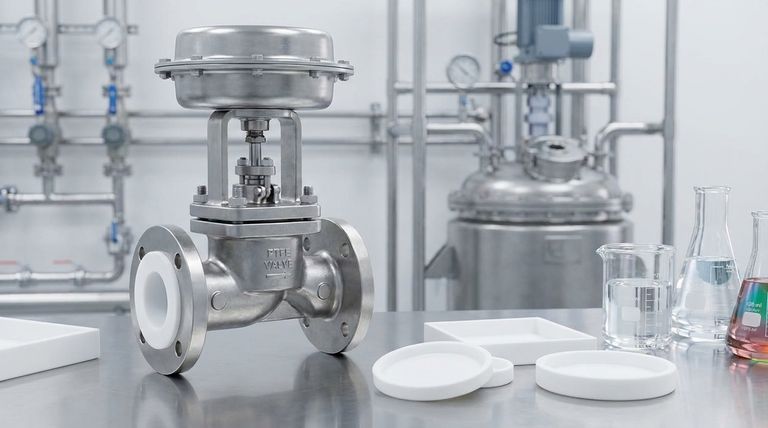
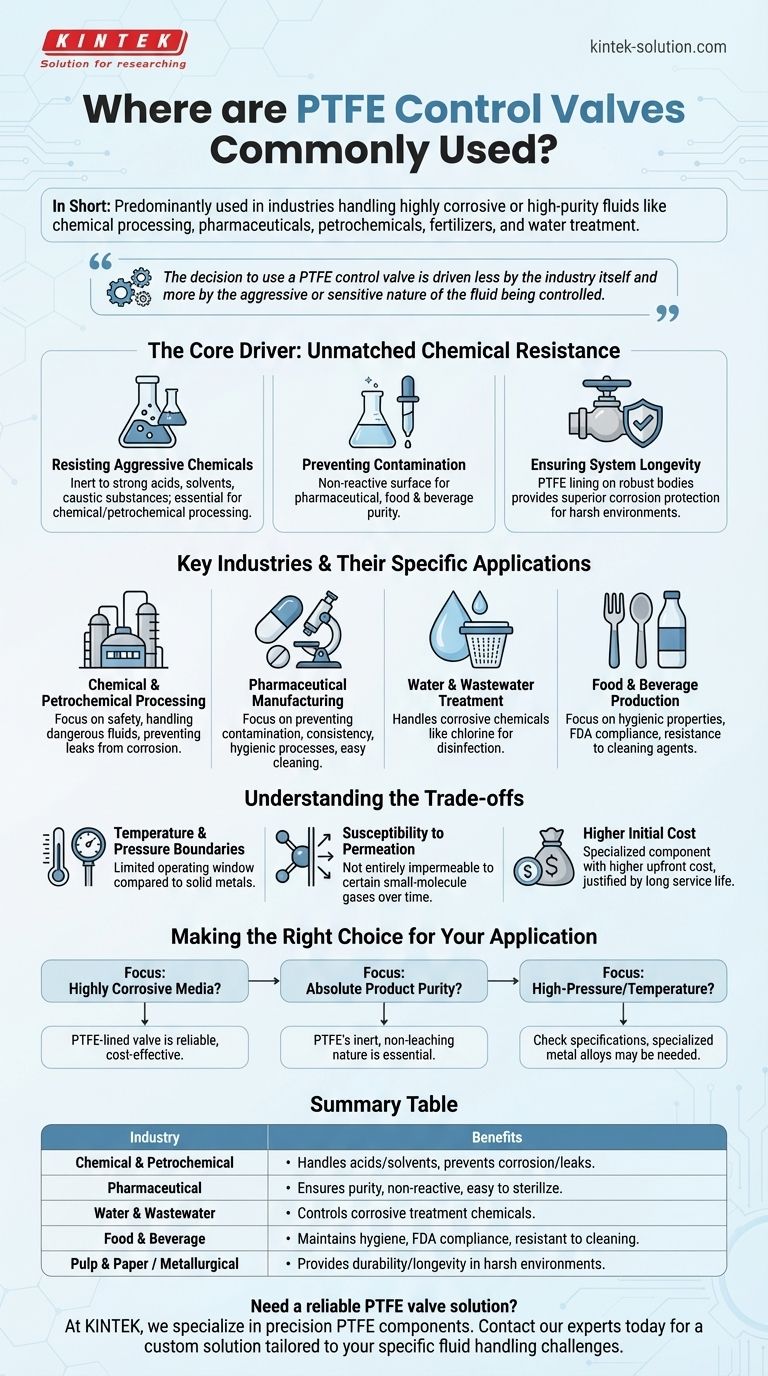
In short, PTFE control valves are predominantly used in industries that handle highly corrosive or high-purity fluids. The most common sectors include chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, petrochemicals, fertilizers, and water treatment, where standard metal valves would quickly corrode or contaminate the process media.
The decision to use a PTFE control valve is driven less by the industry itself and more by the aggressive or sensitive nature of the fluid being controlled. Its core value lies in its exceptional chemical inertness and non-contaminating surface.

The Core Driver: Unmatched Chemical Resistance
The widespread adoption of PTFE valves in demanding industries stems from a unique set of material properties. Understanding these properties reveals why it is the material of choice for specific, critical applications.
Resisting Aggressive Chemicals
PTFE is virtually inert to almost all industrial chemicals, including strong acids, solvents, and caustic substances. This makes it an essential material in chemical and petrochemical processing, where a valve must reliably control corrosive media without degrading.
Preventing Contamination
In the pharmaceutical and food and beverage industries, product purity is paramount. PTFE's non-reactive surface does not leach particles or react with the process fluid, ensuring the final product remains uncontaminated and compliant with standards like those from the FDA.
Ensuring System Longevity
By lining the wetted parts of a valve with PTFE, manufacturers can use a less expensive, structurally robust body material (like carbon or stainless steel) while providing superior corrosion protection. This creates a durable, long-lasting valve for harsh environments found in pulp and paper or metallurgical industries.
Key Industries and Their Specific Applications
While the principle is the same, the specific reason for choosing PTFE varies slightly depending on the industry's primary goal.
Chemical and Petrochemical Processing
The main objective here is safety and reliability when handling dangerous fluids. PTFE-lined valves prevent leaks and failures caused by corrosion, which could lead to hazardous spills or unplanned downtime.
Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
Here, the focus is on preventing contamination and ensuring batch-to-batch consistency. PTFE's smooth, non-stick surface is also easy to clean and sterilize, which is a critical requirement for hygienic processes.
Water and Wastewater Treatment
These facilities often use corrosive chemicals like chlorine, sulfuric acid, or ferric chloride for disinfection and purification. PTFE valves withstand these substances, ensuring the long-term reliability of the treatment infrastructure.
Food and Beverage Production
Similar to pharmaceuticals, this industry relies on PTFE for its hygienic properties and FDA compliance. The material's resistance to harsh cleaning agents used during sanitation cycles is also a major advantage.
Understanding the Trade-offs
PTFE is a premier solution for corrosion and purity, but it is not a universal answer. Objective evaluation requires acknowledging its limitations.
Temperature and Pressure Boundaries
Compared to solid metal alloys, PTFE has a more limited operating window for temperature and pressure. High temperatures can reduce its mechanical strength, and it is not typically specified for extremely high-pressure applications without specialized valve designs.
Susceptibility to Permeation
While highly resistant, PTFE is not entirely impermeable. Certain small-molecule gases or chemicals can slowly permeate the liner over time, which must be considered in highly specialized or sensitive applications.
Higher Initial Cost
A PTFE-lined valve is a specialized component and typically carries a higher upfront cost than a standard cast iron or stainless steel valve. The investment is justified by its dramatically longer service life and the prevention of costly failures in corrosive environments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct valve material is a critical engineering decision that balances performance, safety, and cost.
- If your primary focus is handling highly corrosive media: A PTFE-lined valve is often the most reliable and cost-effective long-term solution for aggressive chemicals.
- If your primary focus is maintaining absolute product purity: The inert, non-leaching nature of PTFE is essential for applications in pharmaceutical, food, and semiconductor manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is high-pressure or high-temperature service: You must carefully check the valve's specifications, as a specialized metal alloy may be required to meet these mechanical demands.
Ultimately, the right choice is always the one that matches the valve's material properties directly to the demands of the process fluid.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Primary Application & Benefit |
|---|---|
| Chemical & Petrochemical | Handling strong acids & solvents; prevents corrosion & leaks. |
| Pharmaceutical | Ensures product purity; non-reactive, easy to sterilize. |
| Water & Wastewater | Controls corrosive treatment chemicals (e.g., chlorine, acids). |
| Food & Beverage | Maintains hygiene & FDA compliance; resistant to cleaning agents. |
| Pulp & Paper / Metallurgical | Provides durability and longevity in harsh processing environments. |
Need a reliable PTFE valve solution for your corrosive or high-purity application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including custom seals, liners, and labware, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures your valves and systems deliver unmatched chemical resistance and contamination-free performance.
Let us help you enhance your system's reliability and longevity. Contact our experts today for a custom solution tailored to your specific fluid handling challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What causes a PTFE butterfly valve to stick or become hard to operate? Diagnose and Fix Common Issues
- Why is PTFE packing preferred in the food and pharmaceutical industries? Ensure Purity and Compliance
- Why is PTFE's biological inertia beneficial for medical use? Ensure Implant Safety and Longevity
- What are PTFE liners and why are they considered a breakthrough in medical sciences? Discover the Key to Safer Medical Devices
- What are the mechanical properties of PTFE and nylon in bushings and thrust washers? A Guide to Material Selection
- What cost benefits do PTFE oil seals offer? Slash Your Total Cost of Ownership
- Why are PTFE Lip Seals considered a game-changer in rotary applications? Unlock Unmatched Performance & Reliability
- Why are PTFE expansion joints considered an optimal solution for industrial systems?



















