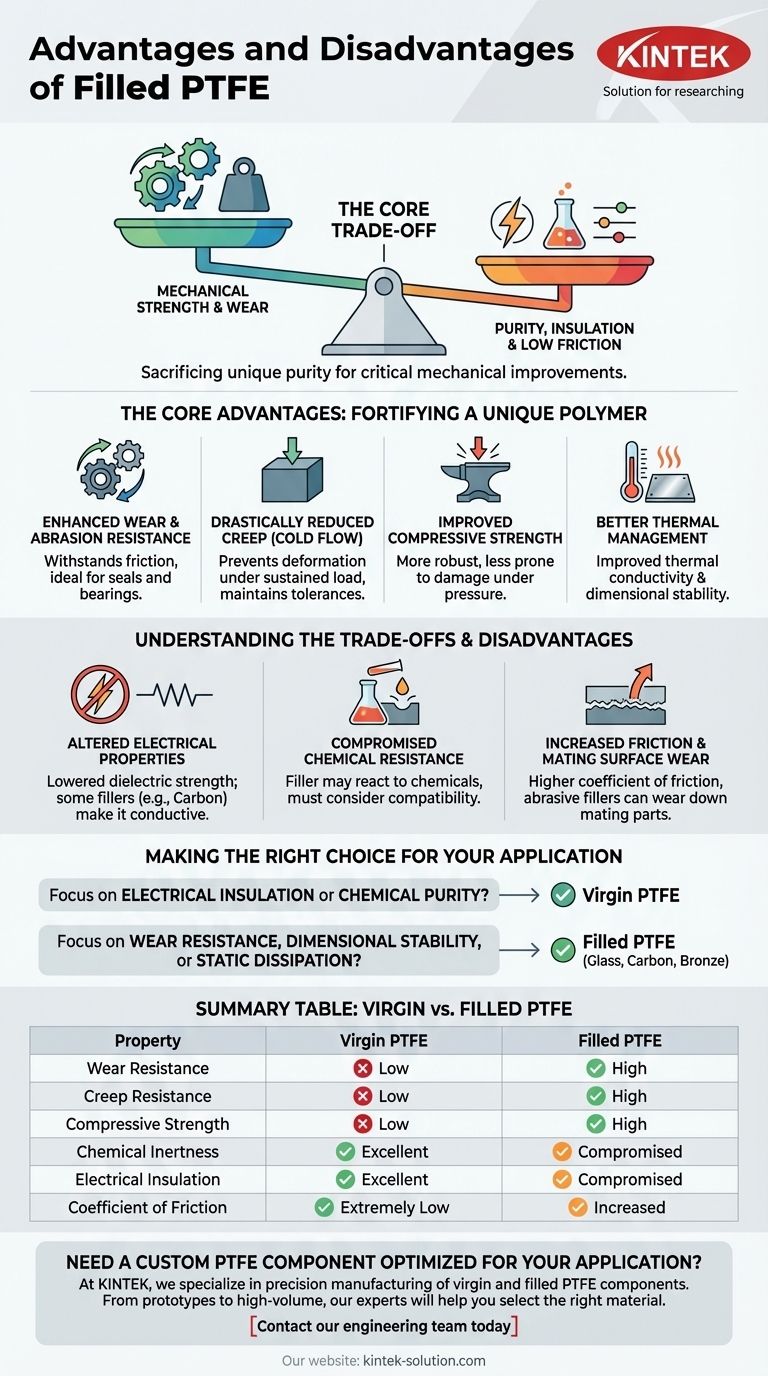
The fundamental advantage of filled PTFE is a significant improvement in mechanical properties, particularly wear resistance and strength. However, these gains come at the cost of compromising some of virgin PTFE's signature characteristics, such as its electrical insulation, chemical inertness, and low coefficient of friction.
The decision to use filled PTFE is a deliberate engineering trade-off. You are sacrificing some of the unique purity of virgin PTFE to gain critical improvements in mechanical strength, wear resistance, and dimensional stability under load for demanding applications.
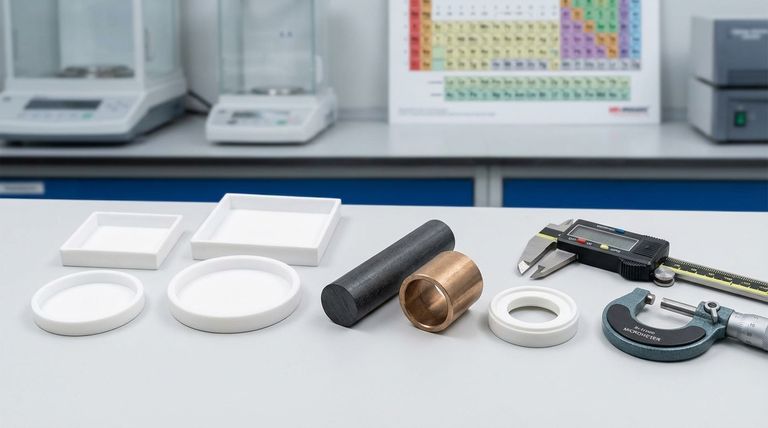

The Core Advantages: Fortifying a Unique Polymer
Virgin (unfilled) PTFE is an exceptional material, but it is mechanically soft. It can deform under pressure, a phenomenon known as creep or cold flow, and it wears down relatively quickly in dynamic applications. Fillers are added to counteract these specific weaknesses.
Enhanced Wear and Abrasion Resistance
The primary reason to choose a filled PTFE is for superior wear resistance. The addition of hard filler particles, like glass or bronze, creates a composite material that can withstand friction and abrasion far better than virgin PTFE.
This makes it ideal for components like seals, bearings, and wear pads.
Drastically Reduced Creep (Cold Flow)
Under a sustained load, virgin PTFE will slowly deform over time. Fillers act as a reinforcing skeleton within the PTFE matrix, significantly improving its creep resistance.
This ensures the component maintains its shape and tolerances under mechanical stress, which is critical for load-bearing parts.
Improved Compressive Strength and Hardness
Fillers increase the material's hardness and its ability to resist compressive forces. This results in a more robust material that is less prone to damage or deformation upon impact or under high pressure.
Better Thermal Management
Some fillers, particularly metallic ones like bronze or stainless steel, improve the thermal conductivity of PTFE. This allows heat to be drawn away from a surface more effectively.
Additionally, most fillers lower the material's rate of thermal expansion, improving its dimensional stability across a range of temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Disadvantages
Adding a second material into the PTFE matrix inevitably alters its fundamental properties. These compromises are not necessarily flaws, but critical factors to consider during material selection.
Altered Electrical Properties
Virgin PTFE is an outstanding electrical insulator. Adding fillers changes this.
Carbon, being conductive, will significantly lower the dielectric strength, making the material suitable for anti-static applications but poor for insulation. Glass fiber fillers generally maintain good insulation but can increase the dissipation factor.
Compromised Chemical Resistance
While the PTFE matrix itself remains highly inert, the filler material may not be. For example, stainless steel-filled PTFE is unsuitable for use with strong oxidizing agents that would attack the metal particles.
You must always consider the chemical compatibility of both the PTFE and its specific filler.
Increased Friction and Mating Surface Wear
Virgin PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid. The addition of harder filler particles will inevitably increase this friction.
Furthermore, abrasive fillers like glass can increase the wear rate of the mating surface the PTFE component slides against, especially if that surface is made of a softer material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct material requires a clear understanding of your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is electrical insulation or ultimate chemical purity: Virgin PTFE is almost always the correct choice.
- If your primary focus is wear resistance in a dynamic seal or bearing: A glass, carbon, or bronze-filled PTFE is the superior option.
- If your primary focus is dimensional stability under load: A filled PTFE is necessary to prevent creep and maintain tolerances.
- If your primary focus is dissipating static electricity: Carbon-filled PTFE is specifically designed for this purpose.
Ultimately, choosing a filled PTFE is about strategically enhancing its mechanical capabilities for a specific demanding role.
Summary Table:
| Property | Virgin PTFE | Filled PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Wear Resistance | Low | High |
| Creep Resistance | Low | High |
| Compressive Strength | Low | High |
| Chemical Inertness | Excellent | Compromised |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent | Compromised |
| Coefficient of Friction | Extremely Low | Increased |
Need a custom PTFE component optimized for your specific application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in precision manufacturing of both virgin and filled PTFE components. Whether your priority is ultimate chemical purity, superior wear resistance, or dimensional stability, our experts can help you select the right material and fabricate the perfect part—from prototypes to high-volume production.
Contact our engineering team today to discuss your project requirements and get a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What are the primary applications of PTFE fasteners and custom parts? Critical Solutions for Extreme Environments
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance



















