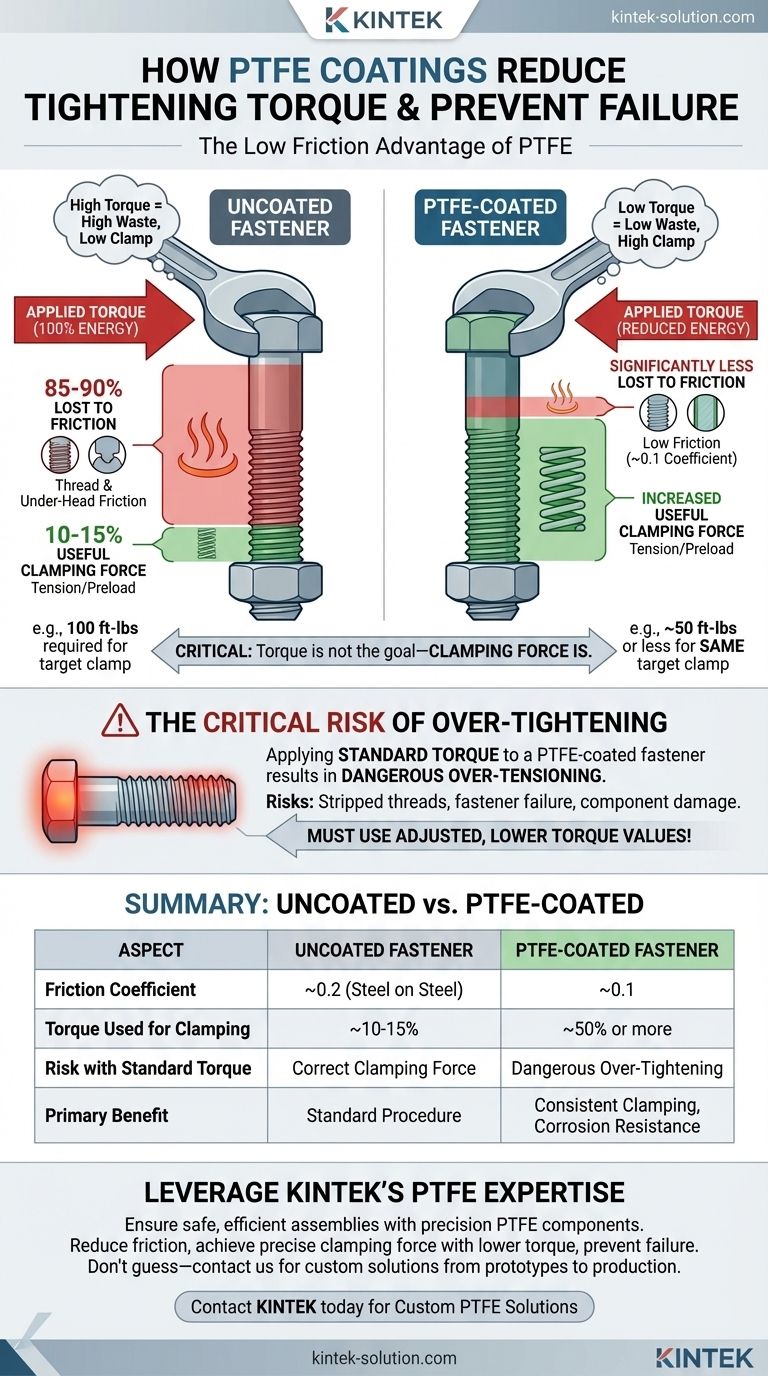
Critically, the low friction of a PTFE coating means less tightening torque is required to achieve the same clamping force. Because PTFE drastically reduces the friction that must be overcome in the threads and under the fastener head, a much greater percentage of the applied rotational energy is converted directly into useful bolt tension. Applying standard torque specifications to a PTFE-coated fastener will result in dangerous over-tightening.
The core issue is that torque is not the goal—clamping force is. PTFE coatings fundamentally change the relationship between the torque you apply with a wrench and the tension (clamping force) you create in the bolt, making it essential to use adjusted torque values to prevent component failure.

The Physics of Torque and Clamping Force
To understand the impact of PTFE, you must first distinguish between the force you apply and the result you want to achieve.
What Tightening Torque Actually Does
Tightening a bolt is an act of converting rotational force (torque) into linear tension. This tension stretches the bolt like a stiff spring, creating the clamping force that holds a joint together.
However, not all of the torque you apply contributes to this useful clamping force.
The Overwhelming Role of Friction
In a standard, uncoated steel fastener, as much as 85-90% of the applied torque is consumed simply by overcoming two sources of friction: friction in the threads and friction under the turning bolt head or nut.
Only the remaining 10-15% of the torque actually generates the bolt tension or preload.
How PTFE Coatings Change the Equation
PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid, typically around 0.1.
When applied to a fastener, this coating dramatically reduces the energy wasted on friction. This means a far greater percentage of your applied torque becomes effective clamping force.
The Practical Implications for Fasteners
This shift in the torque-to-tension relationship has direct consequences for any assembly process.
Less Torque Achieves the Same Clamp Load
Because so little energy is lost to friction, a significantly lower torque value is needed to stretch the bolt to its target preload. The process becomes far more efficient.
For example, a fastener that requires 100 ft-lbs of torque when uncoated might only require 50 ft-lbs or less to achieve the exact same clamping force when coated with PTFE.
The Critical Risk of Over-Tightening
This efficiency creates a significant risk. If a technician uses the standard torque value for an uncoated fastener on a PTFE-coated one, they will inadvertently generate a massive amount of excess tension.
This over-tightening can easily stretch the bolt past its yield point, leading to stripped threads, fastener failure, or damage to the clamped flanges and gaskets.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Using PTFE-coated fasteners requires a change in procedure, but it also offers distinct advantages beyond friction reduction.
The Benefit: Consistency and Corrosion Resistance
PTFE coatings provide a smooth, consistent surface that minimizes the variations in friction often seen between uncoated fasteners. This leads to more predictable and accurate clamping force across an entire joint.
Furthermore, these coatings offer excellent corrosion resistance, preventing galling and seizure, which simplifies future disassembly.
The Challenge: Relying on New Specifications
The primary trade-off is that you cannot use standard torque charts. You must obtain and use the torque specifications provided by the manufacturer of the coated fastener or a qualified engineering source.
Failing to use these specific, reduced torque values negates the benefits and introduces a high risk of catastrophic failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To apply this knowledge effectively, you must adjust your procedures based on your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is joint integrity: Always use torque specifications calculated specifically for the PTFE-coated fastener you are using. Do not guess or use standard charts.
- If your primary focus is preventing component failure: Never apply standard, uncoated torque values to a coated fastener, as this will almost certainly result in dangerous over-tensioning.
- If your primary focus is assembly efficiency: Recognize that PTFE coatings reduce the physical effort and time needed for tightening and often allow for fastener reuse due to anti-galling properties.
By understanding the direct relationship between friction and torque, you can leverage the significant advantages of PTFE coatings while ensuring the safety and reliability of your mechanical assemblies.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Uncoated Fastener | PTFE-Coated Fastener |
|---|---|---|
| Friction Coefficient | ~0.2 (Steel on Steel) | ~0.1 |
| Torque Used for Clamping | ~10-15% | ~50% or more |
| Risk with Standard Torque | Correct Clamping Force | Dangerous Over-Tightening |
| Primary Benefit | Standard Procedure | Consistent Clamping, Corrosion Resistance |
Ensure your assemblies are safe and efficient with precision PTFE components from KINTEK.
Our custom-fabricated PTFE seals, liners, and labware are engineered for the demanding environments of the semiconductor, medical, and industrial sectors. By drastically reducing friction, our coatings help you achieve precise clamping force with lower torque, preventing component failure and enhancing assembly consistency.
Don't risk joint failure by using incorrect torque values. Let our expertise in high-performance polymers guide your design.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom PTFE solution, from prototypes to high-volume production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What industrial benefits do PTFE-machined parts offer? Achieve Peak Performance in Demanding Applications
- What chemical processing applications involve PTFE-machined parts? Essential Components for Corrosive & High-Purity Systems
- What are the main applications of PTFE type Teflon? Unlock Its Versatility for Your Industry
- What challenges arise when machining PTFE (Teflon)? Overcome Softness, Heat, and Instability
- What factors should be considered when choosing between Nylon and PTFE? Select the Right Material for Your Application



















