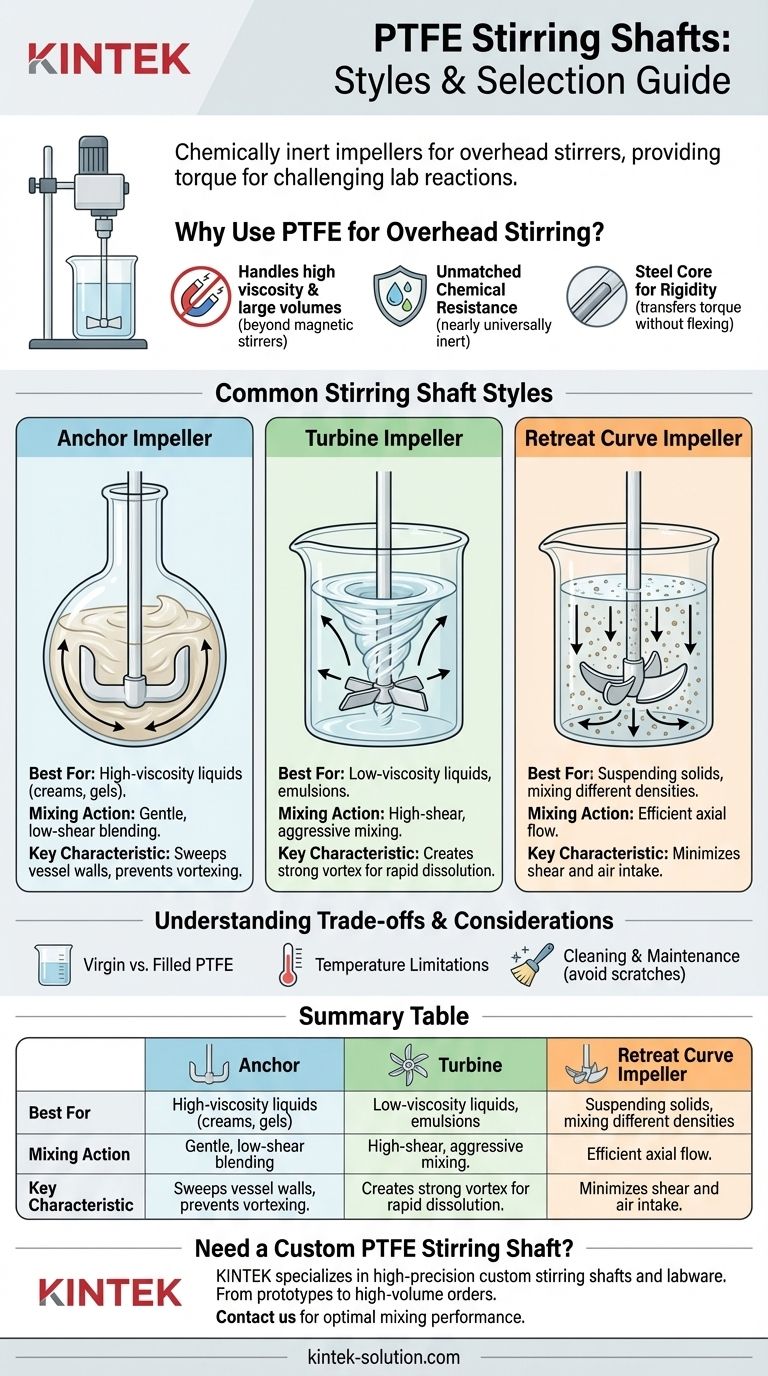
PTFE stirring shafts are chemically inert impellers designed for use with overhead stirrers in laboratory reactions. Unlike simple magnetic stir bars, these shafts connect directly to a motor, providing the torque needed for mixing challenging solutions. The most common styles include the anchor, turbine, and retreat curve designs, each engineered for a specific type of fluid movement.
The core decision in selecting a PTFE stirring shaft comes down to the viscosity of your medium and the type of mixing required. The impeller's shape—whether it's an anchor, turbine, or retreat curve—directly dictates how it transfers energy to the fluid, enabling everything from gentle blending to high-shear mixing.

Why Use PTFE for Overhead Stirring?
Before choosing a style, it's critical to understand why this combination of material and method is so prevalent in chemical synthesis and lab work. The choice is a direct solution to the limits of other common techniques.
The Limits of Magnetic Stirring
Magnetic stir bars are simple and effective for low-viscosity liquids in smaller vessels. However, they lack the power to mix viscous materials, large volumes, or reactions where solids need to be kept in suspension. Overhead stirrers provide the necessary mechanical torque to handle these demanding applications.
The Unmatched Chemical Resistance of PTFE
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is nearly universally inert. It resists attack from virtually all chemicals, solvents, acids, and bases, ensuring that the stirrer itself does not react with or contaminate the experiment. This makes it a superior choice over glass or metal shafts in reactive environments.
The Importance of a Steel Core
While the wetted parts are PTFE, most high-quality shafts feature a steel core. This provides the rigidity needed to transfer torque from the motor to the fluid without the shaft flexing or breaking, especially at high speeds or in thick media.
A Guide to Common Stirring Shaft Styles
Each impeller design creates a different flow pattern. Matching the design to your goal is crucial for an effective and reproducible reaction.
The Anchor Impeller: For Gentle, Low-Shear Mixing
The anchor style features blades that conform to the shape of the reaction vessel. It's designed to sweep the entire bottom and sides of the flask.
This design excels at mixing high-viscosity liquids like creams, gels, or polymers. It provides gentle, uniform blending without incorporating air or creating a vortex, which is often undesirable.
The Turbine Impeller: For High-Shear, Aggressive Mixing
A turbine impeller has multiple angled blades that spin at high speeds to create a strong vortex. This design is highly effective for generating radial flow, moving liquid from the center outward.
This aggressive, high-shear mixing is ideal for low-viscosity liquids, creating emulsions, dissolving solids quickly, or dispersing gases into a liquid.
The Retreat Curve Impeller: For Efficient Axial Flow
This design features curved blades that are swept back from the direction of rotation. It is one of the most efficient designs for generating axial flow—pulling material down from the surface and pushing it out across the vessel floor.
The retreat curve is excellent for suspending solids or mixing liquids of different densities while minimizing shear and air intake. It provides powerful mixing without the deep vortex created by a turbine.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While PTFE is a superior material for many applications, it's important to be aware of its limitations and the associated considerations.
Material Purity and Formulation
PTFE is available in several grades. Virgin (unfilled) PTFE is standard for its purity and chemical resistance. Other formulations, such as glass-filled PTFE, can offer increased rigidity and wear resistance but may not be suitable for all chemical environments.
Temperature Limitations
While PTFE has a wide operating temperature range, it is fundamentally a polymer. It cannot be used in the extremely high-temperature applications where a specialized metal or glass stirrer might be required.
Cleaning and Maintenance
PTFE's non-stick surface simplifies cleaning, but its relative softness means it can be scratched by abrasive cleaning methods. Scratches can create crevices where material can become trapped, potentially causing cross-contamination between reactions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Reaction
Selecting the correct impeller is key to controlling your reaction environment. Base your decision on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is blending high-viscosity liquids or creams: Choose an anchor-style impeller for its gentle, low-shear mixing and ability to scrape the vessel walls.
- If your primary focus is creating an emulsion or rapidly dissolving solids: Choose a turbine-style impeller for its high-shear, aggressive mixing that creates a powerful vortex.
- If your primary focus is keeping solids suspended with minimal vortexing: Choose a retreat curve impeller for its highly efficient axial flow that ensures excellent top-to-bottom turnover.
Ultimately, selecting the proper stirring shaft transforms your overhead stirrer from a simple motor into a precise tool for achieving successful and repeatable results.
Summary Table:
| Stirring Shaft Style | Best For | Mixing Action | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anchor Impeller | High-viscosity liquids (creams, gels) | Gentle, low-shear blending | Sweeps vessel walls, prevents vortexing |
| Turbine Impeller | Low-viscosity liquids, emulsions | High-shear, aggressive mixing | Creates strong vortex for rapid dissolution |
| Retreat Curve Impeller | Suspending solids, mixing different densities | Efficient axial flow | Minimizes shear and air intake |
Need a Custom PTFE Stirring Shaft for Your Application?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including custom stirring shafts and labware for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you need a standard style or a custom-fabricated impeller for a unique reaction vessel, our team can deliver from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and ensure optimal mixing performance for your critical processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer PTFE Magnetic Stirring Bar
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What other PTFE lab accessories are commonly used? Essential Tools for Chemical Resistance & Purity
- What are some specific applications of PTFE shovels in the laboratory? Ensure Sample Purity and Safety
- How does the durability of PTFE shovels compare to plastic shovels? Discover the Superior Choice for Harsh Conditions
- What are PTFE silicone septa and what are they composed of? The Key to Reliable Chromatography Seals
- What are the best practices for using PTFE syringe filters? Achieve Pure, Reliable Filtration
- What are PTFE ferromagnetic support discs composed of? A Dual-Material Design for Superior Grinding & Polishing
- What are the chemical compatibility properties of PTFE-lined bottle caps? Ensure Maximum Safety and Purity
- How does the hydrophobicity of PTFE filters benefit their use? Ensure Uninterrupted Gas Flow and Solvent Filtration



















