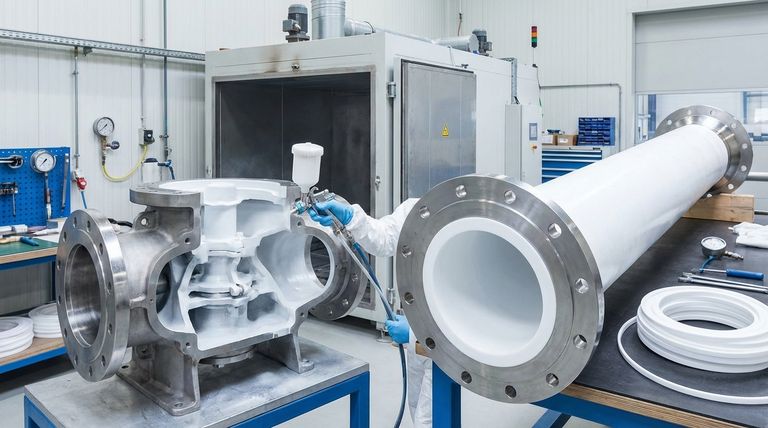
The PTFE lining process is a specialized industrial technique for bonding a layer of Polytetrafluoroethylene to the interior of components like pipes, tanks, and valves. This is most commonly achieved either by inserting a pre-formed PTFE tube that shrinks to create a tight "interference fit" or by spray-coating a liquid dispersion of PTFE that is then heated (sintered) to form a solid, non-porous barrier.
The core objective of any PTFE lining process is not simply to coat a surface, but to create a seamless, chemically inert, and thermally stable barrier. The chosen method depends on the component's geometry, but success always hinges on meticulous surface preparation and a flawless bonding process to ensure complete integrity.

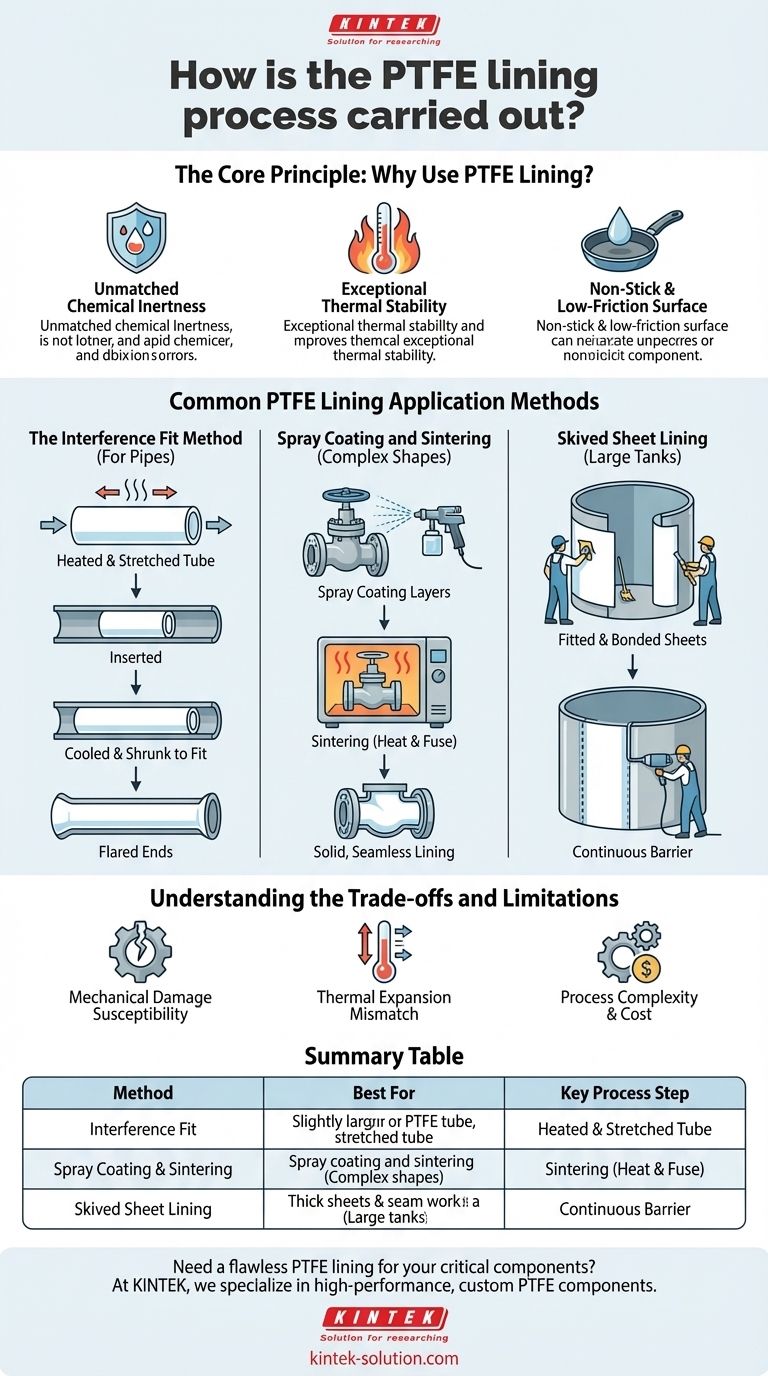
The Core Principle: Why Use PTFE Lining?
Before examining the methods, it is critical to understand why PTFE is the material of choice for demanding applications. Its unique molecular structure provides a combination of properties that few other polymers can match.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
The carbon-fluorine bonds in PTFE are exceptionally strong and stable. This makes the material virtually immune to chemical attack from nearly all acids, bases, solvents, and other corrosive agents, making it indispensable for handling aggressive chemicals.
Exceptional Thermal Stability
PTFE performs reliably across a vast temperature range. It can withstand continuous service temperatures up to 260°C (500°F) without significant degradation and maintains its properties even in cryogenic conditions.
Non-Stick and Low-Friction Surface
PTFE's famous non-stick quality, known technically as a low coefficient of friction, prevents material buildup and facilitates easy cleaning. This is critical in high-purity applications, food processing, and processes where residue is unacceptable.
Common PTFE Lining Application Methods
While the goal is the same, the method of application varies significantly based on the shape and size of the part being lined. The process always begins with thorough surface preparation, such as sandblasting, to ensure the substrate is clean and ready for a strong mechanical bond.
The Interference Fit Method (For Pipes)
This method is primarily used for straight sections of pipe and simple cylinders. A PTFE tube is manufactured with an outer diameter slightly larger than the inner diameter of the metal pipe it will line.
The PTFE tube is heated and stretched, temporarily reducing its diameter. It is then inserted into the pipe. As the PTFE cools and the tension is released, it attempts to shrink back to its original size, creating an extremely tight fit against the pipe's interior wall. The ends are then flared over the pipe flanges to create a continuous sealing surface.
Spray Coating and Sintering
For components with complex geometries like valves, pump housings, or tanks, spray coating is the preferred method. A liquid dispersion of PTFE resin is sprayed onto the prepared interior surface in multiple thin layers.
After the desired thickness is achieved, the entire component is heated in a carefully controlled oven. This critical step, known as sintering, causes the PTFE particles to melt and fuse into a solid, seamless, and non-porous lining that is chemically and mechanically bonded to the substrate.
Skived Sheet Lining
For very large tanks or vessels, a different approach is used. Thick sheets of PTFE are manufactured by "skiving" a thin layer from a large, molded billet of PTFE.
These sheets are then fitted and bonded to the interior walls of the vessel using a specialized adhesive system. The seams between sheets are meticulously welded using heat and pressure to ensure a continuous, leak-proof barrier.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, PTFE lining is not a universal solution. Acknowledging its limitations is key to successful implementation.
Susceptibility to Mechanical Damage
PTFE is a relatively soft material. The lining can be damaged by sharp objects, abrasive slurries, or impact. A scratch or gouge that penetrates the lining will compromise its protective barrier entirely.
Thermal Expansion Mismatch
PTFE expands and contracts with temperature changes at a much higher rate than metal. This differential expansion can create stress at the bond line between the liner and the substrate, potentially leading to delamination over time if the process is not expertly controlled.
Process Complexity and Cost
Applying a defect-free PTFE lining is a highly technical and unforgiving process. It requires specialized equipment and deep expertise, making it a more significant investment compared to standard paints or simpler coatings. Inspection for pinholes and defects is non-negotiable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your choice of lining method and its suitability depend entirely on your primary operational challenge and the geometry of your equipment.
- If your primary focus is corrosion protection in straight-run piping: The interference fit method provides a thick, seamless, and robust liner ideal for harsh chemical transport.
- If your primary focus is lining complex shapes like valves or mixers: A spray coating and sintering process offers the flexibility to conform to intricate geometries while ensuring a fully bonded, non-porous surface.
- If your primary focus is covering large surface areas like storage tanks: Adhered skived sheet lining is often the most practical and effective method for creating a durable protective barrier.
Ultimately, a successful PTFE lining is defined not by the specific technique, but by a precisely controlled process that guarantees a flawless protective barrier for your critical components.
Summary Table:
| Method | Best For | Key Process Step |
|---|---|---|
| Interference Fit | Straight pipes, cylinders | Heating, stretching, and inserting a PTFE tube for a tight fit |
| Spray Coating & Sintering | Complex shapes (valves, pumps) | Spraying PTFE dispersion and heating to fuse into a solid barrier |
| Skived Sheet Lining | Large vessels, tanks | Bonding and welding thick PTFE sheets to the interior surface |
Need a flawless PTFE lining for your critical components?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance, custom PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our precision production and expert fabrication ensure your equipment has a seamless, chemically inert barrier that stands up to aggressive chemicals and extreme temperatures.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project, from prototype to high-volume production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
People Also Ask
- What advantages do PTFE bars offer in chemical industries? Ensure Safety and Efficiency in Demanding Applications
- What are some industrial applications of PTFE lip seals in extreme temperatures? Ensuring Reliability from Cryogenics to High Heat
- What are the advantages of PTFE gaskets in terms of chemical resistance? Achieve Unmatched Sealing in Corrosive Environments
- How do Teflon bearings perform in demanding applications? Superior Performance in Harsh Environments
- Why is PTFE considered a preferred material for high-temperature applications in butterfly valves? Superior Thermal & Chemical Stability
- What standard surface finishes are available for PTFE balls? Tumbled vs. Machined for Optimal Performance
- What are the limitations of machining Teflon (PTFE)? Overcome Challenges for Precision Parts
- What is the temperature range that PTFE bushings can endure? Operate from -200°C to +260°C



















