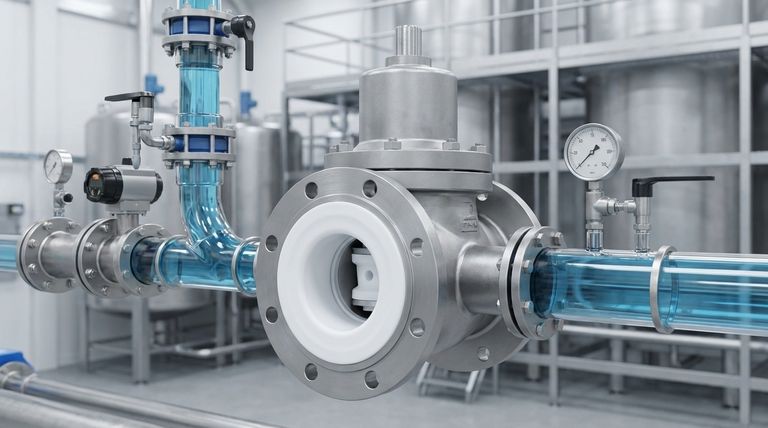
At its core, a PTFE-lined plug valve is a specialized control valve designed for demanding industrial applications. It consists of a standard metal valve body that houses a rotating plug, where all surfaces that come into contact with the fluid are completely lined with a layer of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). Its primary purpose is to provide precise flow control or isolation for highly corrosive or high-purity fluids that would quickly destroy a standard metal valve.
The central challenge in handling aggressive media is not just flow control, but material survival. PTFE-lined valves solve this by combining the mechanical strength of a metal body with the near-total chemical inertness of a PTFE liner, creating a cost-effective and highly reliable solution for corrosive environments.

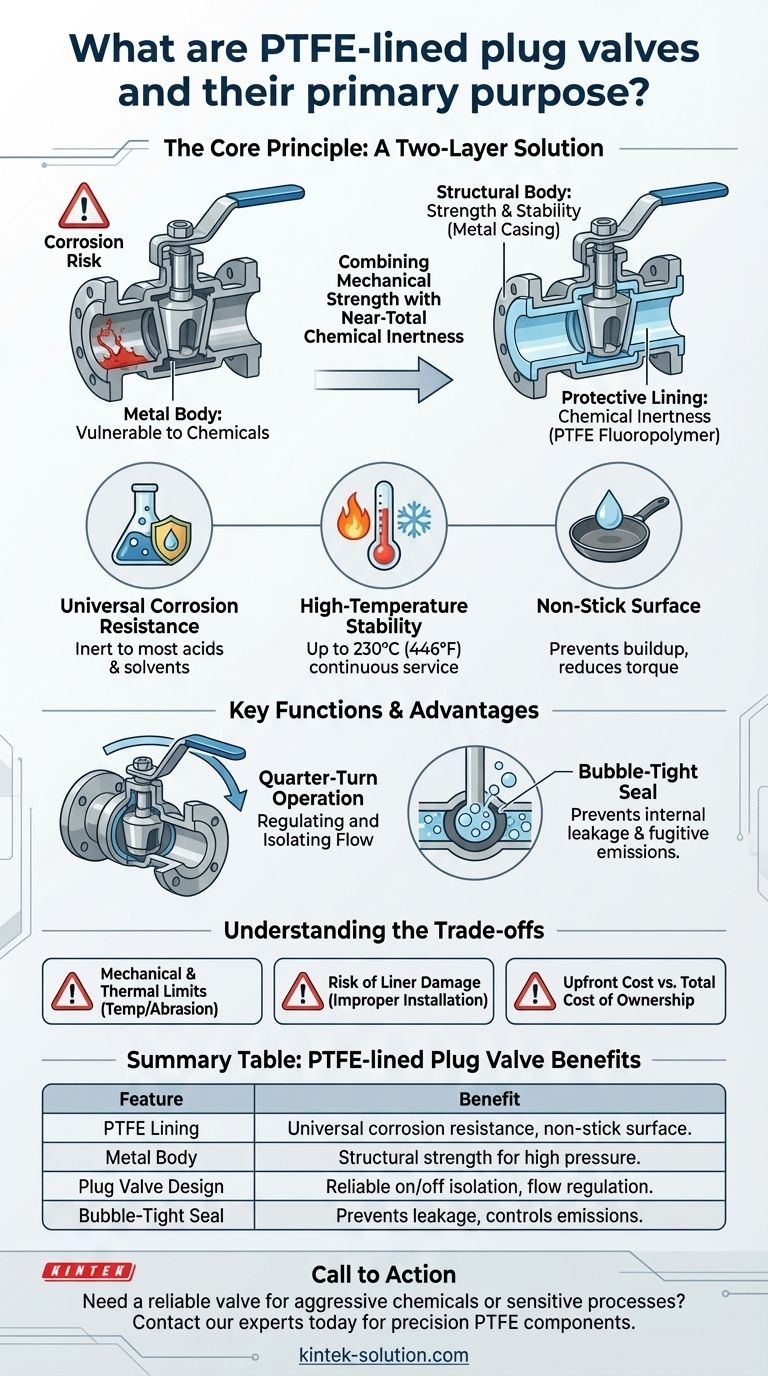
The Core Principle: A Two-Layer Solution
To understand the value of a PTFE-lined plug valve, you must first understand its fundamental design philosophy. It is not a single material, but a composite system designed to leverage the best properties of two different materials.
The Structural Body: Strength and Stability
The outer body of the valve is made from robust metals like ductile iron or stainless steel. This metal casing provides the mechanical strength required to handle high pipeline pressures, absorb operational stress, and connect securely to the surrounding piping.
The metal body alone is vulnerable to chemical attack.
The Protective Lining: Chemical Inertness
The internal surfaces of the valve body and the entire surface of the plug are lined with a thick, seamless layer of PTFE. This fluoropolymer acts as an impenetrable barrier, completely isolating the metal structure from the process fluid.
PTFE is chosen for its exceptional properties:
- Universal Corrosion Resistance: It is inert to nearly all industrial chemicals, acids, and solvents.
- High-Temperature Stability: It maintains its integrity in continuous service at temperatures up to 230°C (446°F).
- Non-Stick Surface: Its low-friction, non-stick nature prevents material buildup, reduces the torque needed for operation, and makes it ideal for high-purity applications where contamination is a concern.
Key Functions and Advantages
While the lining provides protection, the plug valve mechanism provides the function. This combination delivers specific operational benefits.
Regulating and Isolating Flow
The valve is operated by a stem that rotates the tapered plug. A quarter-turn can move the valve from fully open to fully closed, providing reliable on/off isolation. The design also allows for partial rotation, enabling throttling and regulation of the flow rate.
Ensuring a Bubble-Tight Seal
The design creates a large sealing surface area between the PTFE-lined plug and body. This, combined with the slight malleability of PTFE, ensures a tight shutoff that prevents internal leakage.
Crucially, this design also excels at preventing fugitive emissions—leaks from the valve stem into the atmosphere. This is a critical safety and environmental consideration when handling hazardous chemicals.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No technology is a universal solution. An objective evaluation requires acknowledging the limitations.
Mechanical and Thermal Limits
While highly resistant, PTFE has its limits. Applications involving extreme temperatures beyond its rating or the presence of highly abrasive solids (slurries) can potentially damage the liner over time. The structural integrity is still defined by the metal body's pressure rating.
Risk of Liner Damage
The integrity of the valve depends entirely on the integrity of the liner. Improper installation, excessive pipe strain, or mechanical impact can create a tear or scratch in the PTFE, exposing the metal body to the corrosive media and leading to rapid failure.
Upfront Cost vs. Total Cost of Ownership
PTFE-lined valves typically have a higher initial purchase price than standard metal or simple plastic valves. However, their exceptional durability and low maintenance needs in corrosive service often result in a lower total cost of ownership over the valve's lifespan by minimizing downtime and replacement costs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct valve requires matching the technology to your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is safety and handling hazardous chemicals: The key benefit is superior corrosion resistance and bubble-tight sealing, which prevents dangerous leaks and fugitive emissions.
- If your primary focus is maintaining media purity (e.g., pharma, food): The inert, non-leaching, and non-stick properties of the PTFE liner ensure your product is not contaminated by the valve itself.
- If your primary focus is reducing long-term operational costs: This valve is a long-term investment in reliability, offering an extended lifespan and minimal maintenance requirements in services that would destroy lesser valves.
Ultimately, choosing a PTFE-lined plug valve is a strategic decision to ensure safety, purity, and long-term reliability in your most demanding fluid-handling applications.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| PTFE Lining | Universal corrosion resistance and non-stick, high-purity surface. |
| Metal Body | Provides structural strength to handle high pipeline pressures. |
| Plug Valve Design | Quarter-turn operation for reliable on/off isolation and flow regulation. |
| Bubble-Tight Seal | Prevents internal leakage and controls fugitive emissions. |
Need a reliable valve for aggressive chemicals or sensitive processes?
At KINTEK, we specialize in precision PTFE components, including custom-fabricated seals, liners, and labware for the semiconductor, medical, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures your valves and systems deliver maximum safety, purity, and longevity.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and receive a tailored solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE widely used in the automotive industry? Solve Heat, Friction, and Chemical Challenges
- How are extruded PTFE rods manufactured? A Look at the Unique Paste Extrusion & Sintering Process
- What are the key advantages of PTFE O-rings? Superior Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- How does the temperature resistance of PTFE O-rings compare to other materials? Superior Performance from -250°C to +260°C
- How do different glass weave styles affect phase response in RF PCBs? Ensure Phase Coherence for High-Frequency Designs
- What recent advancements have been made in PTFE expansion joint technology? Enhance Durability & Precision
- How should thin-wall PTFE components be clamped during machining? Prevent Deformation with the Right Fixtures
- What happens when clearance develops in a PTFE-lined bearing? A Guide to Catastrophic Failure



















