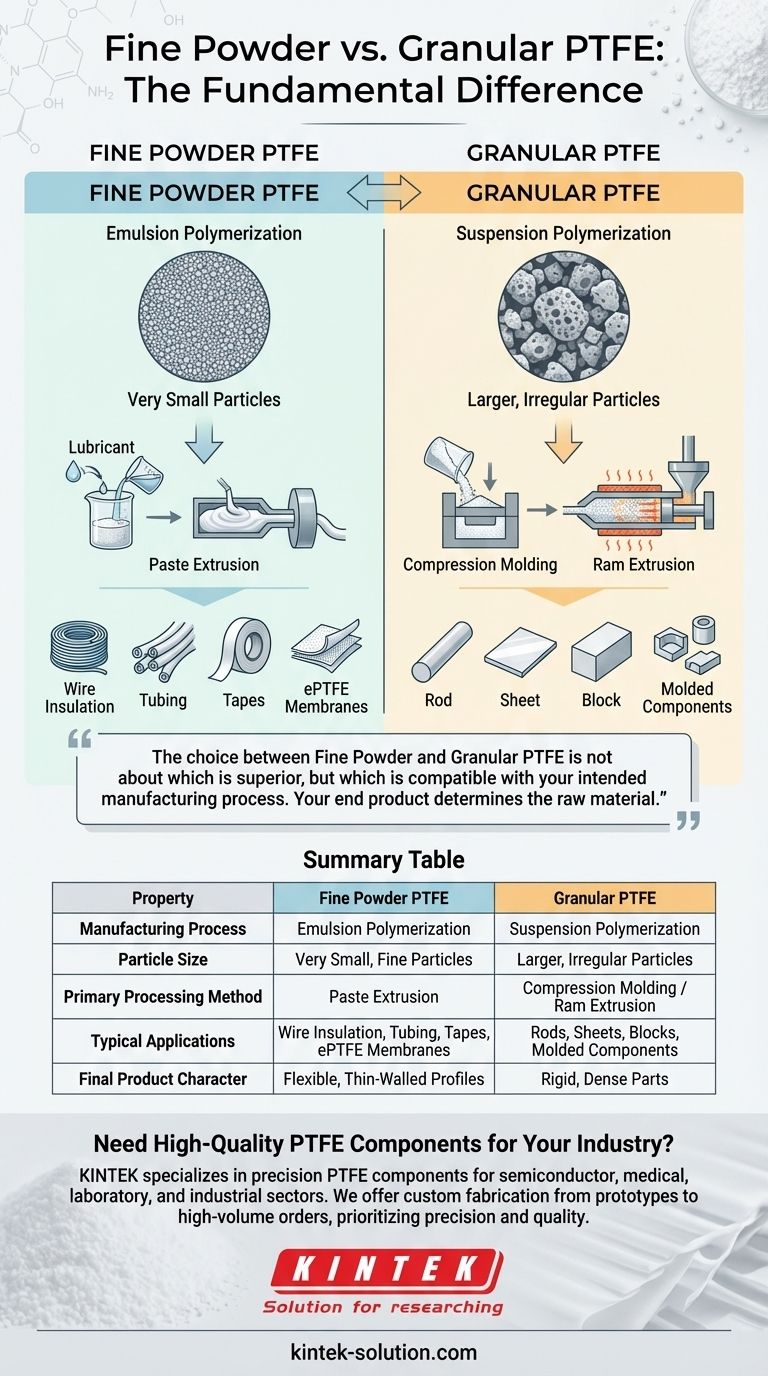
The fundamental difference between Fine Powder PTFE and Granular PTFE lies in their manufacturing process, which dictates their particle size and, consequently, their ideal applications. Fine Powder PTFE is made via emulsion polymerization, creating very small particles suitable for extrusion, while Granular PTFE is made via suspension polymerization, resulting in larger particles best for molding.
The choice between Fine Powder and Granular PTFE is not about which is superior, but which is compatible with your intended manufacturing process. Your end product—whether it's a molded block or a thin wire coating—determines the raw material you must use.

The Core Distinction: How They Are Made
The origin of each PTFE type is the most critical factor influencing its properties and use cases. The polymerization method directly creates the distinct physical forms of the material.
Fine Powder: Emulsion Polymerization
Fine Powder PTFE is produced in a water-based process called emulsion polymerization.
This method creates extremely small, fine-textured particles. These particles have a high surface area and are meant to be processed with a lubricant aid.
Granular PTFE: Suspension Polymerization
Granular PTFE is made through suspension polymerization, another water-based process but one that results in much larger, more irregular, and porous particles.
These larger particles flow more freely, behaving more like a conventional powder, which makes them suitable for different processing techniques.
How Particle Properties Dictate Application
The physical form of the powder directly enables a specific manufacturing method. You cannot use one type in a process designed for the other.
Fine Powder is for Extrusion
The fine particles of this PTFE are designed to be blended with a lubricant (like a hydrocarbon oil) to form a paste-like dough.
This paste is then forced through a die under pressure in a process called paste extrusion. This method is essential for manufacturing continuous, thin-walled, or complex profiles.
Common products include wire insulation, tubing, tapes, and the precursor material for expanded PTFE (ePTFE) gaskets and membranes.
Granular PTFE is for Molding
The larger, free-flowing particles of Granular PTFE are ideal for being poured into a mold.
This material is used in compression molding to create solid "stock" shapes like rods, sheets, and blocks. It is also used in a process called ram extrusion to produce thick-walled rods and tubes. These stock shapes are then often machined into final parts.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a material also means choosing a manufacturing process with its own set of advantages and limitations.
Processing Complexity
Fine Powder paste extrusion is a more involved, multi-step process. It requires careful blending with a lubricant, pre-forming, extruding, and then a drying and sintering phase to remove the lubricant and fuse the PTFE.
Granular PTFE molding is comparatively straightforward: fill a mold, apply heat and pressure, and sinter the part.
Final Product Characteristics
Fine Powder allows for the creation of highly flexible and thin products. The expansion process used to create ePTFE, which starts with fine powder, results in a material that is both strong and highly conformable.
Granular PTFE produces rigid, dense parts. These are excellent for structural components, bearings, and insulators where bulk and rigidity are more important than flexibility.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final goal dictates the material. The decision is not based on preference but on the required manufacturing pathway.
- If your primary focus is creating thin, continuous profiles like wire insulation, flexible tubing, or membranes: Fine Powder PTFE is your only option.
- If your primary focus is producing standard stock shapes like rods, sheets, blocks, or simple molded components: Granular PTFE is the correct and most efficient choice.
- If your primary focus is high-performance gaskets or porous materials with excellent flexibility: You will start with Fine Powder PTFE to create the necessary precursor for expansion.
Ultimately, aligning your material choice with the required manufacturing process is the key to achieving your desired outcome.
Summary Table:
| Property | Fine Powder PTFE | Granular PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Emulsion Polymerization | Suspension Polymerization |
| Particle Size | Very Small, Fine Particles | Larger, Irregular Particles |
| Primary Processing Method | Paste Extrusion | Compression Molding / Ram Extrusion |
| Typical Applications | Wire Insulation, Tubing, Tapes, ePTFE Membranes | Rods, Sheets, Blocks, Molded Components |
| Final Product Character | Flexible, Thin-Walled Profiles | Rigid, Dense Parts |
Need High-Quality PTFE Components for Your Industry?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components (seals, liners, labware, and more) for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether your project requires the flexibility of Fine Powder PTFE for extrusion or the rigidity of Granular PTFE for molding, our expertise ensures the right material and process for optimal performance.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, prioritizing precision and quality.
Contact us today to discuss your specific PTFE needs and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- PTFE Chemical Solvent Sampling Spoon
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability



















