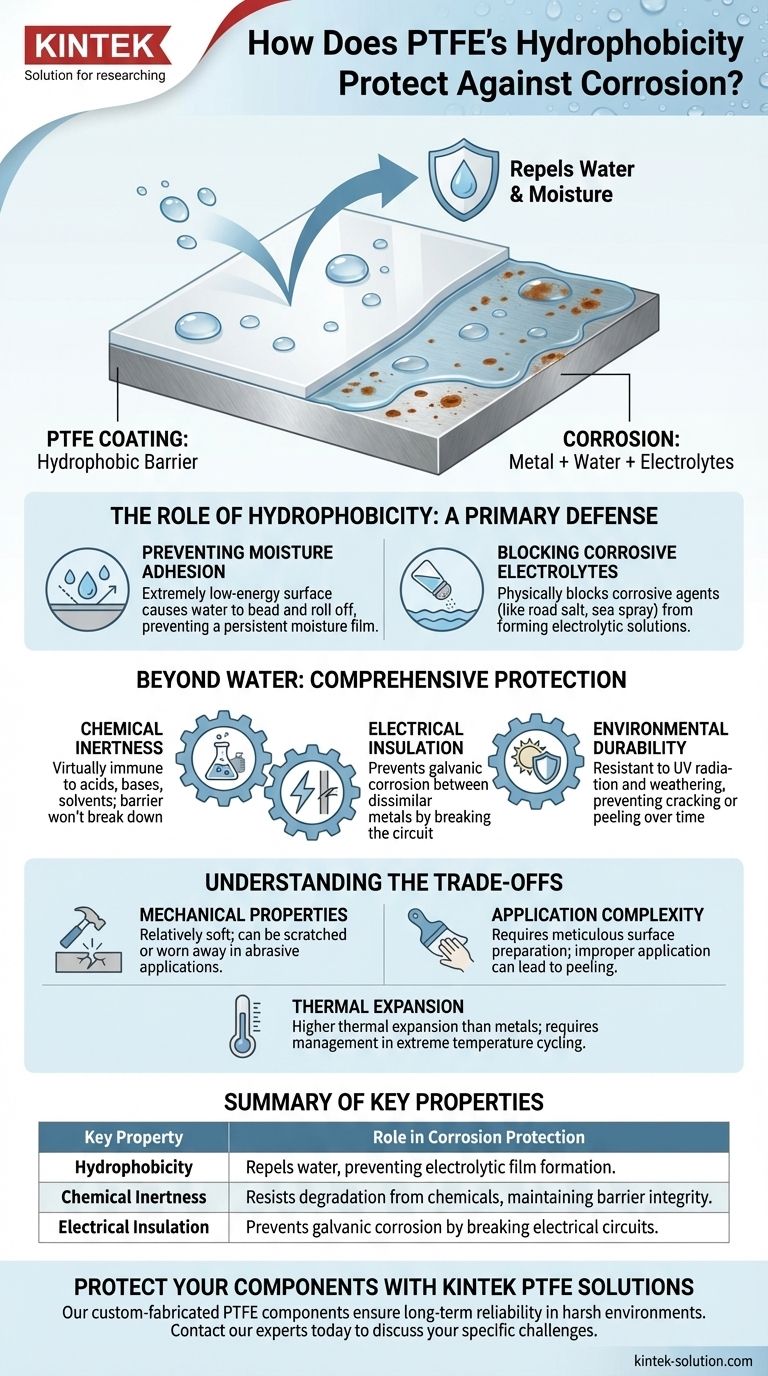
At its core, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) leverages its extreme hydrophobicity to create a powerful physical barrier against corrosion. This property prevents water and moisture—key ingredients for most corrosive reactions—from ever making contact with the underlying metal surface. By actively repelling water, a PTFE coating effectively starves the corrosion process before it can begin.
While its water-repelling nature is the most direct answer, PTFE's true value as an anti-corrosion solution comes from a powerful combination of hydrophobicity, complete chemical inertness, and electrical insulation.
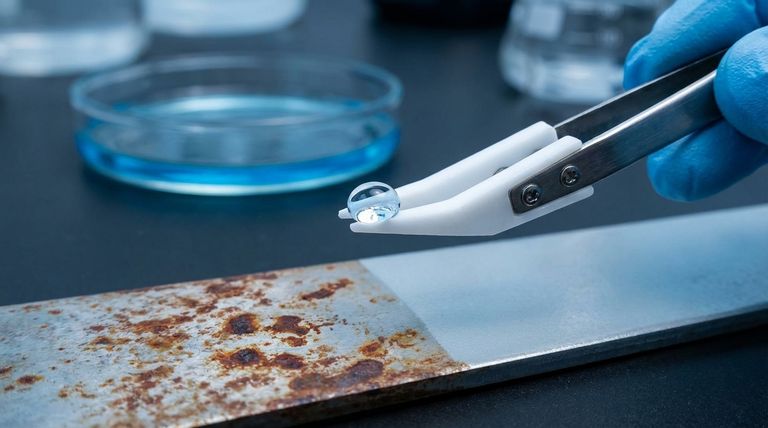

The Role of Hydrophobicity: A Primary Defense
PTFE's ability to shed water is its first and most obvious line of defense. This mechanism is simple but remarkably effective in a wide range of common corrosive environments.
Preventing Moisture Adhesion
The molecular structure of PTFE creates an extremely low-energy surface. Water molecules are strongly attracted to each other but not to the PTFE, causing them to bead up and roll off rather than spreading out and wetting the surface.
This prevents a persistent film of moisture from forming, which is necessary for corrosion to take hold.
Blocking Corrosive Electrolytes
Corrosion is an electrochemical process that requires an electrolyte—typically water containing dissolved salts or pollutants—to function.
By physically blocking water, PTFE prevents corrosive agents like road salt or sea spray from creating an electrolytic solution on the metal's surface, halting the reaction. This is critical in marine, automotive, and offshore applications.
Beyond Water: PTFE's Comprehensive Protection
Hydrophobicity is only one aspect of PTFE's protective capabilities. Its other inherent properties work in concert to create a near-impenetrable shield against multiple forms of degradation.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is one of the most chemically resistant materials known. It is virtually immune to degradation from acids, bases, solvents, and oxidizing agents.
This means that even if a corrosive chemical comes into contact with the coating, the PTFE barrier itself will not break down, ensuring continuous protection for the substrate underneath.
Preventing Galvanic Corrosion
Galvanic corrosion occurs when two dissimilar metals are in electrical contact in the presence of an electrolyte. The less noble metal corrodes at an accelerated rate.
Because PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator, it can be used as a liner or bearing to physically and electrically separate different metals. This breaks the galvanic circuit and stops this specific, often aggressive, form of corrosion.
Extreme Environmental Durability
A coating is only effective if it remains intact. PTFE shows excellent resistance to weathering and degradation from UV radiation.
This ensures the protective barrier does not become brittle, crack, or peel away when exposed to sunlight and harsh outdoor conditions over long periods.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, PTFE is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it correctly.
Mechanical Properties
PTFE is a relatively soft material. In applications with high physical abrasion or impact, the coating can be scratched or worn away, compromising the protective barrier.
Application Complexity
Achieving a durable, well-adhered PTFE coating requires meticulous surface preparation. Improper application can lead to peeling or delamination, creating sites where corrosion can begin underneath the coating.
Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a higher coefficient of thermal expansion than most metals. In environments with extreme temperature cycling, this difference must be managed to prevent stress and potential failure of the coating bond.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting an anti-corrosion strategy requires matching the material's strengths to the specific environmental threat.
- If your primary focus is protection from atmospheric moisture, rain, or road salt: PTFE's hydrophobicity provides a direct and highly effective barrier.
- If your primary focus is immunity to aggressive industrial chemicals or fluids: PTFE's chemical inertness is its most valuable asset, making it ideal for process equipment.
- If your primary focus is preventing corrosion between joined or fastened dissimilar metals: Using PTFE as an insulating liner or washer is the most effective way to stop galvanic corrosion.
Ultimately, choosing PTFE is a decision to prioritize long-term reliability and performance in environments where lesser materials would quickly fail.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Role in Corrosion Protection |
|---|---|
| Hydrophobicity | Repels water, preventing the formation of an electrolytic film necessary for corrosion. |
| Chemical Inertness | Resists degradation from acids, bases, and solvents, maintaining barrier integrity. |
| Electrical Insulation | Prevents galvanic corrosion by breaking the electrical circuit between dissimilar metals. |
Protect your critical components from corrosion with KINTEK's precision PTFE solutions.
Our custom-fabricated PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—are engineered to provide a durable, hydrophobic barrier that ensures long-term reliability in the harshest environments. Whether you're in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sector, we deliver the precise performance you need, from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our PTFE expertise can solve your specific corrosion challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What industrial benefits do PTFE-machined parts offer? Achieve Peak Performance in Demanding Applications
- What chemical processing applications involve PTFE-machined parts? Essential Components for Corrosive & High-Purity Systems
- What challenges arise when machining PTFE (Teflon)? Overcome Softness, Heat, and Instability
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? The 3 Pillars Driving Demand for High-Performance Parts



















