At its core, a Teflon encapsulated silicone o-ring is a hybrid seal. It is constructed from two distinct materials: a flexible inner core made of silicone, which is then completely enclosed within a seamless, protective outer layer of Teflon FEP (Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene) or PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene).
This composite design strategically combines the superior elasticity and memory of a silicone core with the exceptional chemical inertness and low-friction properties of a Teflon shell, creating a single seal that outperforms what either material could achieve alone.
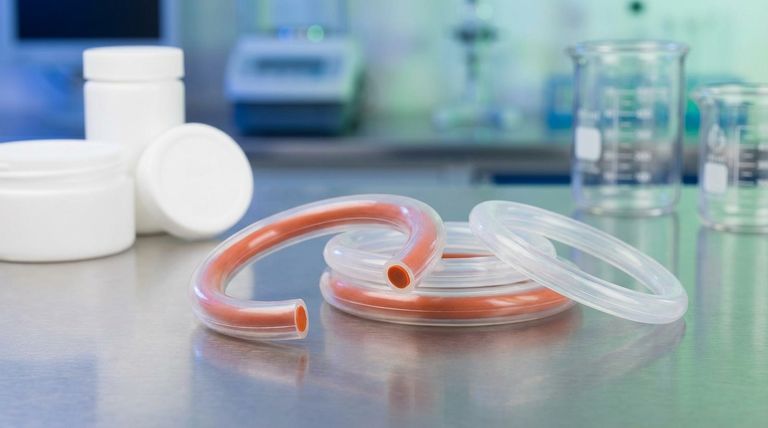
The Anatomy of a High-Performance Seal
To understand the value of an encapsulated o-ring, it's essential to understand the specific role each component plays in its function.
The Elastic Core: Silicone's Role
The inner silicone core provides the o-ring's "springiness." This property, known as compression set resistance, allows the seal to conform to surface imperfections and maintain consistent pressure even after being compressed for long periods.
Without this elastic core, the seal would not be able to effectively prevent leaks under varying pressures and temperatures.
The Protective Shell: Teflon's Contribution
The seamless Teflon (PTFE/FEP) outer layer is the component that directly contacts the system's chemicals and moving parts. Its primary job is to act as a durable, inert barrier.
This shell provides three critical benefits: extreme chemical resistance, a very low coefficient of friction to reduce wear, and a wide operational temperature range, typically from -40°F to 400°F (-40°C to 205°C).
The Seamless Advantage
The fact that the encapsulation is seamless is a critical design feature. A seam would create a weak point where aggressive chemicals could penetrate and degrade the vulnerable silicone core.
This uniform, uninterrupted jacket ensures the integrity of the seal is maintained across its entire surface.
Understanding the Key Benefits
The hybrid construction results in a unique set of advantages that make these seals ideal for demanding industrial and scientific applications.
Superior Chemical Resistance
The Teflon shell effectively isolates the silicone core from aggressive chemicals, solvents, and other media that would cause a standard silicone o-ring to swell, degrade, or fail.
Reduced Wear and Contamination
The smooth, low-friction surface of Teflon minimizes drag and abrasion in dynamic sealing applications. This reduces particulate generation, making these o-rings suitable for high-purity environments.
Unmatched Durability
By protecting the core from both chemical attack and physical wear, the encapsulation significantly extends the life of the seal. This design also gives the o-ring a virtually unlimited shelf life.
How to Apply This to Your Application
Choosing the right seal requires matching its properties to your specific operational demands.
- If your primary focus is aggressive chemical environments: The Teflon shell provides the robust protection necessary for applications where standard elastomers would quickly fail.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction in dynamic systems: The low-friction surface is ideal for rotating or reciprocating parts where minimizing drag and wear is critical.
- If your primary focus is sealing across a wide temperature range: This composite design maintains its integrity in both low and high-temperature conditions where other materials become brittle or deform.
This engineered combination of materials creates a solution for the most challenging sealing applications.
Summary Table:
| Component | Material | Key Function |
|---|---|---|
| Inner Core | Silicone | Provides elasticity and compression set resistance |
| Outer Shell | Teflon (PTFE/FEP) | Offers chemical inertness, low friction, and a wide temperature range |
Facing a challenging sealing application? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including custom encapsulated o-rings. We combine precision production with expert material science to create seals that withstand aggressive chemicals, extreme temperatures, and dynamic motion. Let us engineer a solution for your semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial needs—from prototype to high-volume production. Contact our experts today to discuss your requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key differences between monoaxial and multidirectional expanded PTFE? Choose the Right ePTFE for Your Seal
- What are the automotive applications of Teflon sheets? Enhance Efficiency, Reliability & Durability
- What are the advantages of using PTFE guide strips in industrial applications? Enhance Equipment Life & Efficiency
- What are PTFE O-rings? High-Performance Seals for Extreme Conditions
- How does the self-lubricating property of PTFE rotary shaft seals benefit industrial applications? Achieve Maintenance-Free, High-Performance Sealing
- Why are Teflon bellow mechanical seals suitable for pulp and paper manufacturing?
- What makes PTFE seals suitable for food and pharmaceutical applications? Ensure Purity and Compliance
- What industrial applications utilize extruded PTFE rods? Key Uses in Chemical, Aerospace & More



















