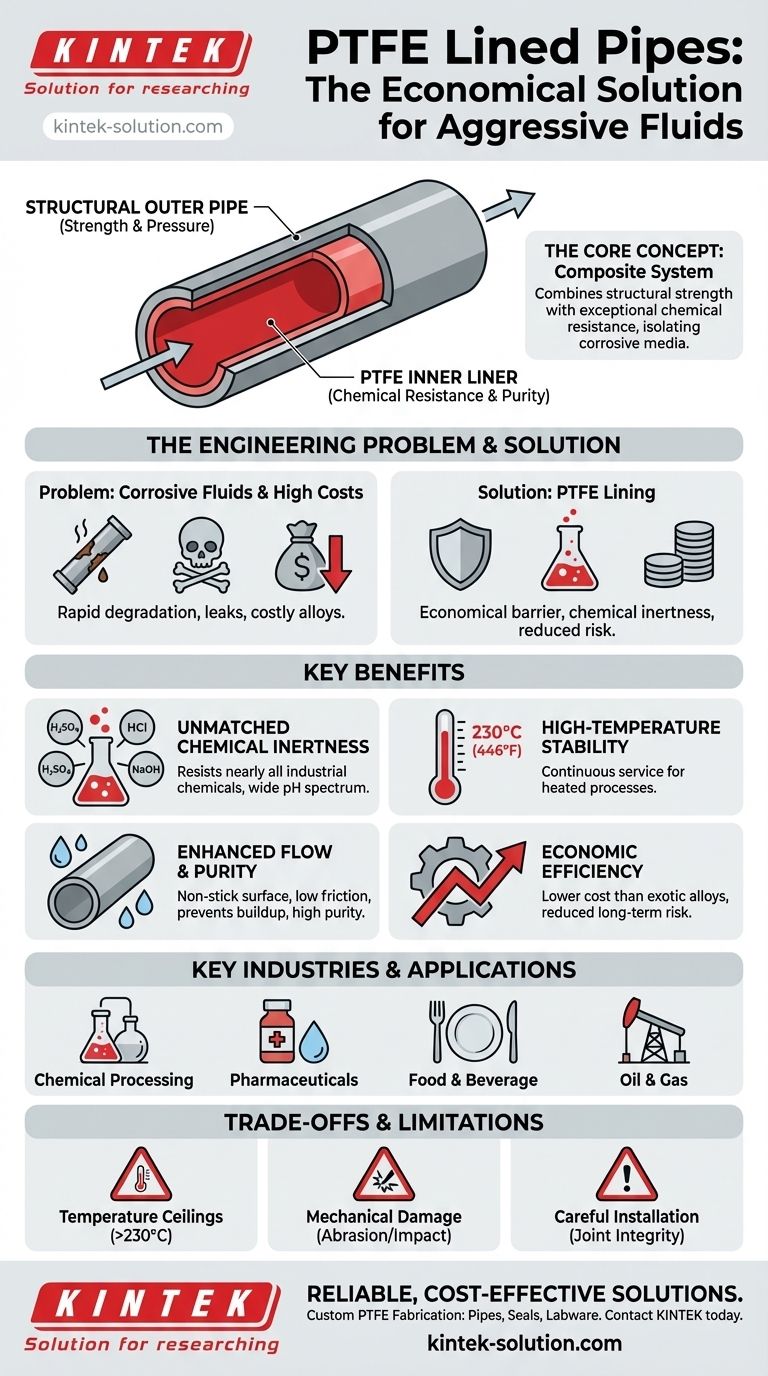
At its core, a PTFE lined pipe is a composite system consisting of a standard structural pipe (often carbon steel or stainless steel) with a Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) liner fused to its interior. This design combines the structural strength and affordability of the outer pipe with the exceptional chemical resistance of the inner liner, making it a premier choice for safely transporting highly corrosive or high-purity fluids that would otherwise require expensive exotic alloys.
The central value of PTFE lined pipe is not just corrosion resistance, but economic efficiency. It allows engineers to use robust, cost-effective structural materials for aggressive chemical applications by isolating the corrosive media with a chemically inert liner, dramatically reducing both initial investment and long-term operational risk.

The Engineering Problem: Safely Transporting Aggressive Fluids
Before understanding the solution, it's critical to appreciate the problem. Transporting fluids that are highly acidic, caustic, or ultra-pure presents a significant engineering challenge.
The High Cost of Corrosion
Using standard metal pipes for corrosive chemicals leads to rapid degradation. This results in costly leaks, process contamination, unscheduled downtime for replacement, and significant safety hazards from exposure to dangerous substances.
The Limitation of Specialty Alloys
The traditional solution is to build entire piping systems from exotic alloys like Hastelloy or titanium. While effective, these materials are prohibitively expensive, driving up project costs immensely.
How PTFE Lining Delivers a Superior Solution
PTFE lined pipe offers a more practical and economical alternative by separating the functions of structural support and chemical resistance.
The Protective Barrier Principle
The outer pipe, typically carbon steel, provides the necessary mechanical strength to handle system pressure and external loads. The inner PTFE liner acts as a seamless, non-reactive barrier, completely shielding the structural pipe from the process fluid.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is famously inert and non-reactive with nearly all industrial chemicals and solvents. It can handle a vast range of acids, bases, and organic compounds across a wide pH spectrum. The only notable exceptions are molten alkali metals and highly reactive fluorine compounds.
High-Temperature Stability
PTFE maintains its integrity and chemical resistance at continuous service temperatures up to 230°C (446°F). This makes it suitable for a wide variety of heated chemical processes where other polymers would fail.
Enhanced Flow and Purity
PTFE has an extremely low coefficient of friction—it is a non-stick surface. This minimizes internal friction, reducing the energy needed to pump fluids. It also prevents material buildup, ensuring smooth flow and making it ideal for high-purity applications in the pharmaceutical and food industries where contamination is not an option.
Key Industries and Applications
The unique properties of PTFE lined pipes make them indispensable in several critical sectors:
- Chemical Processing: The default choice for transferring aggressive chemicals like sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, and sodium hydroxide.
- Pharmaceuticals: Used for high-purity water (WFI) systems and transporting sensitive active ingredients where preventing leaching and contamination is paramount.
- Food & Beverage: Ensures product purity and provides a smooth, easily cleanable surface for processing a variety of foodstuffs.
- Oil & Gas: Handles corrosive chemicals used in extraction and processing, preventing equipment failure in harsh environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly effective, PTFE lined systems are not a universal solution. An objective assessment requires acknowledging their limitations.
Temperature Ceilings
While a 230°C limit is high, some specialized chemical processes operate at even higher temperatures. In these cases, a solid metal alloy pipe may still be necessary.
Susceptibility to Mechanical Damage
The PTFE liner, while tough, is softer than metal. It can be damaged by severe abrasive slurries or by improper handling during installation. Care must be taken to prevent scoring or scratching the liner.
Careful Installation Required
The integrity of a lined piping system depends heavily on proper joint assembly. Flange connections must be carefully torqued to ensure a perfect seal without crushing or damaging the flared PTFE sealing face.
Permeation in Specific Cases
For certain small-molecule gases at high temperatures, microscopic permeation through the PTFE liner can occur over time. While not an issue for most liquid applications, this is a design consideration for highly specific, high-pressure gas services.
Making the Right Choice for Your System
Selecting the right piping material depends on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is broad chemical resistance: PTFE lined pipe is the industry benchmark, offering near-universal compatibility at a fraction of the cost of rare metal alloys.
- If your primary focus is product purity: The non-leaching and non-stick properties of PTFE make it an ideal choice for pharmaceutical, semiconductor, or food-grade applications.
- If your primary focus is long-term reliability and safety: The durability of PTFE lining drastically reduces the risk of catastrophic failure, protecting your personnel, environment, and bottom line.
By understanding these principles, you can confidently specify a piping system that is safe, reliable, and economically sound for its intended service life.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists nearly all acids, bases, and solvents | Not suitable for molten alkali metals or fluorine compounds |
| High-Temperature Stability | Continuous service up to 230°C (446°F) | May not suffice for processes above this temperature |
| Low Friction / Non-Stick | Improves flow, reduces energy use, prevents buildup | Liner can be damaged by severe abrasive slurries |
| Economic Efficiency | Lower cost than exotic metal alloys like Hastelloy | Requires careful installation to ensure joint integrity |
Need a reliable, cost-effective solution for your corrosive fluid handling?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including custom-lined pipes, seals, liners, and labware. Whether you're in the semiconductor, pharmaceutical, laboratory, industrial, or other specialized sectors, our expertise ensures your system is safe, pure, and reliable.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, tailored to your specific chemical and mechanical requirements.
Contact us today to discuss how our PTFE solutions can protect your process and your bottom line.
Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are some industrial applications of PTFE seals? Solve Your Toughest Sealing Challenges
- How resistant are Teflon encapsulated O-rings to compression set? Achieve Long-Term Sealing Reliability
- How do PTFE envelope gaskets address the limitations of pure PTFE gaskets? Enhance Sealing Performance
- What are the diameter tolerances for PTFE balls? A Guide to Precision vs. Standard Grades
- What are the benefits of using Teflon encapsulated silicone o-rings? Achieve Unmatched Sealing in Harsh Environments
- What are the advantages of PTFE liners in medical catheter applications? Enhance Performance & Patient Safety
- What key offerings are associated with Teflon-encapsulated O-Rings? Beyond the Part to Full-System Support
- In which industries or applications are Teflon (PTFE) balls commonly used? Essential for Harsh Environments



















