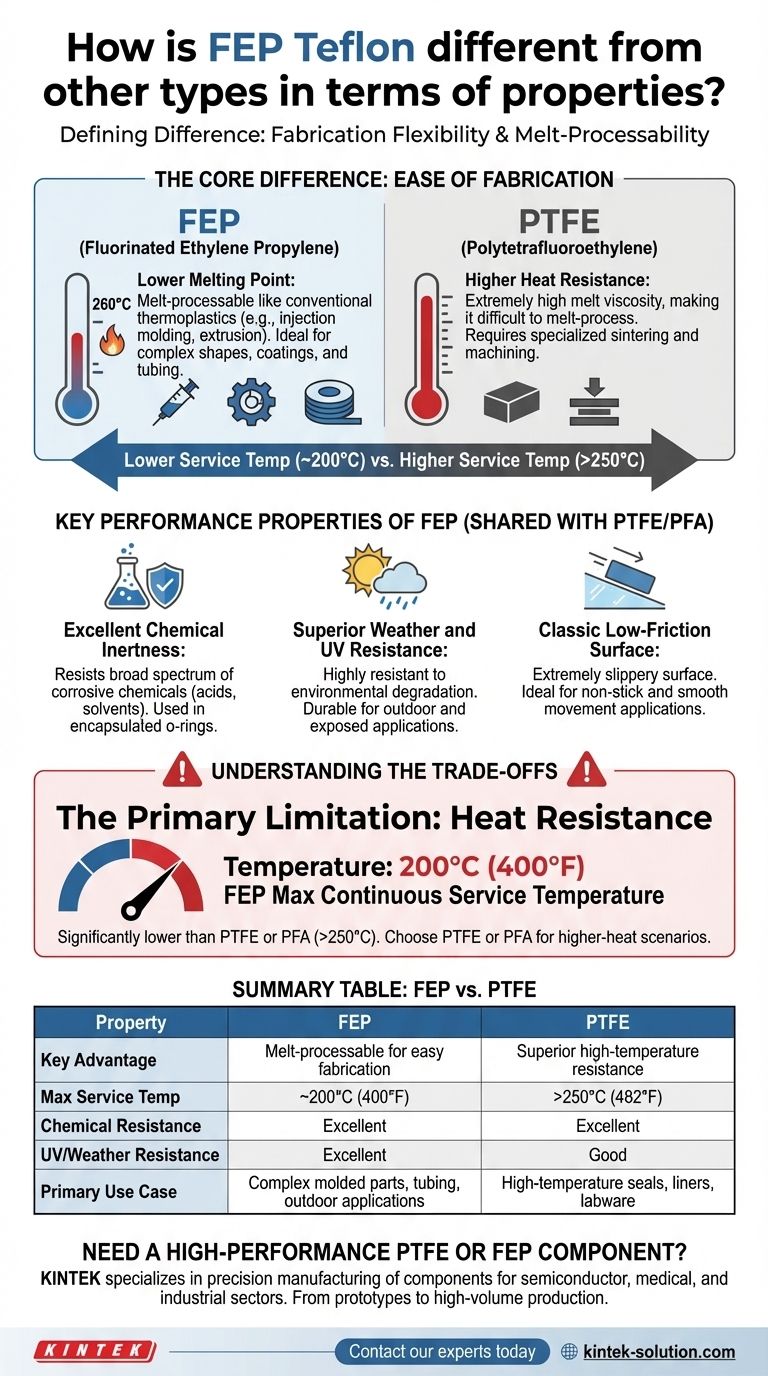
The defining difference between FEP (Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene) and other types of Teflon, particularly PTFE, is its fabrication flexibility. FEP's lower melting point allows it to be processed like a conventional thermoplastic, making it easier to mold and extrude into complex shapes, a significant advantage over the more heat-resistant but harder-to-fabricate PTFE.
FEP offers the classic Teflon benefits of chemical inertness and low friction but in a melt-processable form. This manufacturing advantage comes with a direct trade-off: a lower maximum service temperature compared to materials like PTFE and PFA.

The Core Difference: Ease of Fabrication
FEP was engineered to solve the primary manufacturing challenge of PTFE. While sharing many of the same desirable properties, its molecular structure was modified for one key purpose: easier processing.
FEP's Lower Melting Point
Unlike PTFE, FEP has a distinct and lower melting point around 260°C.
This property is what fundamentally separates it. It allows the material to be melted and flow, which is not practical with PTFE due to its extremely high melt viscosity.
The Manufacturing Advantage
Because it can be truly melted, FEP is melt-processable.
This means it can be used in conventional, high-volume manufacturing techniques like injection molding and extrusion. This makes producing complex parts, thin coatings, and intricate tubing far more efficient and cost-effective.
Key Performance Properties of FEP
While its fabrication is the main differentiator, FEP maintains the core high-performance characteristics associated with the Teflon brand.
Excellent Chemical Inertness
FEP offers outstanding resistance to a broad spectrum of corrosive chemicals.
Its use in encapsulated o-rings demonstrates its reliability in sealing against aggressive substances like acids, aromatic solvents, and petroleum spirits.
Superior Weather and UV Resistance
FEP is particularly resistant to environmental degradation. It stands up exceptionally well to weathering, UV radiation, and atmospheric pollutants, making it a durable choice for outdoor or exposed applications.
Classic Low-Friction Surface
Like all fluoropolymers, FEP has an extremely slippery surface.
This low coefficient of friction, comparable to a skate on ice, makes it ideal for applications requiring non-stick properties or smooth movement between parts.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing FEP involves a clear and important compromise. Its benefits in processing come with a significant limitation in thermal performance.
The Primary Limitation: Heat Resistance
The most critical trade-off is FEP's lower maximum service temperature.
FEP is generally rated for continuous use up to 200°C (400°F). This is significantly lower than PTFE or PFA, which can often handle temperatures above 250°C.
When to Choose PTFE or PFA Instead
If an application's operating temperature will exceed 200°C, FEP is not the appropriate choice.
In these higher-heat scenarios, PTFE or PFA are the required materials, despite their respective processing challenges or higher cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct fluoropolymer depends entirely on balancing the demands of manufacturing, environment, and operating temperature.
- If your primary focus is manufacturability: Choose FEP for its ability to be easily injection molded or extruded into complex geometries.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature performance: Select PTFE or PFA for applications that will consistently operate above 200°C.
- If your primary focus is outdoor durability: FEP is an excellent candidate due to its exceptional resistance to UV and weathering.
- If your primary focus is general chemical resistance: FEP, PTFE, and PFA are all superb choices, so the decision should be based on temperature and fabrication needs.
Understanding this balance between processability and thermal performance is the key to selecting the ideal material for your design.
Summary Table:
| Property | FEP | PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Key Advantage | Melt-processable for easy fabrication | Superior high-temperature resistance |
| Max Service Temp | ~200°C (400°F) | >250°C (482°F) |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Excellent |
| UV/Weather Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Primary Use Case | Complex molded parts, tubing, outdoor applications | High-temperature seals, liners, labware |
Need a High-Performance PTFE or FEP Component?
Choosing the right fluoropolymer is critical for your application's success. At KINTEK, we specialize in the precision manufacturing of PTFE and FEP components—from custom seals and liners to complex labware—for the semiconductor, medical, and industrial sectors.
Our expertise ensures you get the optimal material and fabrication process for your specific needs, whether you require prototypes or high-volume production.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project and receive a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Crucibles for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Evaporating Dishes for Diverse Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the primary properties of Teflon that make it a 'powerhouse plastic'? Unlock Unmatched Performance
- How does PTFE perform in extreme conditions like aerospace environments? Ensuring Mission-Critical Reliability
- What are the critical conditions for the polymerization step in PTFE manufacturing? Mastering Temperature, Pressure, and Initiator Control
- What are the emerging market applications for PTFE? Driving Innovation in Semiconductors, EVs, and Medical Tech
- What are the thermal properties of FR4 PCB material? Master Heat Management for Reliable Circuits
- When did the industrial production of PTFE begin? From Military Secret to Industrial Revolution
- What are the uses of PTFE in the automotive industry? Ensuring Reliability in Extreme Conditions
- Why is PTFE widely used in the medical device industry? Its Biocompatibility & Low-Friction Drive Safety



















