In short, the coefficient of friction in a PTFE slide bearing is minimized under a specific combination of high pressure, low speed, and ideal material choices. These conditions encourage the unique molecular behavior of PTFE, where increasing load actually reduces the frictional resistance, a principle that runs counter to classic friction models.
Unlike most materials where friction increases with load, PTFE's coefficient of friction decreases as bearing pressure rises. Achieving the lowest possible friction is a matter of maximizing this pressure (within the material's limits) while ensuring the interacting surfaces are optimized.

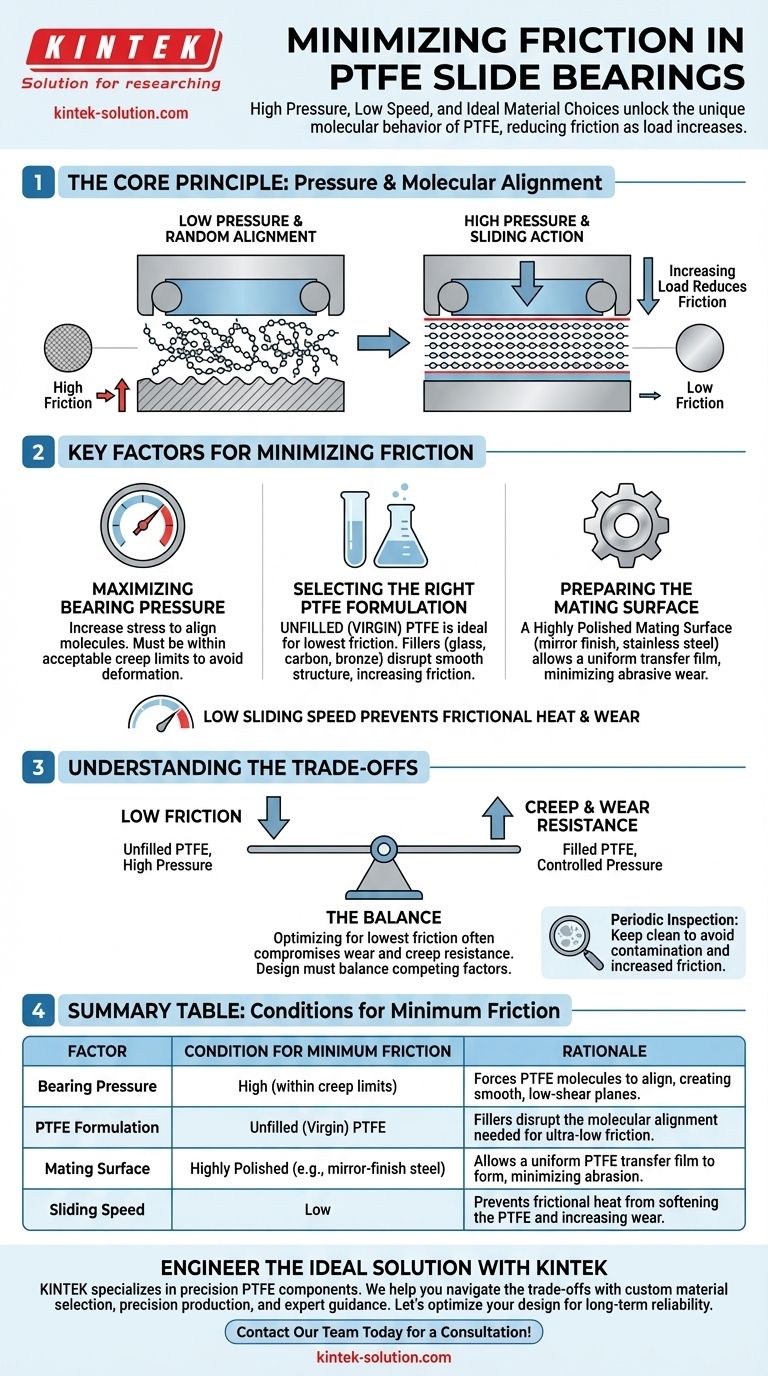
The Core Principle: Pressure and Molecular Alignment
To understand how to minimize PTFE's friction, you must first understand its unique molecular structure. PTFE is a polymer made of long, chain-like molecules that are not strongly bonded to each other.
How Sliding Action Reduces Friction
Under low pressure, these molecular chains are randomly oriented, creating a relatively rough "molecular landscape" that generates friction.
As pressure and sliding motion are applied, a thin layer of PTFE transfers to the mating surface. The long polymer chains in both the bearing and the transfer film align parallel to the direction of motion. This alignment creates smooth, low-shear planes that can slide over each other with very little resistance.
The Role of High Pressure
Higher pressure forces more of these molecules to align, perfecting the low-shear transfer film. This is the fundamental reason why the coefficient of friction for PTFE on a hard surface like polished steel drops as the load increases.
Key Factors for Minimizing Friction
Achieving the lowest friction coefficient requires controlling three primary variables: bearing pressure, material formulation, and the mating surface.
Maximizing Bearing Pressure
The single most important factor for reducing PTFE's friction coefficient is maximizing the stress on the bearing. The higher the pressure, the lower the friction will be.
However, this must be done within the acceptable creep limits of the material. Exceeding the material's compressive strength will cause permanent deformation (creep) and lead to bearing failure.
Selecting the Right PTFE Formulation
For the absolute lowest friction, unfilled (or "virgin") PTFE is the ideal choice. The presence of fillers inherently disrupts the smooth, aligned molecular structure that provides the low-friction characteristic.
Common fillers like glass, carbon, or bronze are added to improve other properties like wear resistance and compressive strength, but they always come at the cost of a higher coefficient of friction.
Preparing the Mating Surface
A highly polished mating surface is critical. A smooth surface, typically stainless steel with a mirror finish, minimizes abrasive wear on the PTFE.
This allows a uniform, thin transfer film of PTFE to form on the mating surface, which is essential for achieving the lowest possible friction. A rougher surface will abrade the PTFE, increasing friction and wear.
The Impact of Velocity
PTFE's self-lubricating properties are most effective at low sliding speeds. High velocities can generate frictional heat, which can soften the PTFE, increase the rate of wear, and negatively impact its low-friction performance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Optimizing for the lowest possible friction often involves compromises in other critical performance areas. A successful design requires balancing these competing factors.
Friction vs. Creep and Wear
The conditions for minimum friction (unfilled PTFE, high pressure) are precisely the conditions that are worst for creep and wear resistance. Unfilled PTFE deforms easily under sustained high loads.
This is the central trade-off in PTFE bearing design. Fillers are used to combat creep and wear, but they increase friction. Your design must find the right balance between acceptable friction and the required mechanical integrity for the life of the component.
Maintenance and Contamination
While PTFE bearings are considered maintenance-free, their performance depends on a clean sliding interface. Debris or grit caught between the surfaces can score the mating surface and disrupt the transfer film, dramatically increasing friction and wear.
Periodic inspection to ensure the area is clean is a simple but effective way to maintain long-term performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your design goal will determine the optimal setup for your PTFE slide bearing.
- If your primary focus is the absolute lowest possible coefficient of friction: Use unfilled PTFE, operate at the highest pressure the material can safely handle without excessive creep, and use a highly polished mating surface.
- If your primary focus is a balanced, real-world structural design: Select a filled PTFE (e.g., glass- or carbon-filled) that meets your project's load and wear requirements, accepting a slightly higher but stable coefficient of friction.
- If your primary focus is managing high loads with minimal wear: Prioritize a filled PTFE compound known for high compressive strength and wear resistance, and design the bearing area to keep pressure within the recommended limits for that specific material.
Ultimately, engineering a successful slide bearing is about balancing the remarkable low-friction properties of PTFE with the mechanical demands of the application.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Condition for Minimum Friction | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Bearing Pressure | High (within creep limits) | Forces PTFE molecules to align, creating smooth, low-shear planes. |
| PTFE Formulation | Unfilled (Virgin) PTFE | Fillers disrupt the molecular alignment needed for ultra-low friction. |
| Mating Surface | Highly Polished (e.g., mirror-finish steel) | Allows a uniform PTFE transfer film to form, minimizing abrasion. |
| Sliding Speed | Low | Prevents frictional heat from softening the PTFE and increasing wear. |
Need a PTFE Bearing Optimized for Your Specific Demands?
Balancing low friction with mechanical strength and wear resistance is a complex challenge. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including seals, liners, and custom bearings for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We can help you navigate the trade-offs:
- Custom Material Selection: Choose from unfilled or filled PTFE compounds to perfectly match your friction, load, and wear requirements.
- Precision Production: Ensure optimal performance with components made to your exact specifications.
- Expert Guidance: From prototypes to high-volume orders, we provide the expertise to optimize your design for long-term reliability.
Let's engineer the ideal solution for your application. Contact our team today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What industrial benefits do PTFE-machined parts offer? Achieve Peak Performance in Demanding Applications
- What factors should be considered when choosing between Nylon and PTFE? Select the Right Material for Your Application
- What chemical processing applications involve PTFE-machined parts? Essential Components for Corrosive & High-Purity Systems
- What are the main applications of PTFE type Teflon? Unlock Its Versatility for Your Industry
- What finishing techniques are effective for machined Teflon parts? Achieve Functional Performance and Dimensional Stability



















