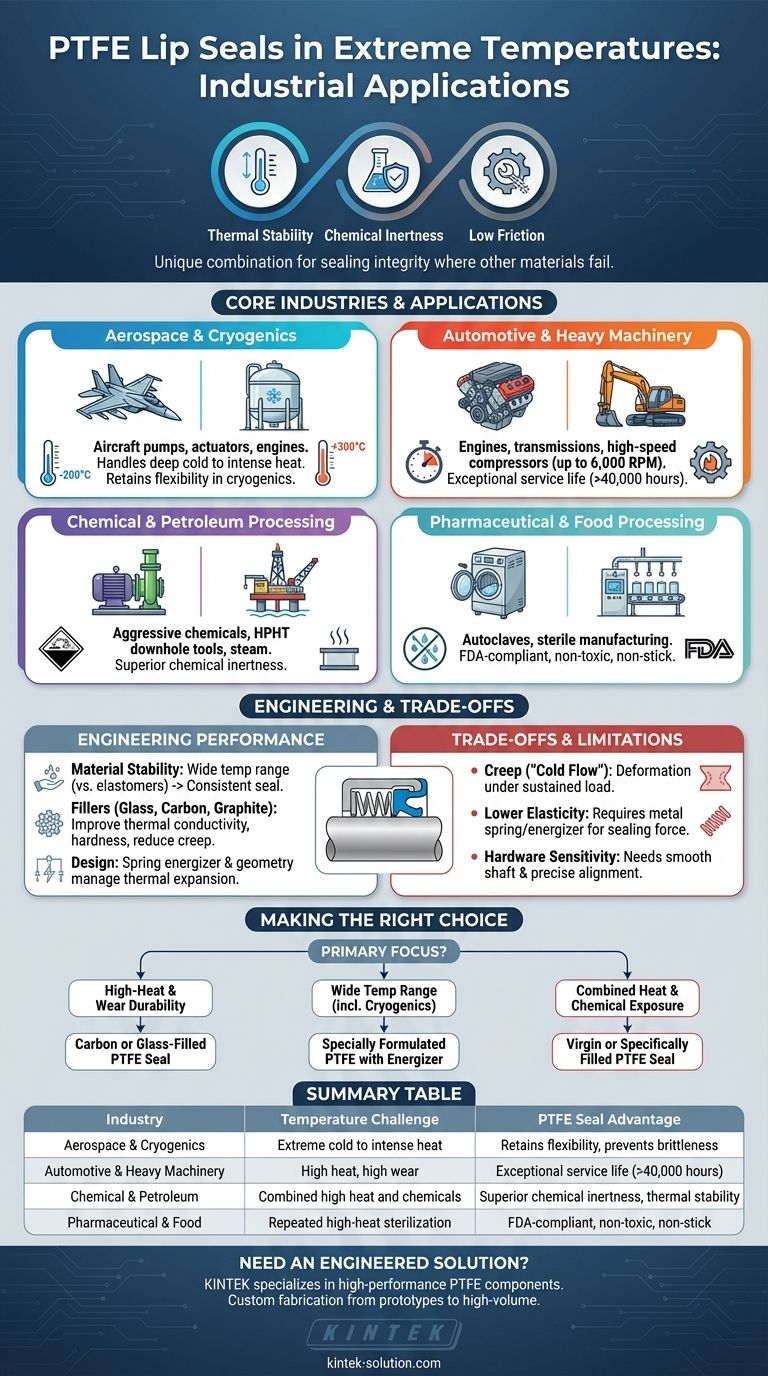
In extreme temperature environments, PTFE lip seals are used extensively in industries like aerospace, cryogenics, chemical processing, and automotive manufacturing. Their application ranges from high-speed compressors and engine components to pumps handling sub-zero fluids, succeeding where traditional elastomer seals would quickly degrade and fail.
The true value of PTFE seals in extreme temperatures is not just their ability to withstand heat or cold. It is their unique combination of thermal stability, chemical inertness, and low friction that allows them to maintain sealing integrity under conditions that cause other materials to become brittle, decompose, or seize.

Core Industries and High-Demand Applications
PTFE lip seals are engineered solutions for machinery operating outside the temperature range of conventional materials. Their reliability is critical in processes where seal failure would be catastrophic.
Aerospace and Cryogenics
In aerospace, components must function reliably across an enormous temperature spectrum, from the deep cold of high altitude to the intense heat of engine systems.
PTFE seals are used in aircraft pumps, hydraulic actuators, engines, and brakes. They are essential in cryogenic applications for handling liquefied gases where temperatures can plummet, as they retain a degree of flexibility when other materials become completely brittle.
Automotive and Heavy Machinery
High-heat and high-wear environments are standard in engines, transmissions, and industrial compressors.
PTFE seals provide exceptional service life, with documented performance of over 40,000 hours in air compressors. They are used in rotary screw compressors operating at high speeds (up to 6,000 RPM) and in construction machinery like excavators and loaders where durability is paramount.
Chemical and Petroleum Processing
This sector combines extreme temperatures with aggressive chemicals, creating a uniquely harsh environment.
PTFE seals are a default choice for chemical pumps, mixers, and blowers. In the oil and gas industry, they are critical for high-pressure, high-temperature (HPHT) downhole tools and subsea equipment, as well as in steam applications where temperatures often exceed 200°F (93°C).
Pharmaceutical and Food Processing
Sterilization processes, such as in autoclaves, subject equipment to repeated cycles of high heat and pressure.
PTFE seals are used here due to their thermal resistance and the fact that they can be formulated with FDA-compliant materials. Their non-stick and non-toxic properties are essential for preventing contamination in sterile manufacturing environments.
The Engineering Behind Thermal Performance
The success of PTFE seals in extreme temperatures is a result of both inherent material properties and sophisticated engineering design.
The Advantage of Material Stability
Unlike elastomers that break down or harden, PTFE maintains its fundamental properties—most notably low friction and chemical resistance—over a very wide temperature range. This stability prevents seizure and chemical degradation, ensuring a consistent seal.
Enhancing Performance with Fillers
Base PTFE is often blended with fillers to optimize it for specific thermal challenges.
Materials like glass, carbon, and graphite are added to the PTFE matrix. These fillers significantly improve thermal conductivity, increase hardness, and reduce creep (the tendency to deform under sustained stress), which is crucial for stability at high temperatures.
Critical Design Considerations
The physical geometry of the seal is as important as its material composition. An effective design must accommodate the physical changes that occur during temperature swings.
The seal's shape must distribute stress evenly and manage thermal expansion and contraction without losing contact with the shaft. Key factors like the lip contact area, spring energizer force, and sealing angle are precisely engineered to maintain a reliable seal across the entire operating temperature range.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly effective, PTFE seals are not a universal solution. Understanding their limitations is key to successful implementation.
The Challenge of Creep
Even with fillers, PTFE is more susceptible to creep (or "cold flow") than metals. Under sustained high pressure and temperature, the seal material can slowly deform, potentially leading to a loss of sealing force over time.
Lower Elasticity vs. Elastomers
PTFE is a polymer, but it is not an elastomer. It lacks the "bounciness" of rubber. This means PTFE seals almost always require a metal spring or energizer to provide the constant force needed for effective sealing, especially at low temperatures.
Sensitivity to Hardware Condition
Their lower elasticity also makes PTFE seals less forgiving of shaft imperfections, misalignment, or runout compared to more compliant rubber seals. Achieving a reliable, long-lasting seal requires careful attention to the entire system, including shaft hardness and surface finish.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct sealing technology requires matching the material and design to the specific operational challenge.
- If your primary focus is high-heat and high-wear durability: A carbon or glass-filled PTFE seal is engineered to resist thermal degradation and creep in applications like industrial compressors and engines.
- If your primary focus is a wide temperature range, including cryogenics: A specially formulated PTFE with an appropriate energizer is required to maintain flexibility at sub-zero temperatures and stability at high temperatures, common in aerospace.
- If your primary focus is combined heat and chemical exposure: A virgin or specifically filled PTFE seal provides the chemical inertness needed to survive in chemical pumps, mixers, and petroleum processing equipment.
Ultimately, choosing the right seal comes from understanding that performance is a function of the entire system, not just a single component.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Application | Temperature Challenge | PTFE Seal Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace & Cryogenics | Aircraft pumps, hydraulic actuators, cryogenic fluid handling | Extreme cold to intense engine heat | Retains flexibility, prevents brittleness |
| Automotive & Heavy Machinery | Engines, transmissions, compressors (up to 6,000 RPM) | High heat, high wear | Exceptional service life (>40,000 hours) |
| Chemical & Petroleum Processing | Chemical pumps, HPHT downhole tools, steam applications | Combined high heat and aggressive chemicals | Superior chemical inertness and thermal stability |
| Pharmaceutical & Food Processing | Autoclaves, sterile manufacturing equipment | Repeated high-heat sterilization cycles | FDA-compliant, non-toxic, non-stick properties |
Need a PTFE Seal Engineered for Your Extreme Environment?
PTFE lip seals are critical for reliability in applications where temperature extremes cause traditional seals to fail. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We prioritize precision production and offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders to meet your exact specifications. Let our expertise ensure your equipment operates reliably, even in the most demanding conditions.
Contact KINTEB today to discuss your specific requirements and get a solution tailored to your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- Why is dimensional stability a concern when machining PTFE? Ensure Accurate, Stable PTFE Components
- When and by whom was PTFE discovered? A Tale of Accidental Innovation
- How is PTFE used in industrial processes? Maximize Safety and Efficiency
- What are some applications of CNC machined PTFE parts? Critical Components for Medical, Electrical & Food Industries



















