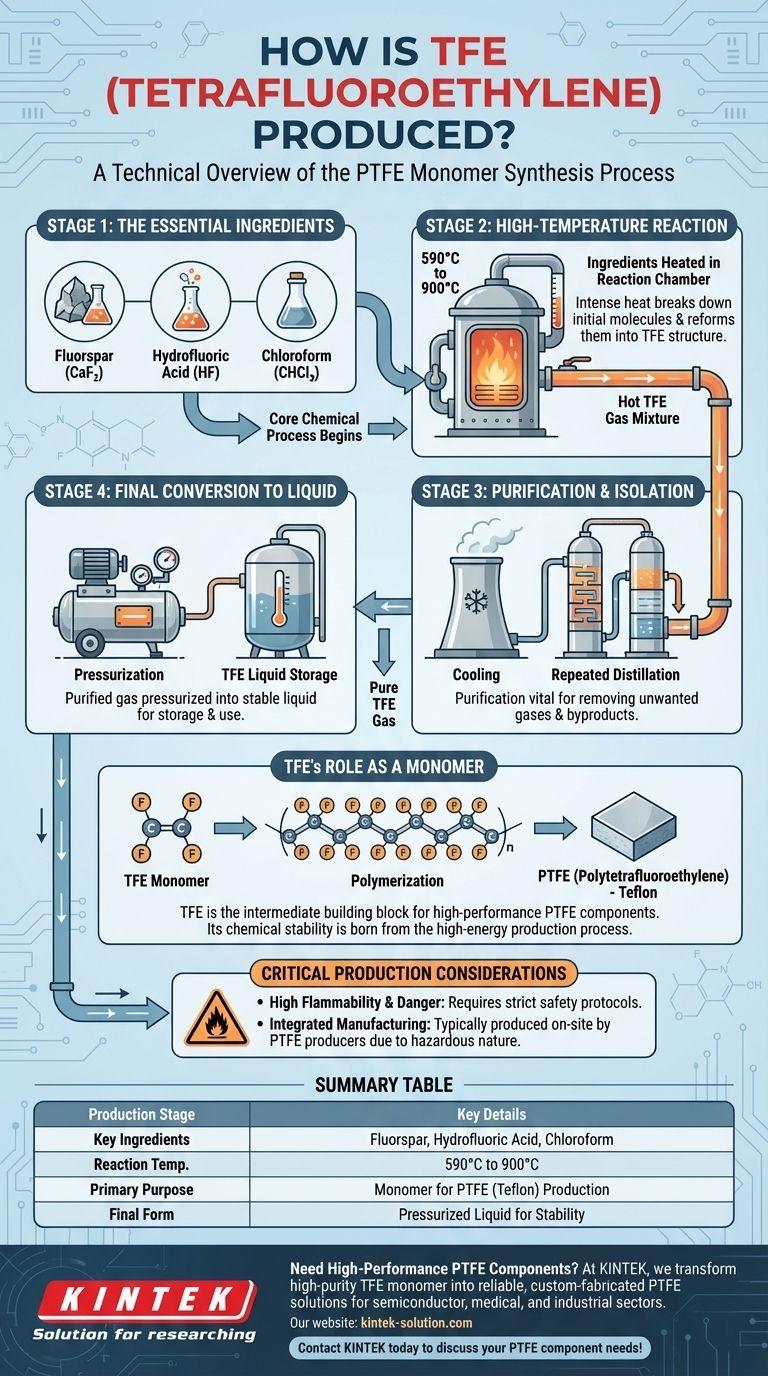
To produce tetrafluoroethylene (TFE), three key ingredients—fluorspar, hydrofluoric acid, and chloroform—are heated together in a reaction chamber to extremely high temperatures, between 590 and 900 degrees Celsius. The resulting gas is then put through a series of cooling and distillation cycles to remove impurities, yielding pure TFE. Finally, this purified gas is pressurized into a liquid state for storage and subsequent use.
The production of TFE is a high-energy chemical synthesis designed to create a pure, but hazardous, building block (monomer). This monomer is almost exclusively used to manufacture polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), the material widely known as Teflon.

The Core Chemical Process
The creation of TFE is a precise, multi-stage industrial process. Each step is critical for ensuring the purity and stability of the final monomer before it can be used to create polymers.
The Essential Ingredients
The synthesis begins with three specific chemical inputs: fluorspar, hydrofluoric acid, and chloroform. These materials provide the necessary carbon, fluorine, and hydrogen atoms that are rearranged during the reaction.
High-Temperature Reaction
These ingredients are fed into a reaction chamber and heated to a critical temperature range of 590°C to 900°C. This intense heat drives the chemical reaction, breaking down the initial molecules and reforming them into the TFE structure.
Purification and Isolation
The hot gas exiting the reactor is a mixture of TFE and other byproducts. This gas is cooled and then repeatedly distilled. This purification process is vital for removing unwanted gases, leaving behind a pure stream of TFE.
Final Conversion to Liquid
Once purified, the TFE gas is pressurized, causing it to convert into a liquid. This step makes the material more stable and easier to handle for transportation and storage, typically on the same site where it will be used.
TFE's Role as a Monomer
Understanding TFE production is incomplete without understanding its primary purpose. TFE is rarely the end product; it is an intermediate chemical.
The Building Block for PTFE
TFE is the monomer used to create polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). Through a process called polymerization, individual TFE molecules are linked together into long chains, forming the stable, solid polymer known for its extreme chemical resistance and low-friction surface.
Properties of the End Product
The unique properties of PTFE, such as its high melting point and inability to be processed by conventional injection molding, stem directly from the strong carbon-fluorine bonds established in the TFE monomer. This chemical stability is born from its high-energy production process.
Critical Production and Handling Considerations
The nature of TFE makes its production and handling a specialized and hazardous task. This is a key reason why it is not a widely traded commodity.
High Flammability and Danger
TFE is a highly flammable and potentially dangerous gas. Its instability requires strict safety protocols and specialized equipment to manage safely.
Integrated Manufacturing
Due to these dangers, TFE is typically manufactured directly by PTFE producers. This on-site production minimizes the risks associated with transporting a hazardous material and ensures a fresh, pure supply for the polymerization process.
Making Sense of the Process
Understanding the origin of a material provides critical insight into its application and value. The TFE production process directly informs the characteristics of the final PTFE products we use.
- If your primary focus is material science: The high-energy, multi-stage production of TFE is directly responsible for the exceptional thermal and chemical stability of PTFE.
- If your primary focus is industrial safety: The hazardous nature of TFE gas necessitates that its production is almost always vertically integrated with PTFE manufacturing, limiting its transport and handling.
- If your primary focus is product cost: The complex and energy-intensive synthesis of this monomer is a significant factor contributing to the higher cost of finished PTFE components.
By understanding how this fundamental building block is made, you gain a clearer appreciation for the final material's unique capabilities and limitations.
Summary Table:
| Production Stage | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Key Ingredients | Fluorspar, Hydrofluoric Acid, Chloroform |
| Reaction Temperature | 590°C to 900°C |
| Primary Purpose | Monomer for PTFE (Teflon) Production |
| Final Form | Pressurized Liquid for Stability |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components?
Understanding the complex production of TFE highlights the precision required for quality PTFE. At KINTEK, we transform this high-purity monomer into reliable, custom-fabricated PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We prioritize precision manufacturing and offer custom solutions from prototypes to high-volume orders. Let us provide the material expertise and manufacturing excellence your application demands.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your PTFE component needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Three Neck Flasks for Advanced Chemical Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials



















