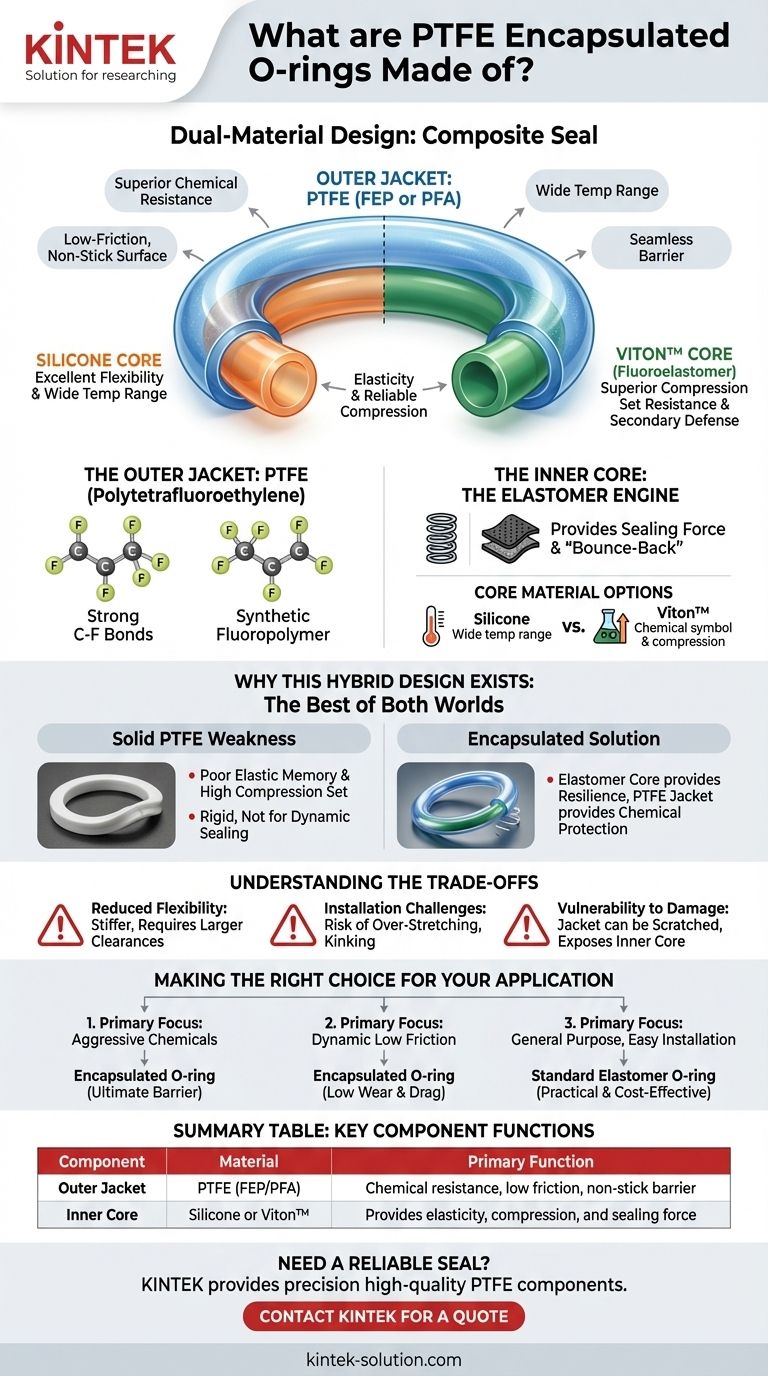
At its core, a PTFE encapsulated O-ring is a composite seal made of two distinct materials working in concert. It consists of a tough, seamless outer jacket of PTFE (specifically FEP or PFA) that completely encloses a flexible, energized inner core made of either silicone or Viton™ (a fluoroelastomer).
This dual-material design strategically combines the superior chemical resistance and low-friction properties of PTFE with the elasticity and reliable compression of a rubber elastomer core.
The Two-Component Anatomy
To understand the performance of an encapsulated O-ring, you must understand its two fundamental parts: the outer jacket that faces the process environment and the inner core that provides the sealing force.
The Outer Jacket: PTFE (FEP/PFA)
The protective outer shell is made from a synthetic fluoropolymer known as Polytetrafluoroethylene, or PTFE.
This material is composed entirely of carbon and fluorine atoms. The exceptionally strong bonds between these atoms give PTFE its signature properties: extreme chemical resistance and a wide operating temperature range.
This PTFE jacket serves as the primary barrier, providing a low-friction, non-stick surface that is virtually impervious to most chemicals.
The Inner Core: The Elastomer Engine
The inner core is the engine of the seal, providing the physical force and flexibility required to maintain a tight seal.
This core is made from a standard elastomer—a rubber-like material. It provides the "bounce-back" or compression set resistance that a solid PTFE ring lacks.
Core Material Options: Silicone vs. Viton™
The two most common core materials are silicone and Viton™.
Silicone offers a wider temperature range and better flexibility, while Viton™ provides superior compression set resistance and better chemical compatibility with certain media, acting as a reliable secondary defense if the jacket is compromised.
Why This Hybrid Design Exists
The encapsulated O-ring was engineered to solve a specific problem: leveraging the benefits of PTFE without its significant drawbacks in sealing applications.
The Strength of PTFE
PTFE is one of the most chemically inert materials available, making it ideal for aggressive chemical and high-purity applications where a standard elastomer would quickly degrade.
The Weakness of Solid PTFE
However, solid PTFE is a relatively rigid material. It suffers from poor elastic memory and high compression set, meaning it does not spring back to its original shape effectively after being compressed. This makes it a poor choice for most dynamic sealing needs.
The Best of Both Worlds
The encapsulated design solves this perfectly. The elastomer core provides the constant, resilient sealing force, while the seamless PTFE jacket provides the chemical protection and low-friction surface.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, this composite design is not a universal solution. It comes with specific limitations you must consider.
Reduced Flexibility
The PTFE jacket is stiffer than a standard rubber O-ring. This makes encapsulated rings less forgiving and requires them to be fitted into glands designed with slightly larger clearances.
Installation Challenges
This inherent stiffness can make installation more difficult, especially with smaller diameter rings. Care must be taken to avoid over-stretching or kinking the ring, which can permanently damage it.
Vulnerability to Damage
The PTFE jacket, while durable, can be scratched or nicked during installation. Any breach in the jacket creates a direct leak path and exposes the vulnerable inner core to the process media, leading to premature failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct seal requires matching its properties to your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is sealing against aggressive chemicals: The encapsulated O-ring provides the ultimate chemical barrier that standard elastomers cannot match.
- If your primary focus is a dynamic application requiring low friction: The PTFE surface offers significantly lower friction than any standard elastomer, reducing wear and drag.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose sealing with easy installation: A standard, single-material elastomer O-ring (like Viton™ or EPDM) is often a more practical and cost-effective choice.
This engineered composite seal solves a critical challenge by delivering performance characteristics that no single material can offer alone.
Summary Table:
| Component | Material | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Outer Jacket | PTFE (FEP/PFA) | Chemical resistance, low friction, non-stick barrier |
| Inner Core | Silicone or Viton™ | Provides elasticity, compression, and sealing force |
Need a Reliable Seal for Demanding Applications?
PTFE encapsulated O-rings are engineered for superior performance in aggressive environments. KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of high-quality PTFE components, including custom encapsulated O-rings, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We deliver the chemical resistance and low friction you need, with the sealing reliability you depend on.
Let us provide the perfect sealing solution for your project—from prototype to high-volume production.
Contact KINTEK today for a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What makes PTFE stand out among materials used in sealing technology? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What is the overall operating temperature range for PTFE seals, gaskets, and O-rings? Achieve Sealing Integrity from -200°C to +260°C
- What are the key properties of PTFE that make it suitable for sealing applications? | High-Performance Seals for Extreme Conditions
- What are the benefits of using PTFE seals in demanding industries? Solve Extreme Sealing Challenges
- What are the benefits of PTFE seals in terms of prototyping and production? Accelerate R&D and Ensure Elite Performance



















