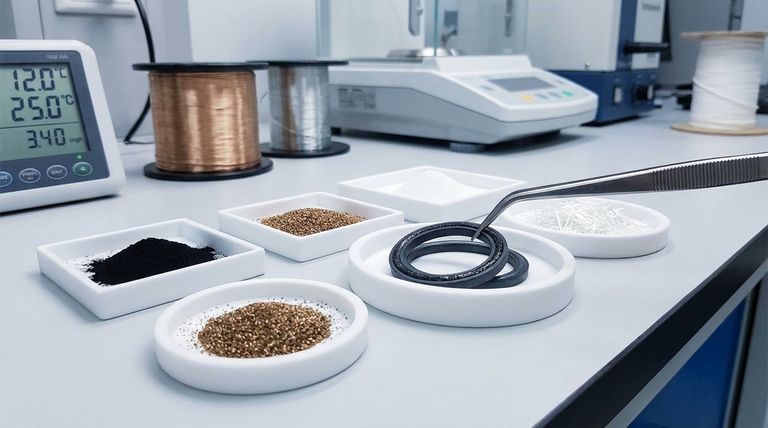
In short, a filled PTFE seal is a composite material where the base Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) plastic is blended with other materials, known as fillers. This process enhances specific properties of the PTFE, such as wear resistance or thermal conductivity, creating a high-performance seal tailored for more demanding applications where standard PTFE might fall short.
The core concept is simple: while pure, or "virgin," PTFE offers an exceptional combination of chemical inertness and low friction, it has inherent mechanical limitations. Adding fillers is a strategic engineering choice to overcome these limitations for specific, challenging operational environments.

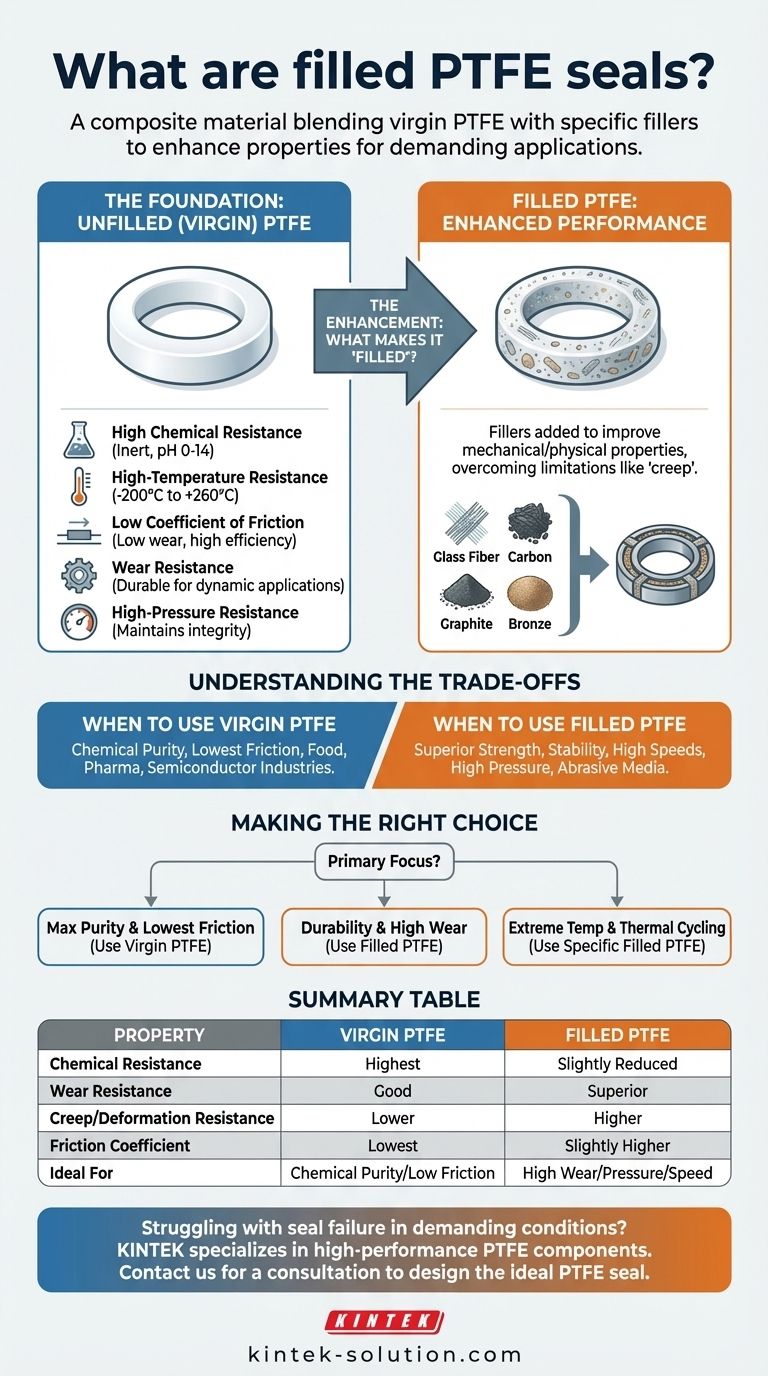
The Foundation: Understanding Unfilled (Virgin) PTFE
To understand why fillers are used, we must first appreciate the remarkable properties of the base material.
What is PTFE?
PTFE is a synthetic fluoropolymer, a high-performance plastic composed of carbon and fluorine atoms. It is often referred to by its original trade name, Teflon.
Core Characteristics
Often called the "King of Plastics," virgin PTFE is valued for a unique combination of five key characteristics.
- High Chemical Resistance: It is exceptionally inert, making it ideal for handling corrosive fluids and operating in environments with a pH range from 0 to 14.
- High-Temperature Resistance: It functions reliably across an enormous temperature range, typically from -200°C to +260°C (-328°F to +500°F).
- Low Coefficient of Friction: It has one of the lowest friction values of any solid material, which reduces wear, minimizes heat generation, and improves efficiency in dynamic applications.
- Wear Resistance: Its inherent durability makes it suitable for reciprocating and rotary applications, reducing the need for frequent maintenance.
- High-Pressure Resistance: It maintains its integrity and sealing properties even in high-pressure systems.
The Enhancement: What Makes a PTFE Seal "Filled"?
While virgin PTFE is impressive, it isn't perfect for every scenario. This is where fillers become critical.
The Concept of Fillers
Fillers are specific additives, such as glass fiber, carbon, graphite, or bronze, that are blended into the PTFE resin powder before it is molded and machined into a final seal.
The Goal of Filling PTFE
The purpose of adding a filler is to enhance one or more of PTFE's mechanical or physical properties. Virgin PTFE can be relatively soft and prone to deformation under load (a phenomenon known as "creep" or "cold flow").
Fillers are used to improve characteristics like hardness, compressive strength, and wear resistance, making the seal more robust for dynamic, high-pressure, or high-speed applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between a virgin and a filled PTFE seal involves evaluating the specific demands of your system. There is no universally "better" option, only the right choice for the job.
When to Use Virgin PTFE
Unfilled PTFE offers the highest degree of chemical purity and the lowest coefficient of friction. It is the preferred choice for applications in the food, pharmaceutical, or semiconductor industries where contamination is a major concern, or in systems where minimizing friction is the absolute top priority.
When to Use Filled PTFE
Filled PTFE provides superior mechanical strength and stability. It excels in applications involving high speeds, significant pressure, or abrasive media where the improved wear resistance and reduced creep of a filled compound are necessary to ensure a long service life. However, the filler may slightly reduce the seal's overall chemical resistance or increase its coefficient of friction compared to a virgin compound.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by your primary operational challenge.
- If your primary focus is maximum chemical purity and the lowest possible friction: A virgin PTFE seal is almost always the correct choice.
- If your primary focus is durability in a high-wear, dynamic, or high-pressure system: A filled PTFE seal is likely necessary to achieve the required performance and lifespan.
- If your primary focus is managing extreme temperatures and thermal cycling: Specific fillers can improve thermal conductivity and dimensional stability, making a filled compound the more reliable option.
Ultimately, selecting the correct PTFE seal means matching the material's engineered properties to the precise demands of your operating environment.
Summary Table:
| Property | Virgin PTFE | Filled PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Highest | Slightly Reduced |
| Wear Resistance | Good | Superior |
| Creep/Deformation Resistance | Lower | Higher |
| Friction Coefficient | Lowest | Slightly Higher |
| Ideal For | Chemical Purity, Low Friction | High Wear, Pressure, Speed |
Struggling with seal failure in demanding conditions?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including custom-filled PTFE seals tailored for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in precision production ensures your seals deliver enhanced durability, reduced creep, and longer service life—even in high-pressure, high-speed, or abrasive environments.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring the perfect material compound for your specific application.
Contact KINTEK today for a consultation and let our experts help you select or design the ideal PTFE seal for your critical operations.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- How do the non-stick properties of Teflon bushings benefit their performance? Boost Reliability & Cut Maintenance
- How are PTFE coatings used in the aerospace industry? Ensuring Reliability in Extreme Conditions
- What pressure conditions should be maintained for PTFE lined butterfly valves? Avoid Costly Valve Failure
- What materials are used to overcome the limitations of standard PTFE in ball valve seats? Upgrade to High-Performance Polymers
- How do the non-stick properties of PTFE benefit sealing technology? Enhance Seal Life and Purity
- How does a Stretched PTFE Lip Rotary Shaft Seal work? A Low-Friction, Springless Sealing Solution
- What are the thermal and electrical performance characteristics of Teflon PTFE? Master Its Properties for Demanding Applications
- What are the benefits of low friction in PTFE lined valves? Achieve Smoother Operation and Lower Costs



















