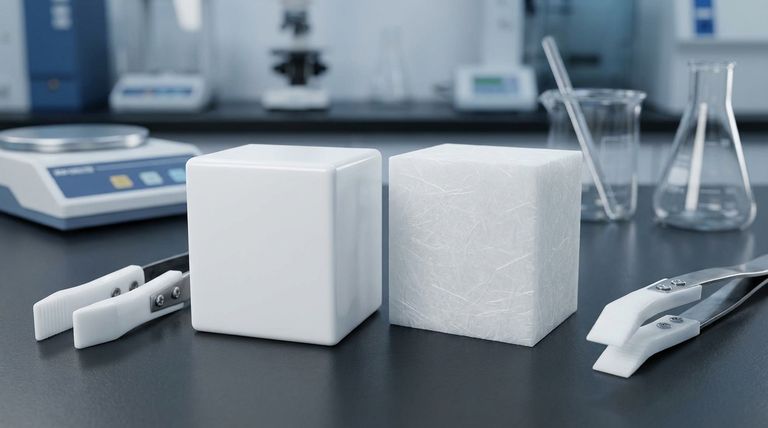
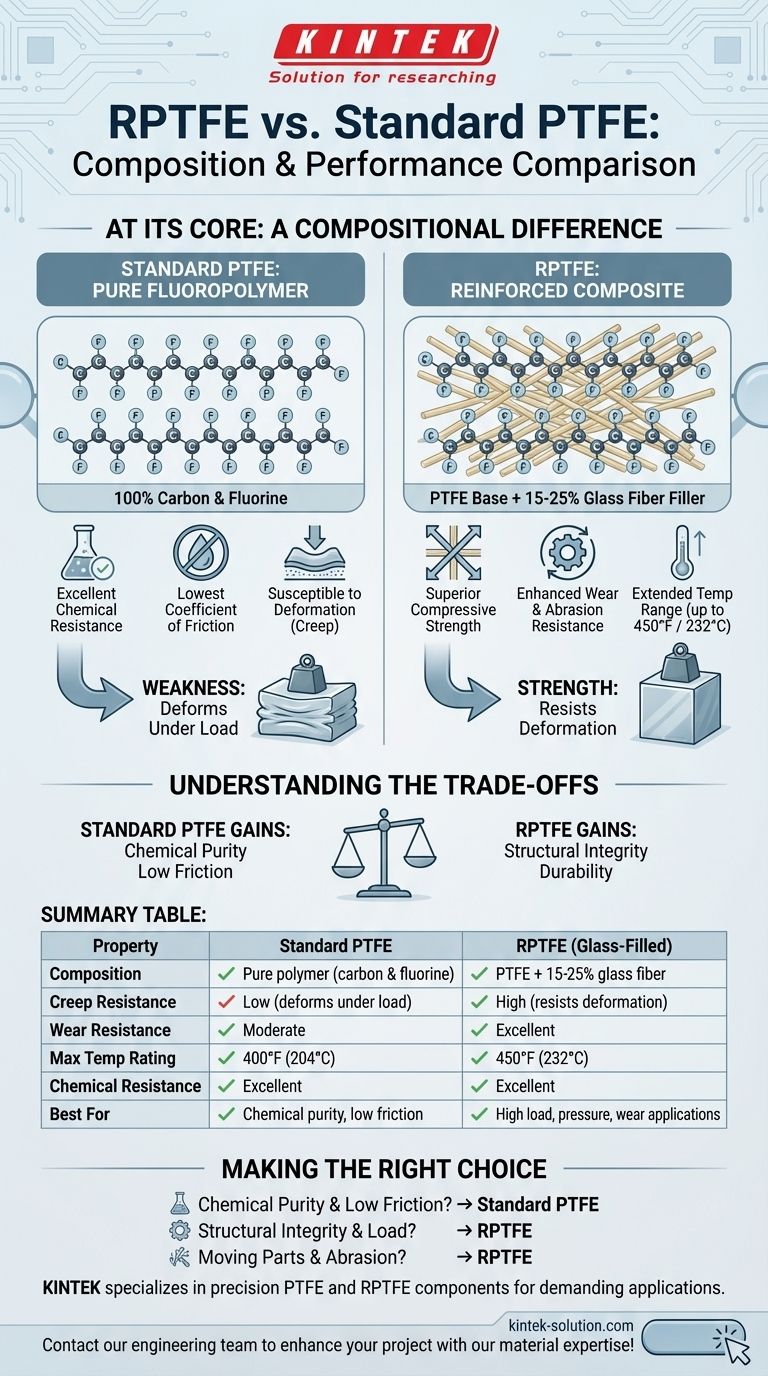
At its core, RPTFE is standard PTFE that has been mechanically enhanced with reinforcing fillers. While standard Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a pure polymer made exclusively of carbon and fluorine, RPTFE (Reinforced Polytetrafluoroethylene) is a composite material. The most common formulation of RPTFE contains between 15% and 25% fibrous glass mixed into the virgin PTFE base.
The compositional difference isn't just a minor variation; it's the solution to a fundamental problem. RPTFE was developed specifically to overcome the primary weakness of standard PTFE—its tendency to deform under pressure—by adding structural fillers like glass fiber.

Deconstructing the Composition: Pure vs. Composite
The difference between these two materials begins at the molecular level and extends to their macroscopic properties. Understanding this distinction is key to selecting the right one for a specific application.
Standard PTFE: A Pure Fluoropolymer
Standard PTFE is a high-molecular-weight compound consisting solely of carbon and fluorine atoms.
This simple, strong C-F bond structure is responsible for its most famous characteristics: exceptional chemical resistance, a very low coefficient of friction (non-stick), and excellent dielectric properties.
However, this purity also results in a relatively soft material that can be susceptible to deformation, a phenomenon known as "creep," when placed under a sustained load.
RPTFE: An Enhanced Composite
RPTFE begins with the same PTFE base but introduces other materials into the matrix. This transforms it from a pure polymer into a composite.
The "R" in RPTFE stands for "Reinforced," and while various fillers can be used, the designation most commonly refers to PTFE reinforced with glass fiber.
This addition of a filler material fundamentally alters the mechanical properties of the base PTFE without sacrificing its core chemical benefits.
Why Reinforce PTFE? Solving for Performance Gaps
The creation of RPTFE was driven by the need to preserve the desirable qualities of PTFE while mitigating its structural limitations. The filler material provides the mechanical backbone that pure PTFE lacks.
Overcoming Structural Weakness
The primary reason to use RPTFE is to gain strength and rigidity. The glass fibers act as a reinforcing skeleton within the PTFE matrix.
This reinforcement makes RPTFE far less susceptible to deformation and creep, allowing it to maintain its shape and integrity under significant mechanical load and pressure.
Improving Wear and Durability
The added fillers significantly increase the material's wear resistance. RPTFE components last longer in applications involving friction and abrasive forces compared to their standard PTFE counterparts.
Expanding the Temperature Range
The addition of glass fibers also provides a modest but meaningful improvement in thermal stability.
Standard PTFE is typically rated for use up to 400°F (204°C). RPTFE pushes this upper limit slightly higher to 450°F (232°C), increasing its operational window.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing RPTFE is a deliberate engineering decision that involves balancing benefits with potential considerations. It is not universally "better," but rather better for specific types of stress.
What You Gain with RPTFE
The primary advantages are mechanical. You get a material with superior compressive strength, enhanced dimensional stability under load, and greater resistance to wear and abrasion.
What Remains Unchanged
Critically, RPTFE retains the properties that make PTFE so valuable in the first place.
It still offers outstanding resistance to corrosives and chemicals, is hydrophobic (resists water), and maintains a non-stick surface. Both materials are often sold under the Teflon™ brand name.
What to Consider
The addition of fillers means RPTFE is no longer a pure polymer. In applications requiring absolute chemical purity or the lowest possible coefficient of friction, standard PTFE remains the superior choice. The fillers can also make the material slightly more abrasive to softer mating surfaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct material requires a clear understanding of the mechanical and chemical stresses it will face.
- If your primary focus is chemical purity and the lowest possible friction: Standard PTFE is the ideal choice, especially when mechanical loads are minimal.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity under load and pressure: RPTFE is vastly superior due to its resistance to deformation and creep.
- If your application involves moving parts and abrasive wear: The enhanced durability of RPTFE makes it a much more reliable and long-lasting option.
Ultimately, RPTFE is not a replacement for PTFE but a targeted enhancement for mechanically demanding environments.
Summary Table:
| Property | Standard PTFE | RPTFE (Glass-Filled) |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Pure polymer (carbon & fluorine) | PTFE + 15-25% glass fiber |
| Creep Resistance | Low (deforms under load) | High (resists deformation) |
| Wear Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Max Temp Rating | 400°F (204°C) | 450°F (232°C) |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Excellent |
| Best For | Chemical purity, low friction | High load, pressure, wear applications |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components for Demanding Applications?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE and RPTFE components (seals, liners, labware, and more) for semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial applications. We understand the critical differences between material formulations and can help you select the optimal solution for your specific mechanical and chemical requirements.
Our expertise includes:
- Custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume production
- Precision manufacturing for superior performance and durability
- Technical guidance on material selection for your unique application
Let us enhance your project with our material expertise and manufacturing precision. Contact our engineering team today to discuss your PTFE or RPTFE component needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What is PTFE and what are its key attributes? The Ultimate Guide to Its Properties & Uses
- What are the different types of Teflon available? A Guide to PTFE, FEP, PFA, and More
- What factors can cause variations in the actual properties of PTFE? Don't Rely on Generic Data Sheets
- What is Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) composed of? The Power of Carbon & Fluorine
- What quality control measures are used in PTFE production? Ensure Material Integrity for Your Application
- Why is PTFE used in medical and pharmaceutical applications? The Ultimate Guide to Safety and Performance
- What are the key characteristics of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)? Unlocking High-Performance Material Properties
- What are the standard sizes available for PTFE sheets and rods? Optimize Your Design & Sourcing



















