At its core, the exceptional chemical resistance of PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) oil seals provides a critical benefit: unwavering reliability in harsh environments. This property ensures the seal maintains its physical integrity and sealing performance when exposed to aggressive chemicals, preventing leaks that could lead to equipment failure, downtime, and safety hazards.
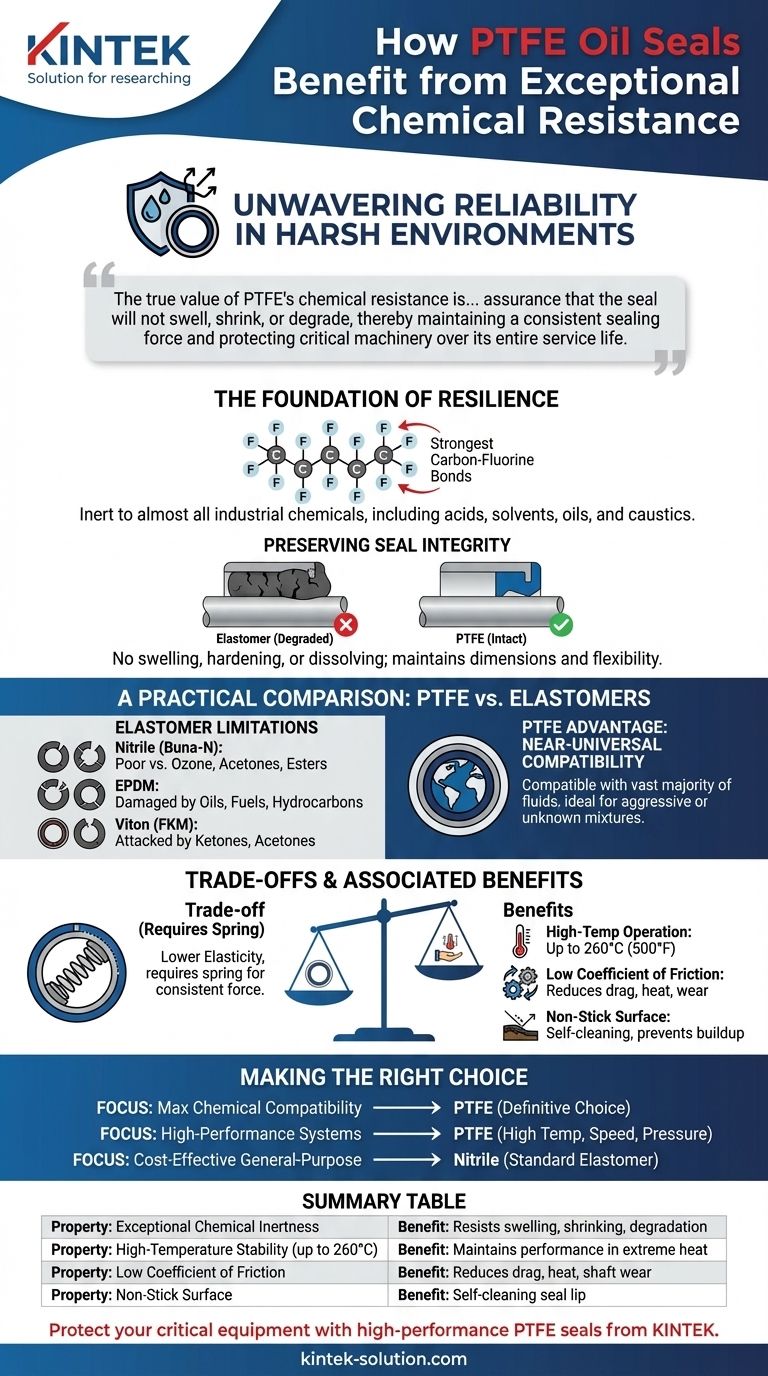
The true value of PTFE's chemical resistance is not just its ability to survive contact with corrosive substances. It is the assurance that the seal will not swell, shrink, or degrade, thereby maintaining a consistent sealing force and protecting critical machinery over its entire service life.
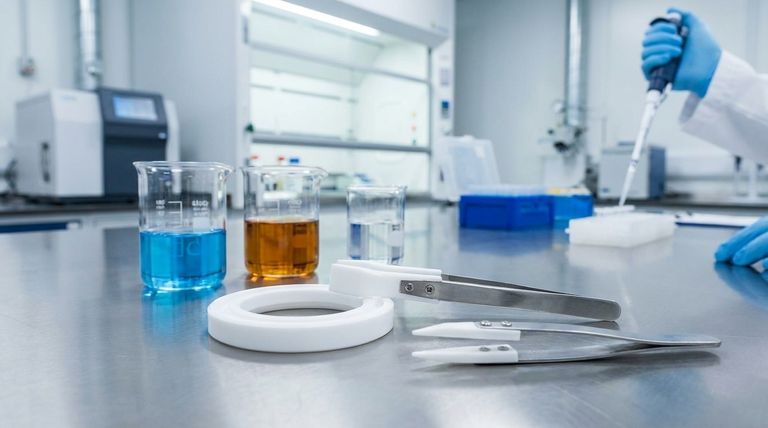

The Foundation of PTFE's Resilience
The benefit of PTFE begins at the molecular level. Its unique chemical structure is what makes it an elite material for demanding sealing applications.
The Power of Carbon-Fluorine Bonds
PTFE's molecular backbone consists of a chain of carbon atoms completely shielded by a sheath of fluorine atoms. The carbon-fluorine bond is one of the strongest single bonds in organic chemistry.
This powerful bond makes the molecule incredibly stable and non-reactive. As a result, PTFE is inert to almost all industrial chemicals, including aggressive acids, solvents, oils, and caustics.
Preserving Seal Integrity and Performance
When a seal material is not compatible with a chemical, it can swell, harden, or dissolve. This degradation fundamentally changes its shape and mechanical properties, leading to an almost certain loss of sealing force.
Because PTFE is chemically inert, it does not undergo these changes. It maintains its intended dimensions and flexibility, ensuring a consistent, leak-free seal on the shaft.
Protecting Equipment from Chemical Damage
An oil seal's primary function is to contain lubricants and exclude contaminants. If a seal fails due to chemical attack, it allows these fluids to mix or leak out.
This can cause catastrophic damage to bearings, gears, and other internal components. The reliability of a PTFE seal in a corrosive environment directly translates to the protection and longevity of the entire piece of equipment.
A Practical Comparison: PTFE vs. Common Elastomers
To understand the advantage of PTFE, it is useful to compare it directly to traditional rubber (elastomer) seals, which have specific chemical vulnerabilities.
Why Elastomer Seals Have Limitations
Elastomers are excellent for many general-purpose applications, but their chemical compatibility is narrow. Choosing the wrong elastomer for a given fluid can lead to rapid failure.
Nitrile (Buna-N)
A widely used and cost-effective material, Nitrile performs poorly when exposed to ozone, acetone, esters, and methyl ethyl ketone (MEK).
EPDM
While EPDM has good resistance to water and steam, it is highly susceptible to damage from oils, fuels, and hydrocarbons. Using an EPDM seal in an oil-based system is a common mistake.
Viton (FKM)
Viton offers good resistance to many fuels and oils but can be attacked by ketones and acetones.
The PTFE Advantage: Near-Universal Compatibility
PTFE sidesteps this complex and risky selection process. It is compatible with the vast majority of fluids, making it the default choice for applications involving aggressive chemical mixtures or where the exact chemical composition is unknown.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Associated Benefits
While chemical resistance is the primary driver, other properties of PTFE contribute to its performance, but they also come with trade-offs.
High-Temperature Operation
PTFE's thermal stability is a significant advantage. It can operate effectively in continuous temperatures up to 260°C (500°F), environments where most elastomers would degrade rapidly.
Low Coefficient of Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest friction coefficients of any solid material. This "slipperiness" reduces rotational drag, minimizes heat generation, and significantly reduces wear on both the seal and the shaft.
Non-Stick Surface
The non-stick nature of PTFE prevents contaminants, sludge, and other debris from adhering to the seal lip. This self-cleaning characteristic helps maintain a clean sealing edge, reducing the risk of abrasive wear and failure.
Lower Elasticity
Unlike highly flexible rubbers, PTFE is a more rigid material. This means it has less natural "bounce back" and often requires a spring energizer (a metal spring in the seal lip) to provide a consistent sealing force, especially on shafts with minor imperfections.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct seal material is a critical engineering decision that balances performance against cost. Use the following guidelines to make an informed choice.
- If your primary focus is maximum chemical compatibility: PTFE is the definitive choice for aggressive, complex, or unknown chemical media where seal failure is not an option.
- If your primary focus is high-performance systems: For applications involving high temperatures, high surface speeds, or significant pressure (up to 3.0 MPa), a PTFE seal is engineered to handle these combined stresses.
- If your primary focus is a cost-effective, general-purpose seal: A standard elastomer like Nitrile is often sufficient for simple applications with well-defined, non-aggressive lubricants like standard mineral oil.
Ultimately, choosing a PTFE oil seal is an investment in reliability and risk mitigation for your most critical and challenging applications.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit for Oil Seals |
|---|---|
| Exceptional Chemical Inertness | Resists swelling, shrinking, and degradation from acids, solvents, and caustics. |
| High-Temperature Stability (up to 260°C/500°F) | Maintains performance in extreme heat where elastomers fail. |
| Low Coefficient of Friction | Reduces rotational drag, heat generation, and shaft wear. |
| Non-Stick Surface | Prevents buildup of contaminants for a self-cleaning seal lip. |
Protect your critical equipment with high-performance PTFE seals from KINTEK.
Our precision-manufactured PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—are engineered for the harshest conditions in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We deliver the reliability you need, from custom prototypes to high-volume production.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific sealing challenges and discover how our solutions can enhance your equipment's longevity and performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech



















