In the medical field, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is used for two distinct purposes: as a highly biocompatible material for implants and devices inside the body, and as a durable, low-friction component in medical instruments and equipment. Its adoption is driven by its unique ability to coexist with human tissue without causing adverse reactions.
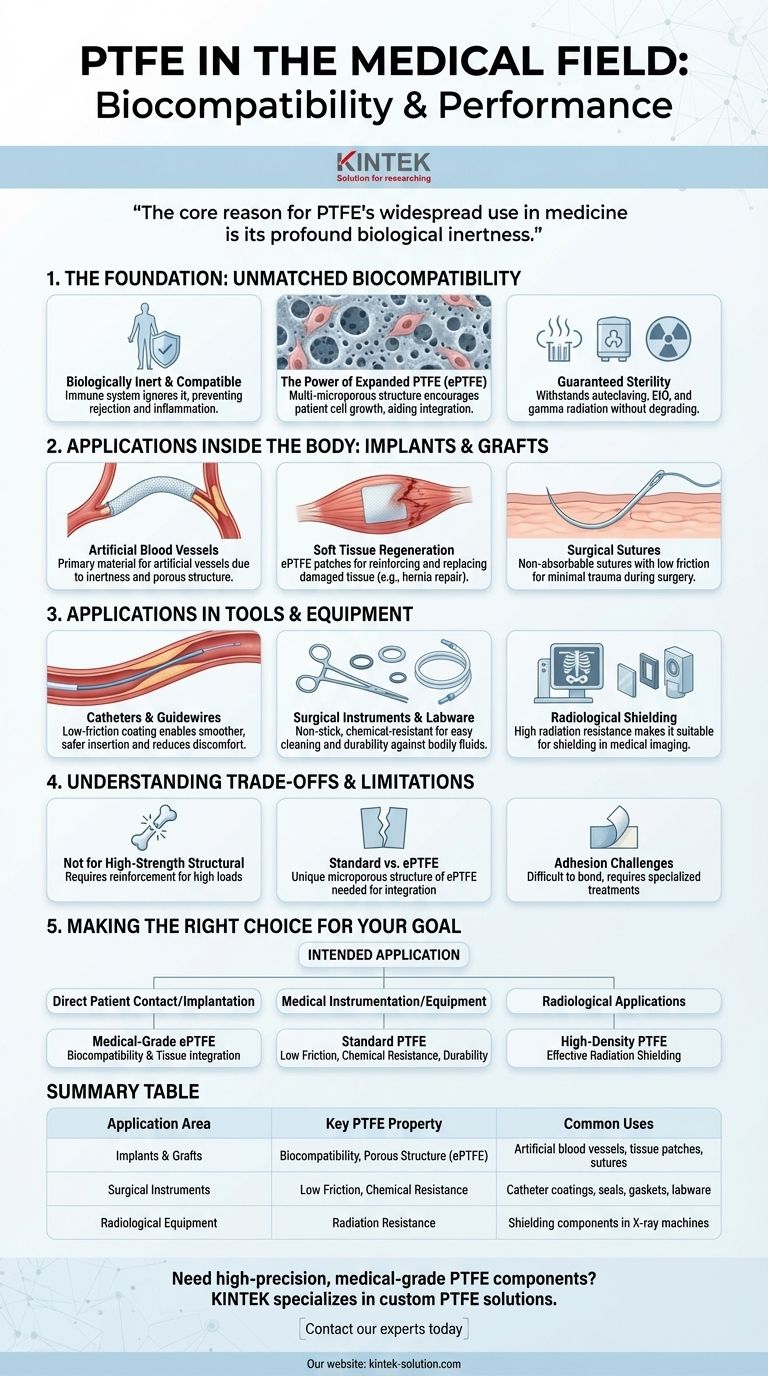
The core reason for PTFE's widespread use in medicine is its profound biological inertness. This means the human body does not reject it, making it an exceptionally safe and reliable material for everything from artificial blood vessels to surgical tools.
The Foundation: Unmatched Biocompatibility
Why the Body Accepts PTFE
PTFE is biologically inert and compatible, which means the body's immune system largely ignores it. This prevents the rejection, inflammation, or other physiological side effects that can occur with foreign materials.
The Power of Expanded PTFE (ePTFE)
A specific form called expanded PTFE (ePTFE) features a multi-microporous structure. This web of tiny pores encourages the patient's own cells to grow into the material, aiding integration and healing, which is critical for implants.
Guaranteed Sterility
A crucial property for any medical material is its ability to be sterilized. PTFE can withstand any common sterilization method, including autoclaving (steam), ethylene oxide (EtO), and gamma radiation, without degrading.
Applications Inside the Body: Implants and Grafts
Artificial Blood Vessels
Due to its inertness and the porous nature of ePTFE, it is a primary material for manufacturing artificial blood vessels and vascular grafts. These are used to bypass or replace blocked or damaged arteries.
Soft Tissue Regeneration
PTFE is fabricated into soft tissue regeneration patches. These are used in cardiac, general, and plastic surgeries to reinforce or replace damaged tissue, such as in hernia repairs.
Surgical Sutures
PTFE's combination of strength and low friction makes it an ideal material for specific non-absorbable surgical sutures. The smooth surface allows it to pass through delicate tissue with minimal trauma.
Applications in Tools and Equipment
Catheters and Guidewires
The extremely low friction of PTFE makes it an excellent coating for catheters and guidewires. This allows for smoother and safer insertion into blood vessels and other parts of the body, reducing patient discomfort.
Surgical Instruments and Labware
PTFE is used to manufacture parts of forceps, seals, gaskets, and chemical tubing. Its non-stick surface is easy to clean, and its chemical resistance ensures it won't degrade when exposed to bodily fluids or harsh cleaning agents.
Radiological Shielding
An often-overlooked property is PTFE's high radiation resistance. This makes it a suitable material for shielding components within X-ray machines and other radiological equipment, protecting both patients and operators.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Not a High-Strength Structural Material
While durable, PTFE is a relatively soft polymer. It is not suitable for high-load-bearing applications, such as the primary components of an artificial hip or knee joint, without significant reinforcement.
Standard PTFE vs. Expanded PTFE (ePTFE)
It is critical to distinguish between standard PTFE and ePTFE. The remarkable properties for tissue integration are specific to the microporous structure of ePTFE and are not present in solid, standard PTFE components.
Adhesion and Bonding Challenges
The same non-stick property that makes PTFE valuable also makes it very difficult to bond to other materials. This requires specialized surface treatments, adding complexity and cost to manufacturing processes where adhesion is required.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When selecting PTFE, the intended application dictates the necessary grade and form.
- If your primary focus is direct patient contact or implantation: You must use medical-grade, expanded PTFE (ePTFE) for its proven biocompatibility and porous structure that encourages tissue integration.
- If your primary focus is medical instrumentation or equipment: Standard PTFE is an excellent choice for its low friction, chemical resistance, and durability in components like seals, catheters, and tubing.
- If your primary focus is radiological applications: A specific, high-density grade of PTFE should be selected for its effective radiation shielding properties.
Ultimately, understanding the specific properties of different PTFE variants is the key to leveraging this versatile polymer safely and effectively in any medical context.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key PTFE Property | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Implants & Grafts | Biocompatibility, Porous Structure (ePTFE) | Artificial blood vessels, tissue patches, sutures |
| Surgical Instruments | Low Friction, Chemical Resistance | Catheter coatings, seals, gaskets, labware |
| Radiological Equipment | Radiation Resistance | Shielding components in X-ray machines |
Need high-precision, medical-grade PTFE components? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing custom PTFE seals, liners, labware, and more for the medical, semiconductor, and laboratory industries. From prototypes to high-volume orders, we ensure the precision and biocompatibility your applications demand. Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements and receive a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments



















